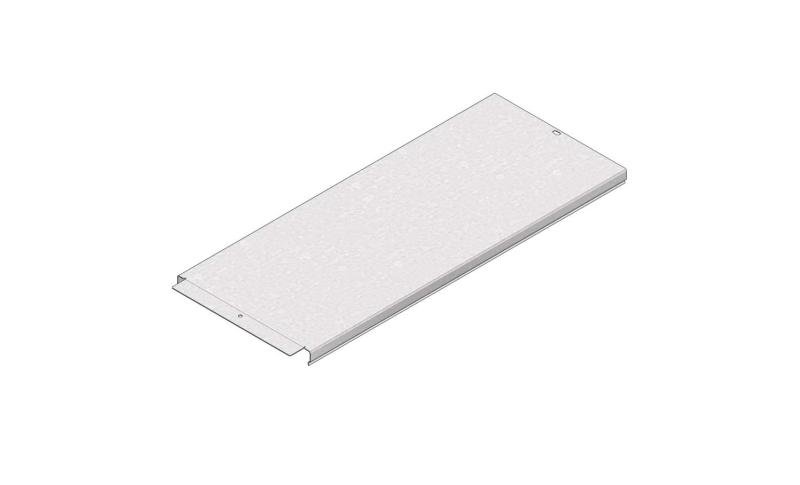
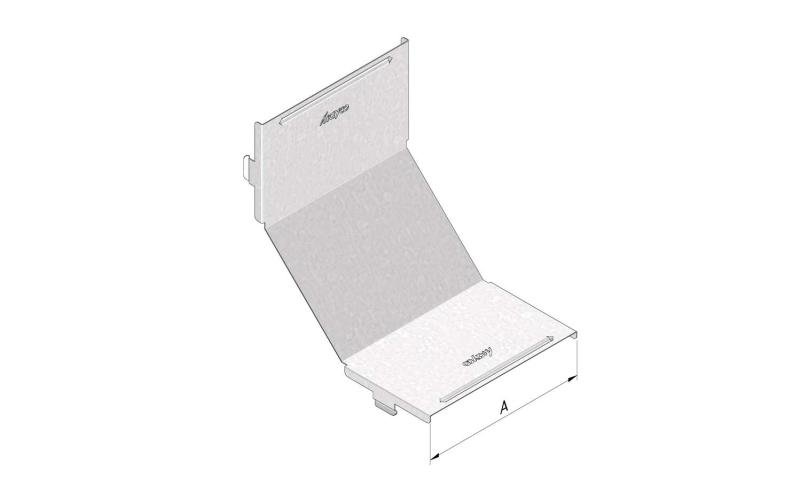
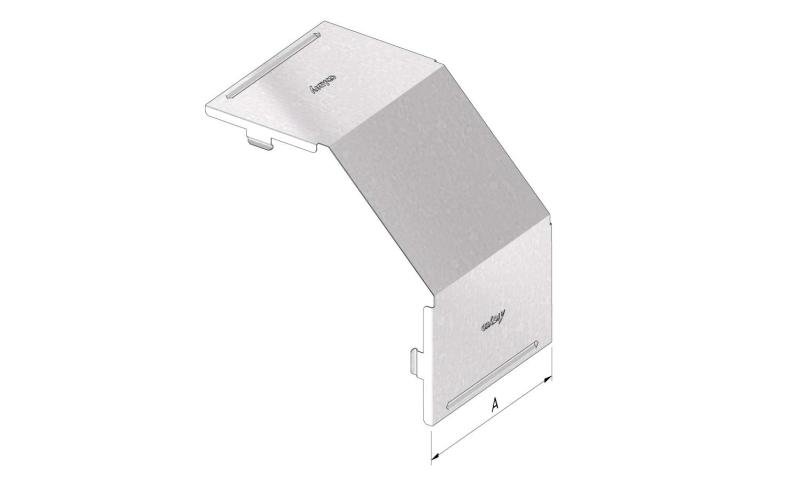
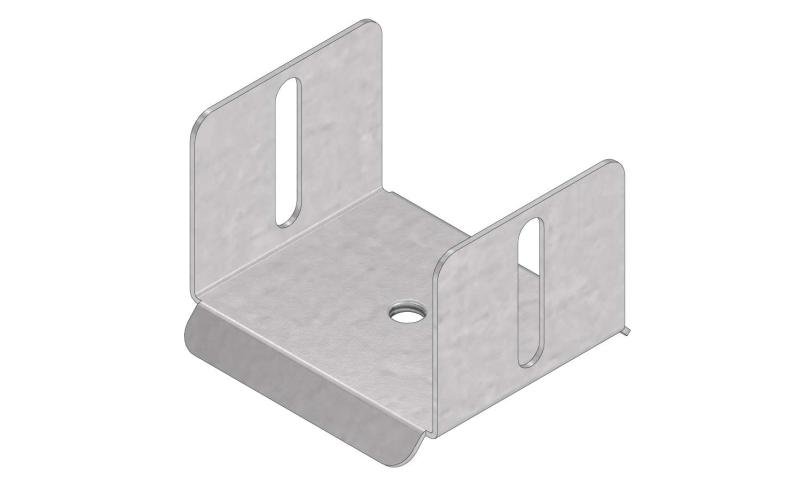
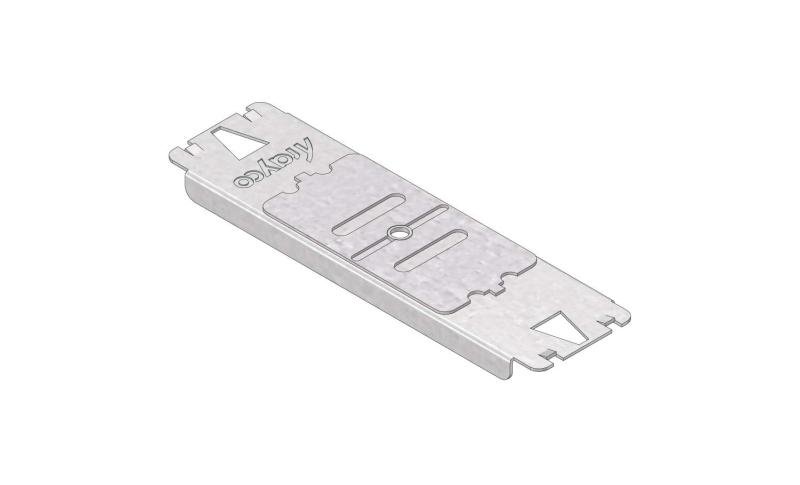
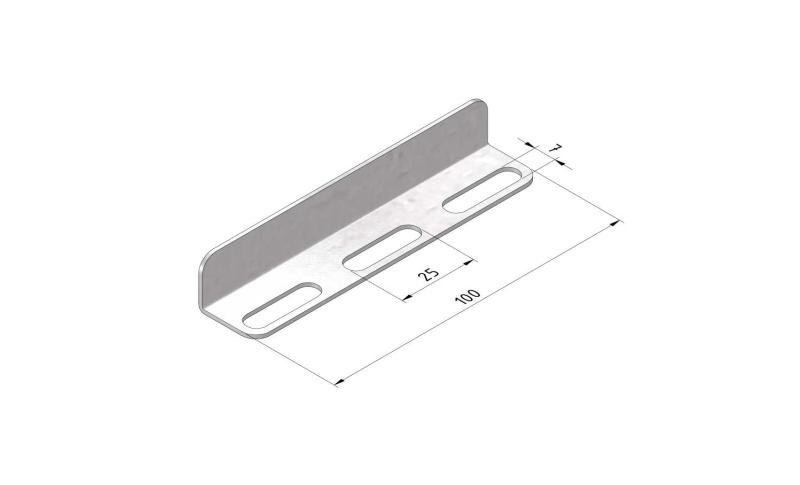
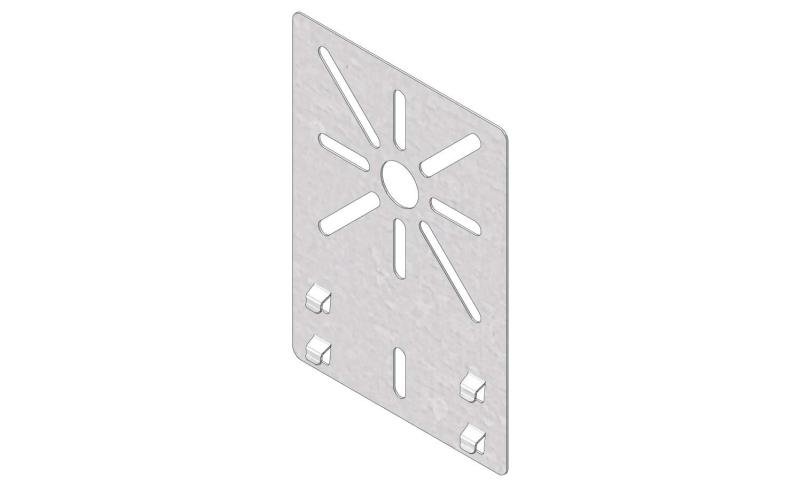
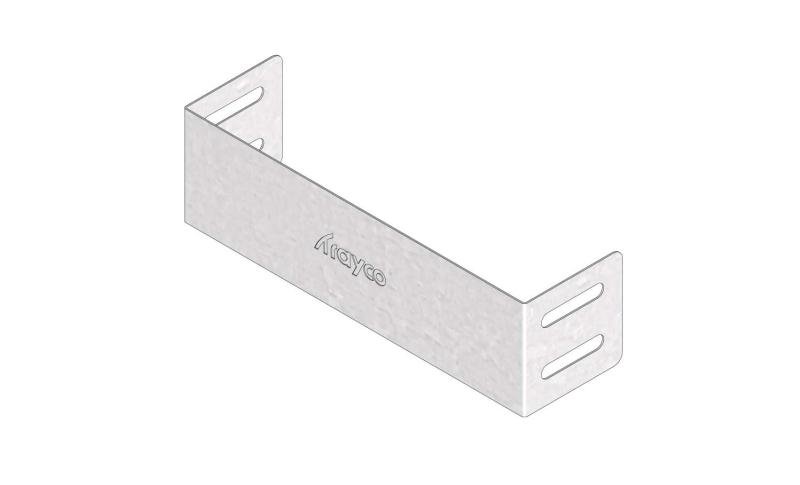
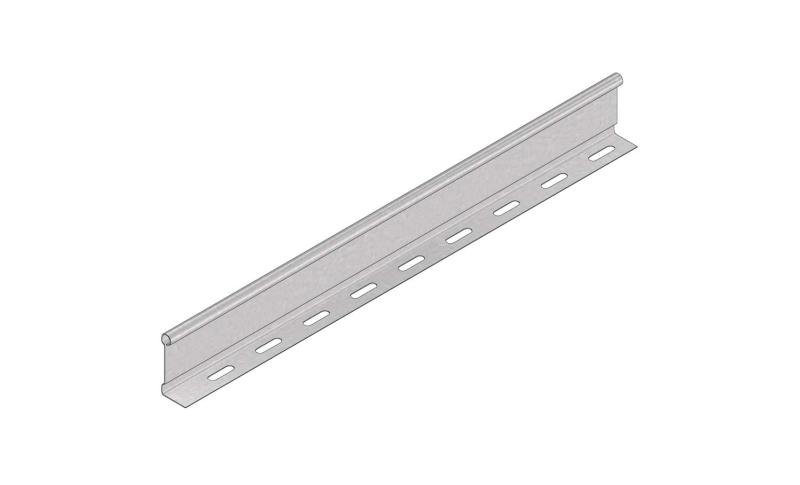
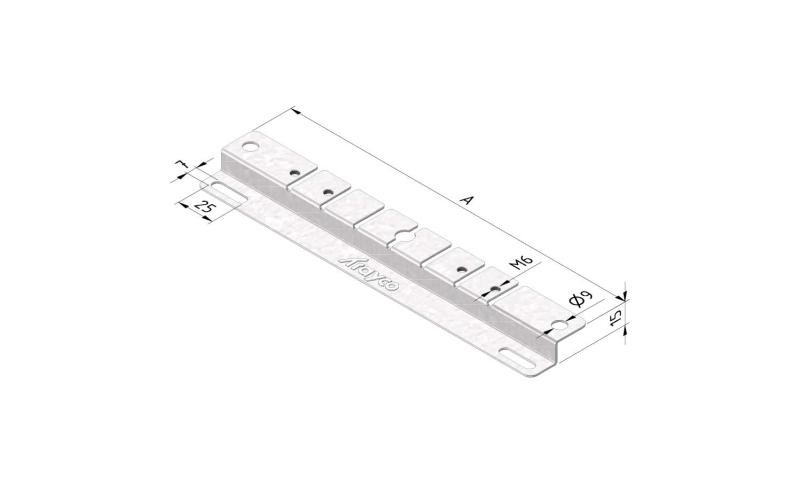
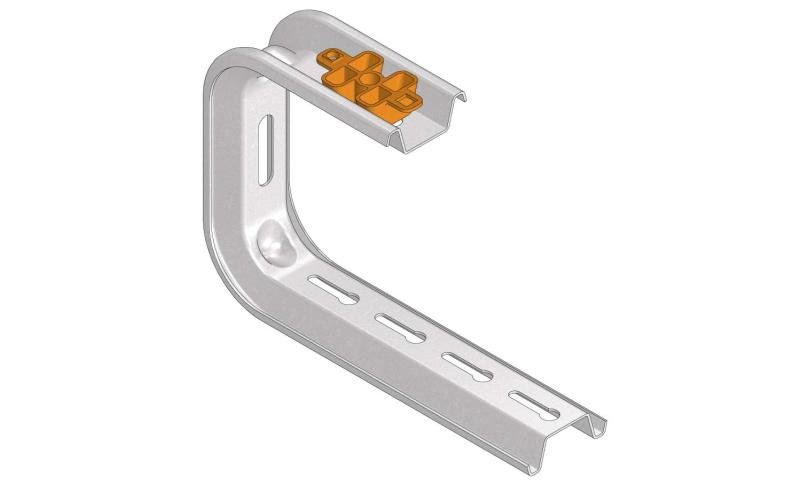
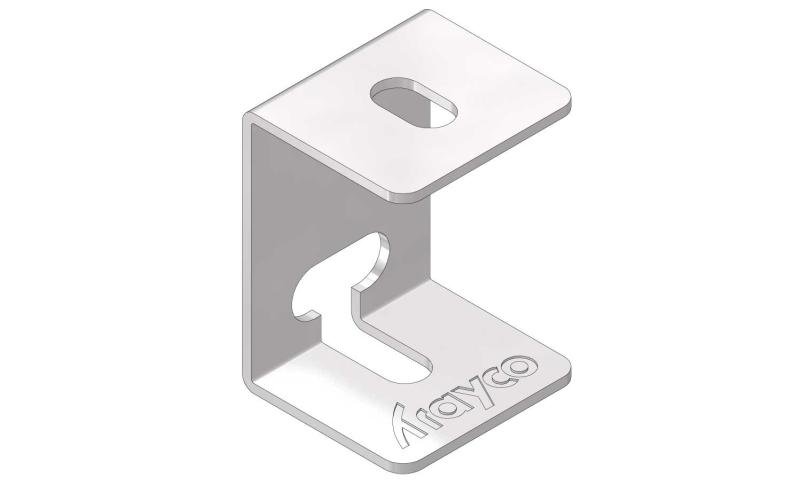
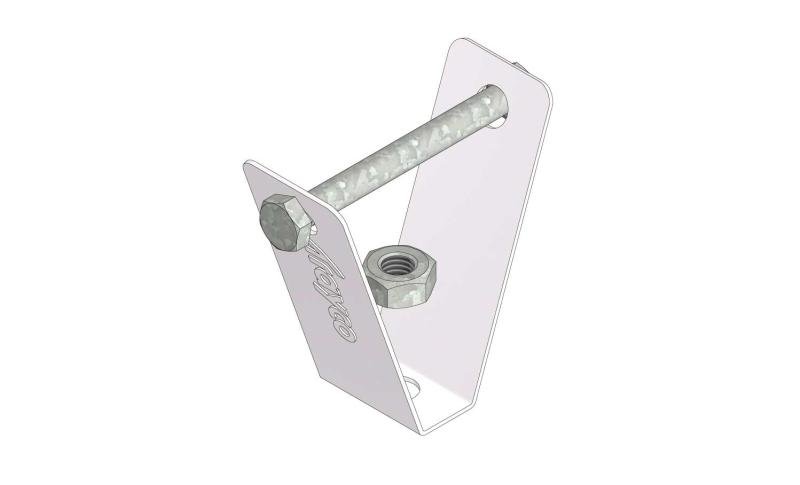
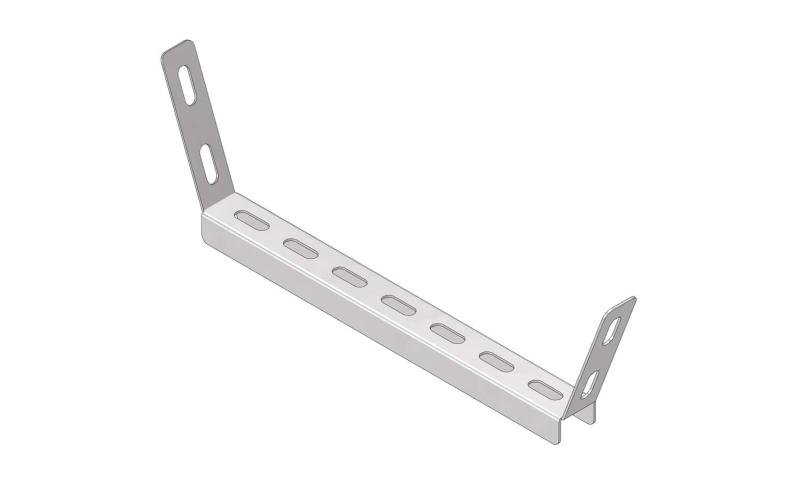
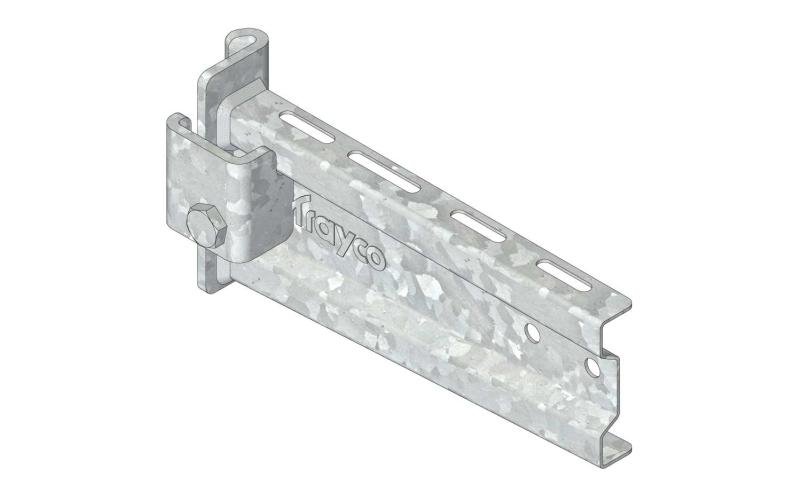
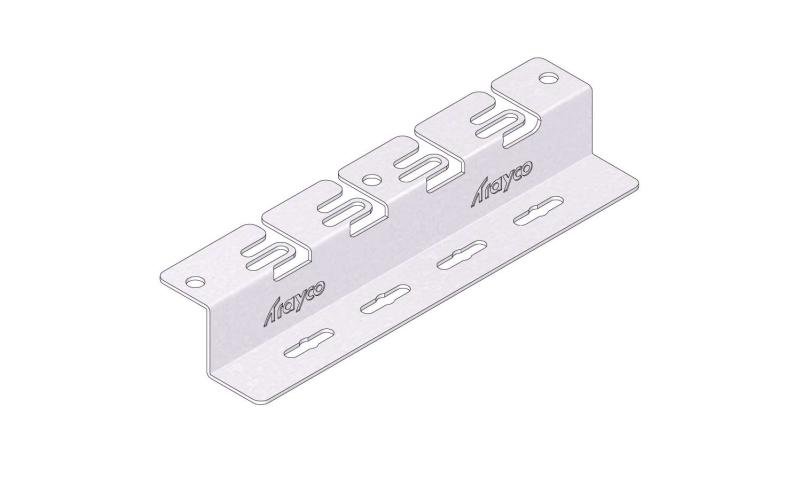
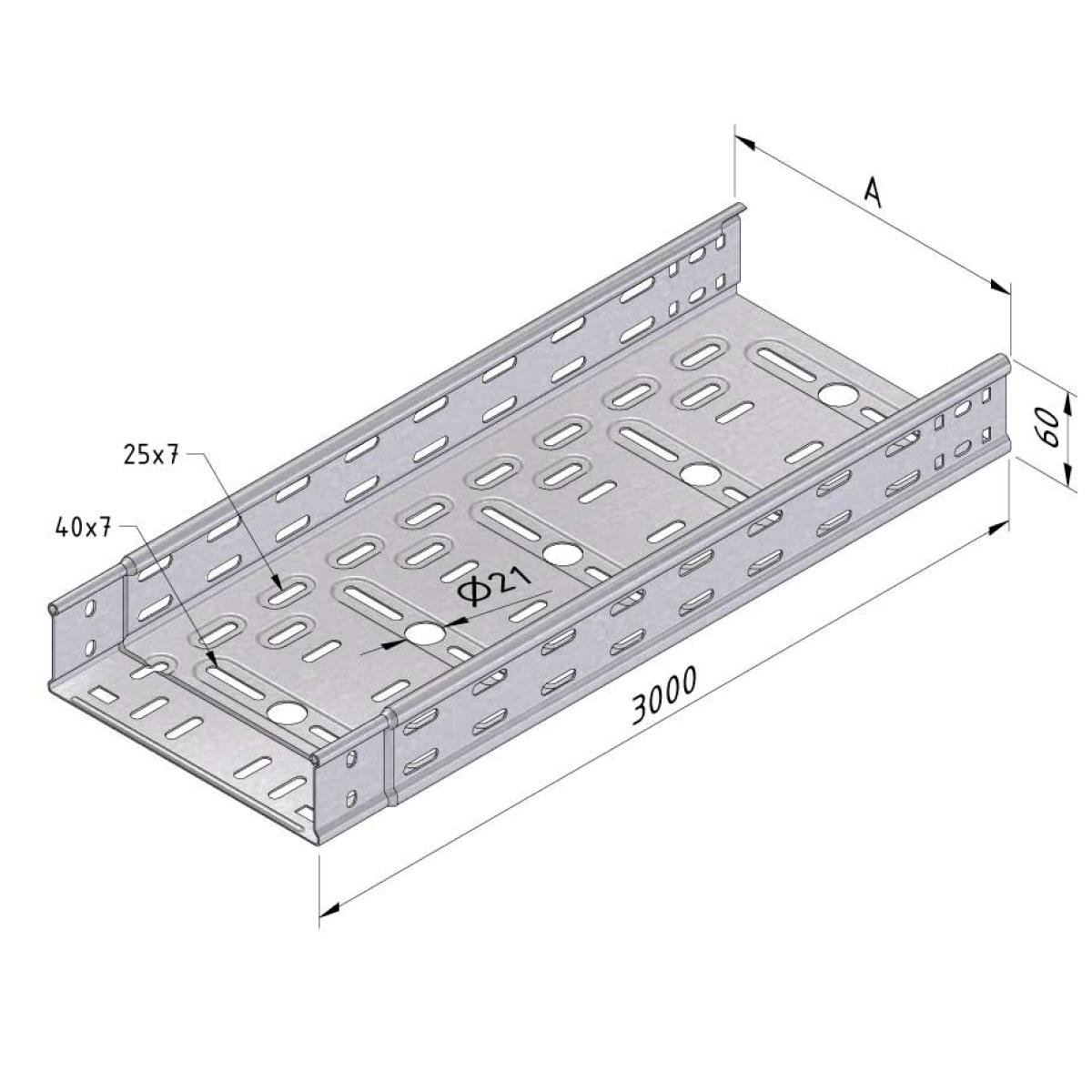
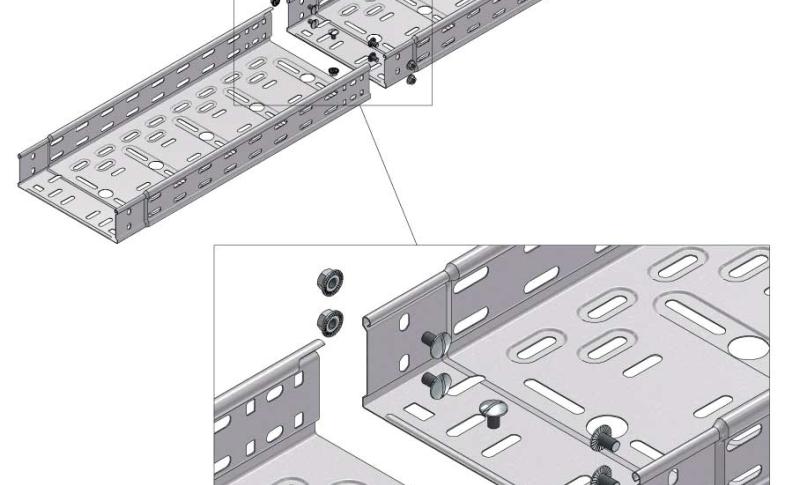
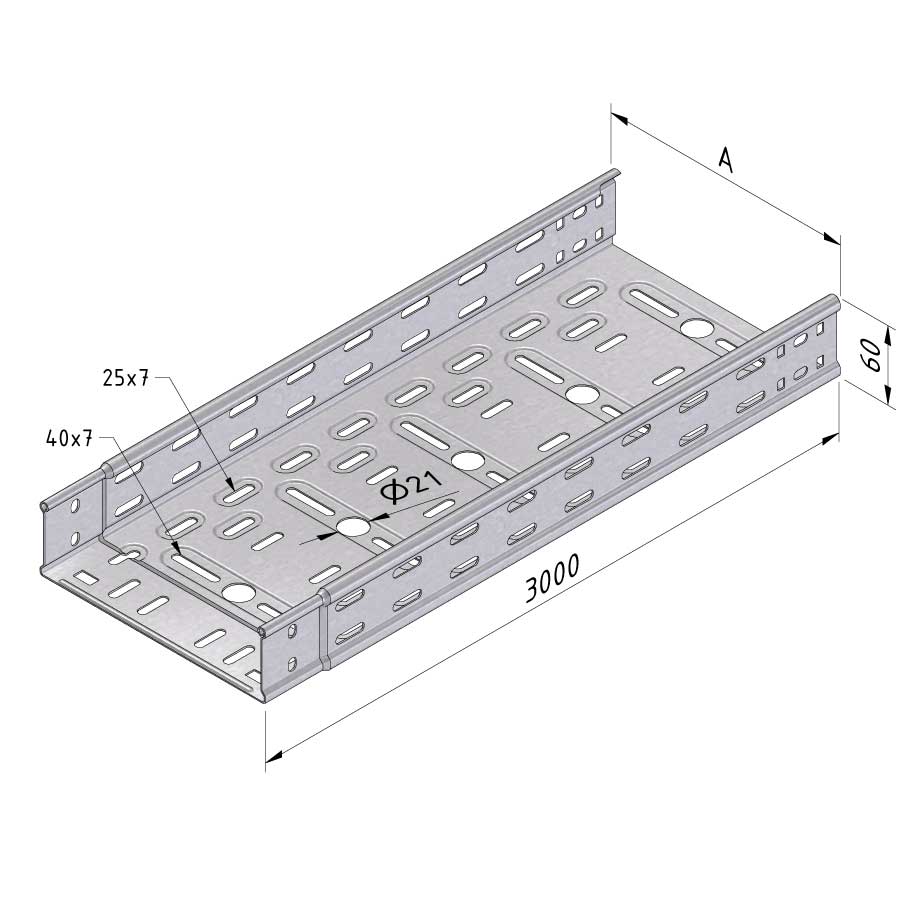
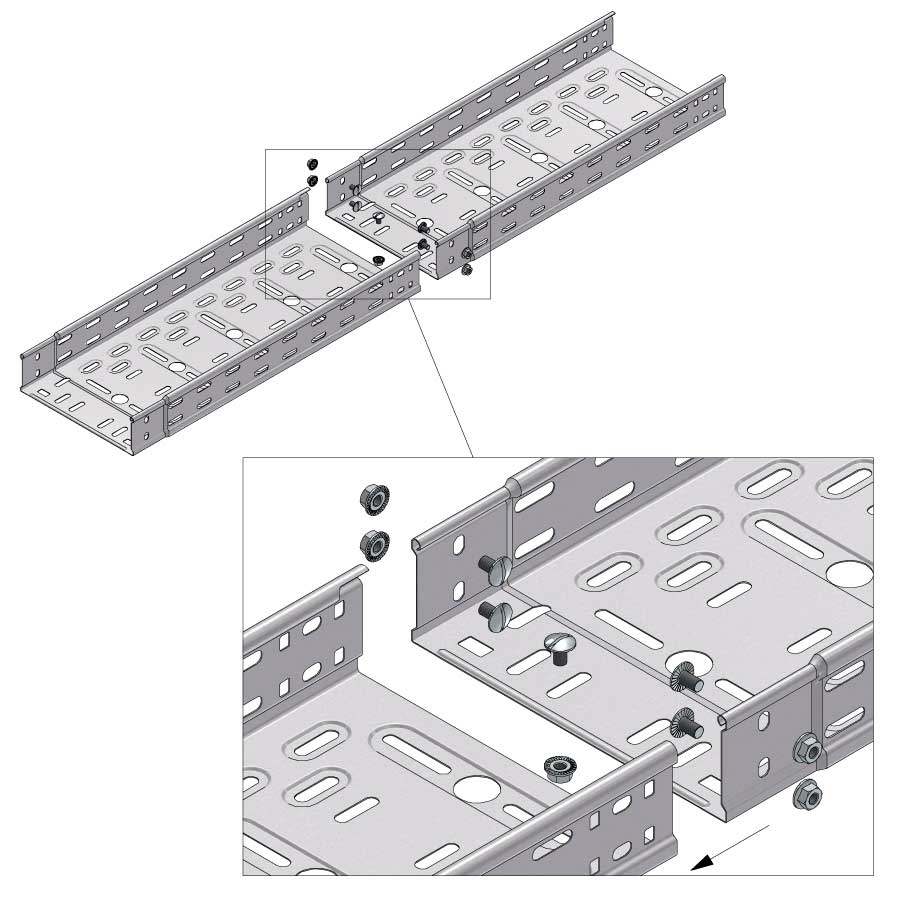
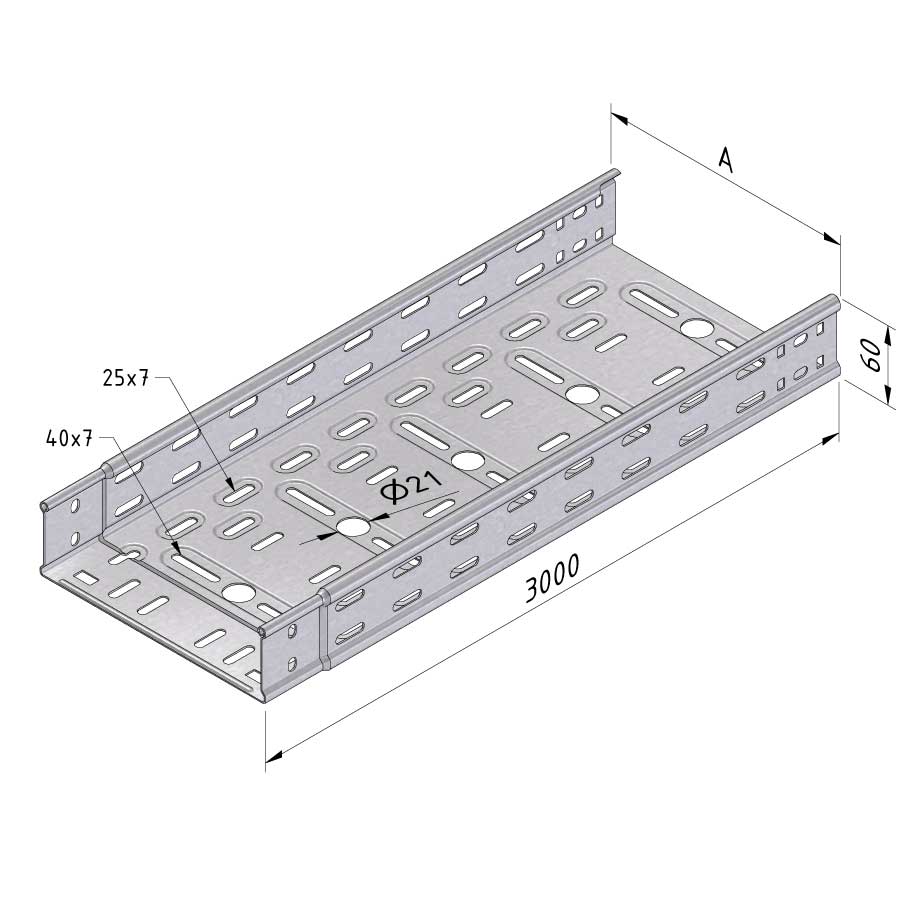
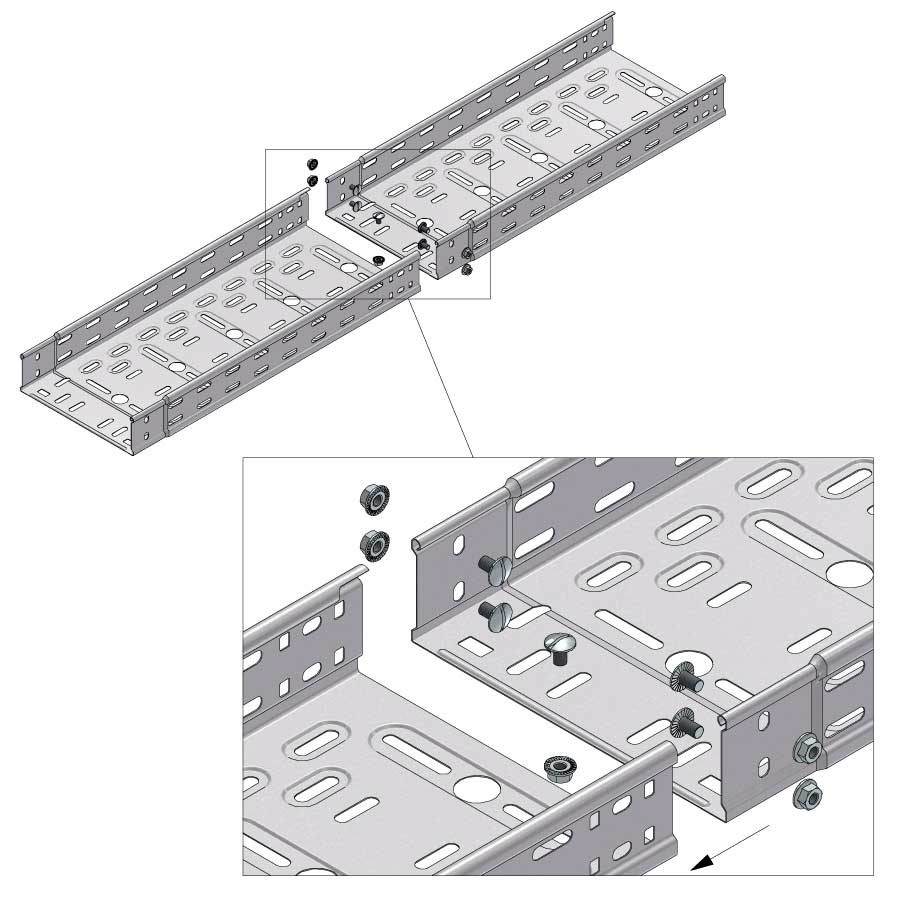
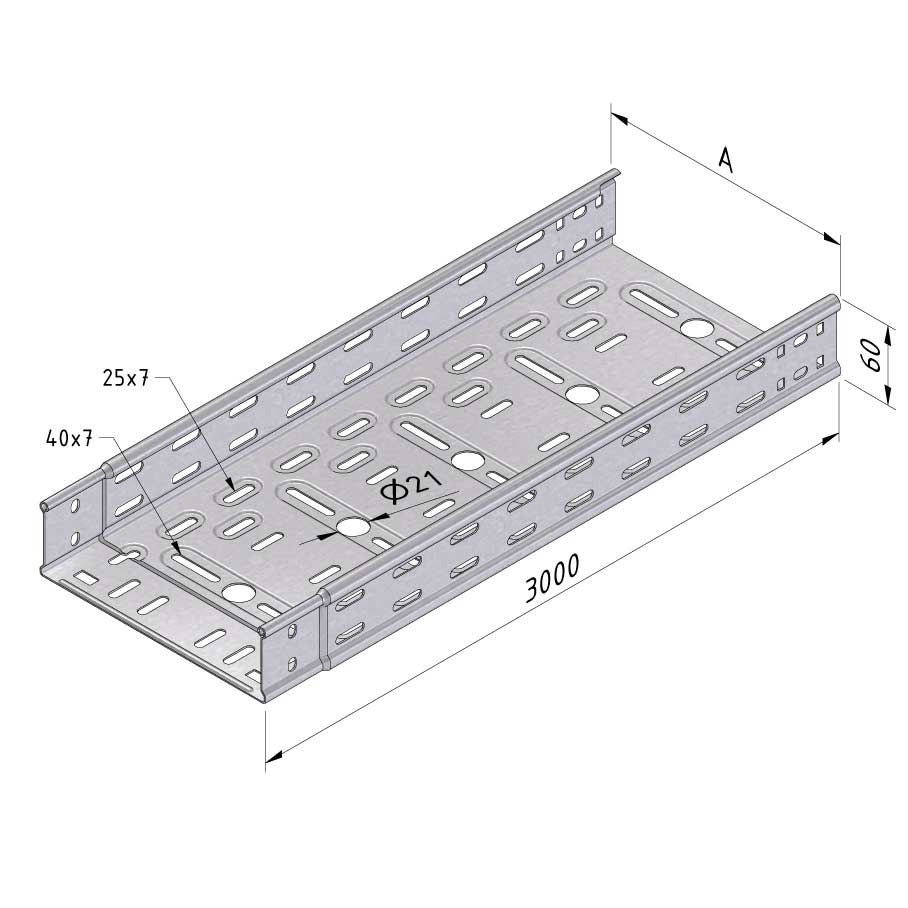
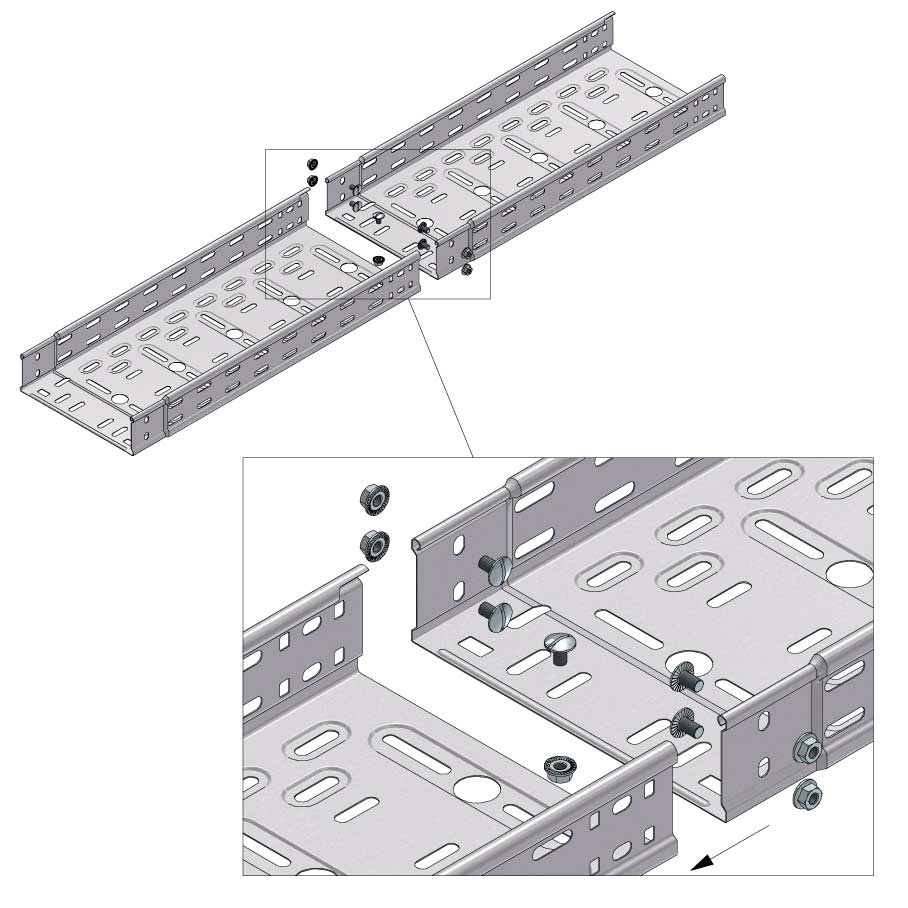
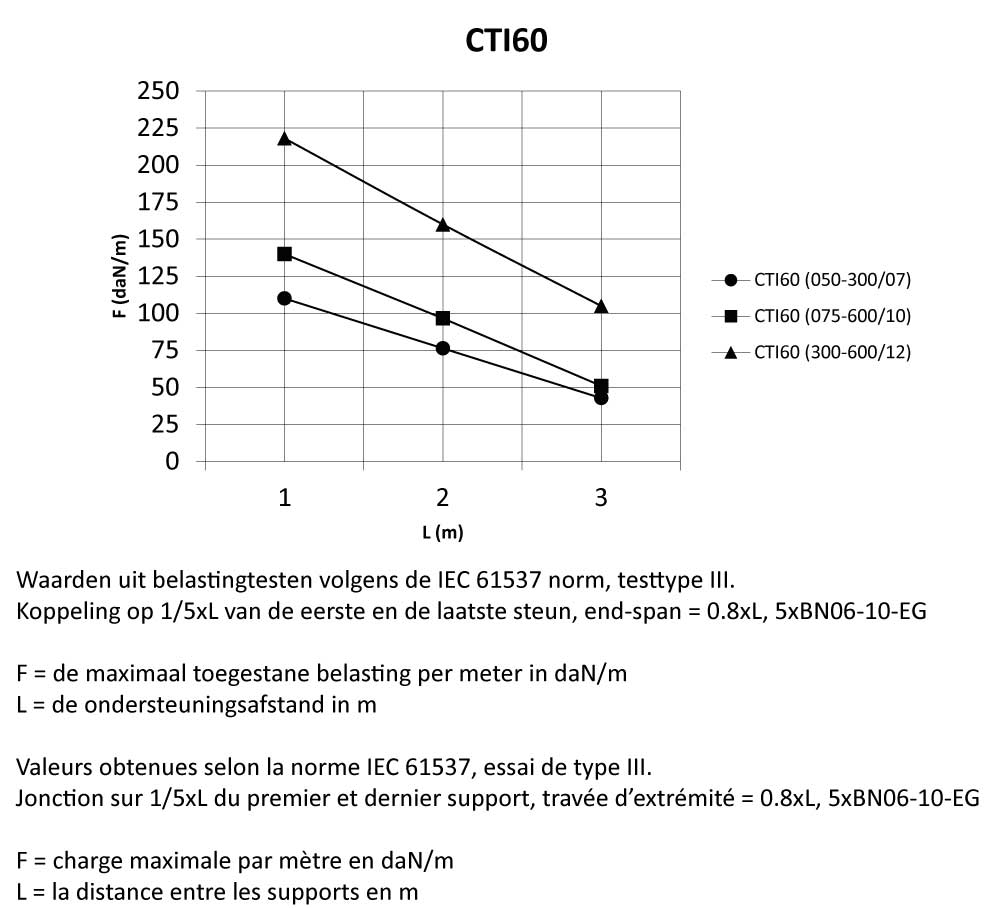
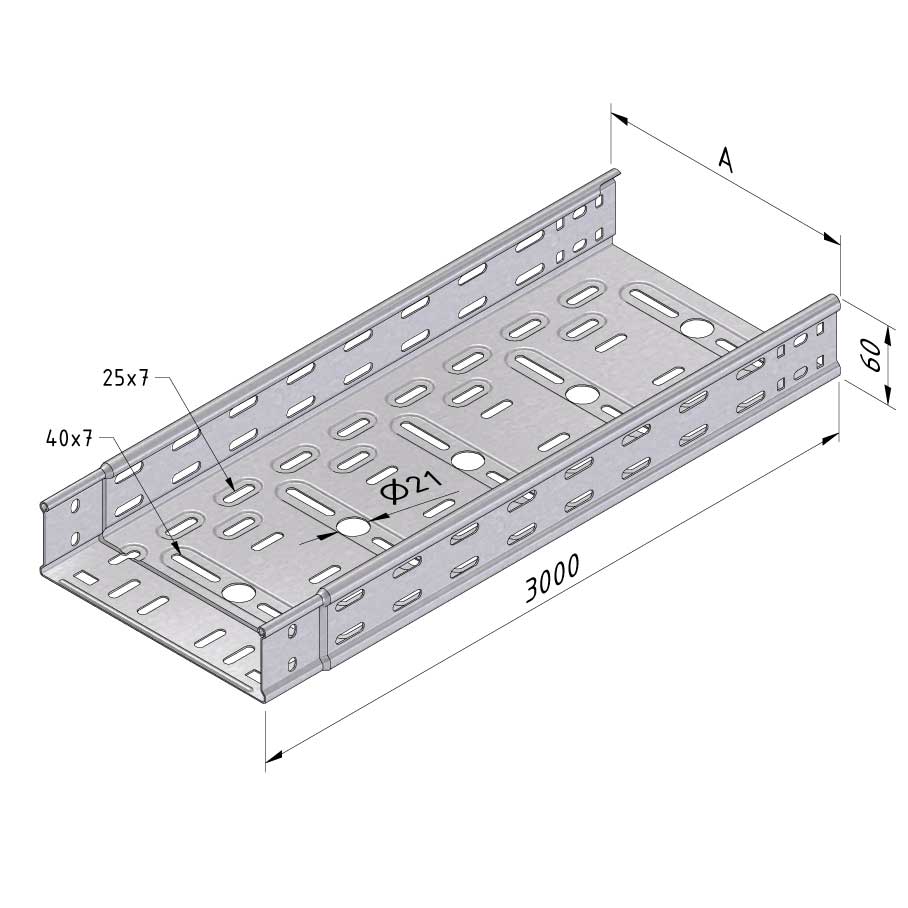
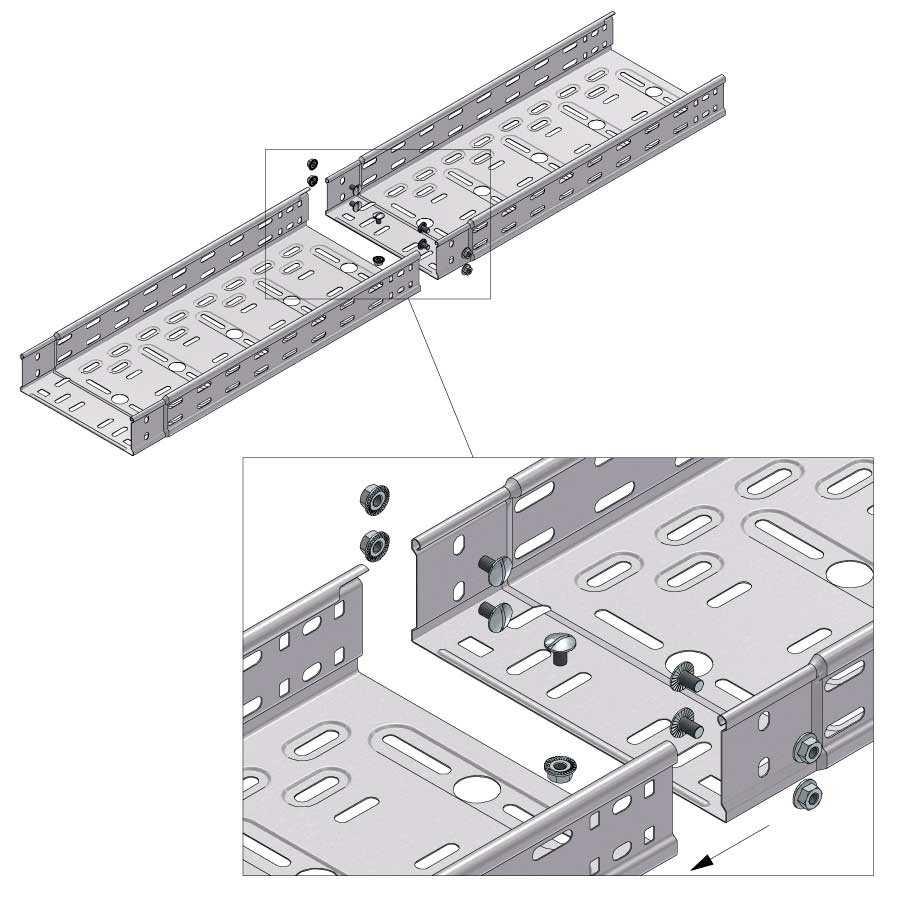
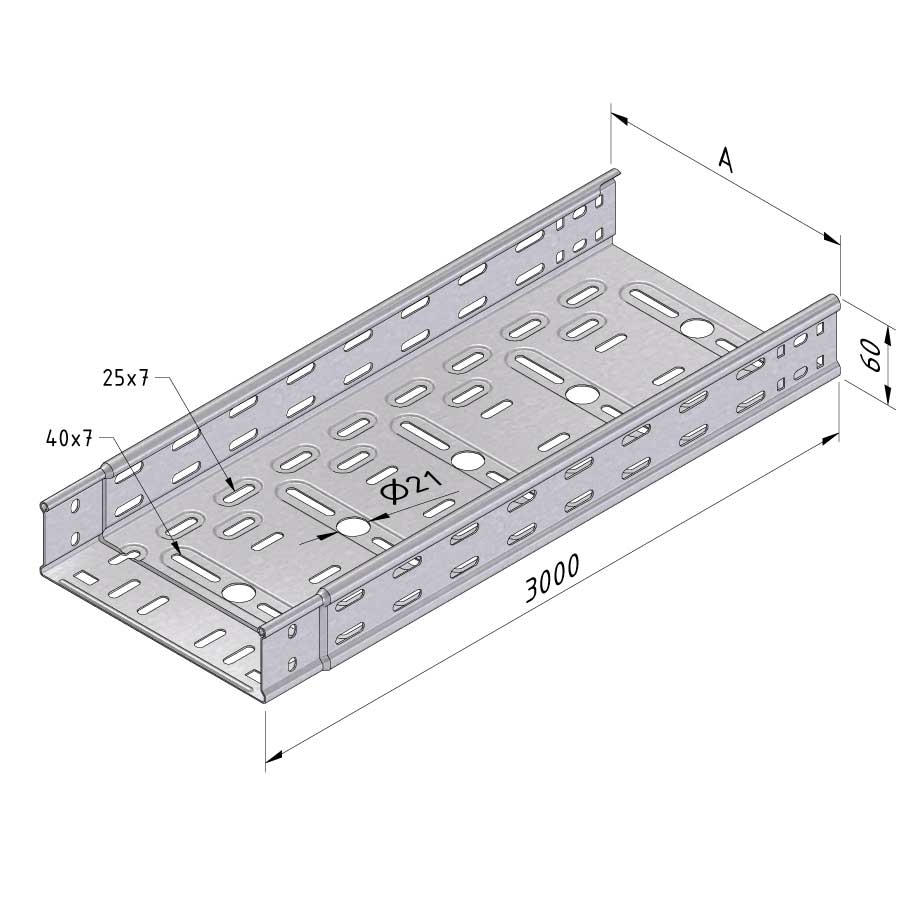
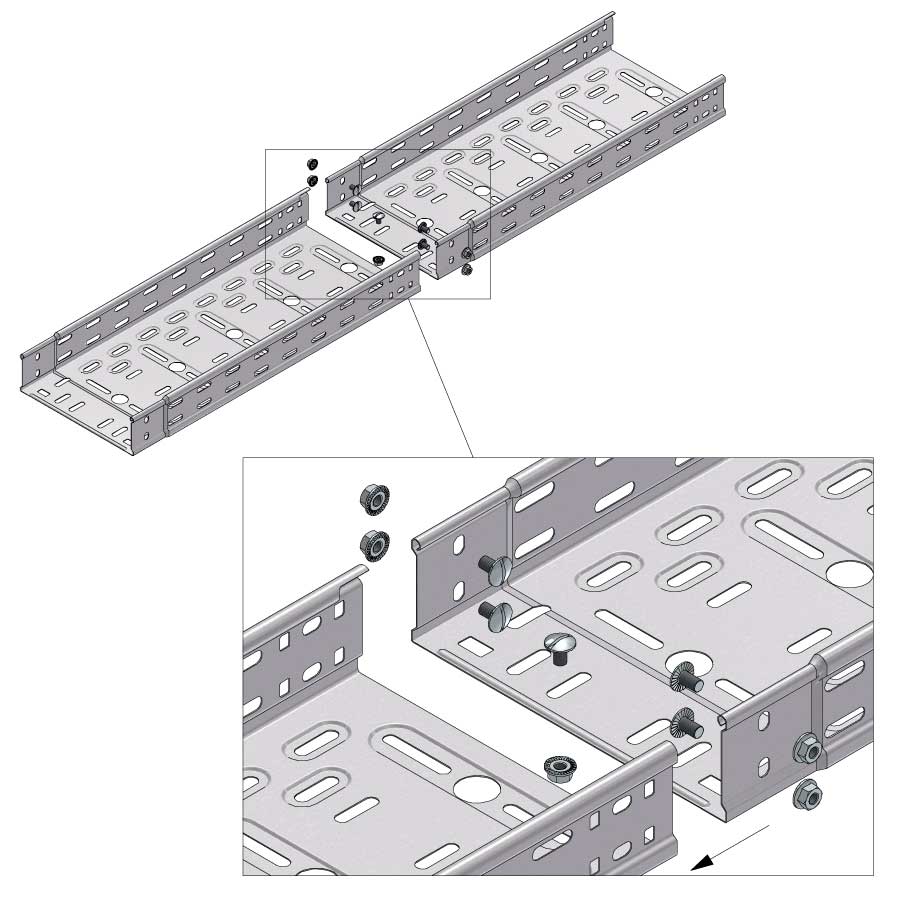
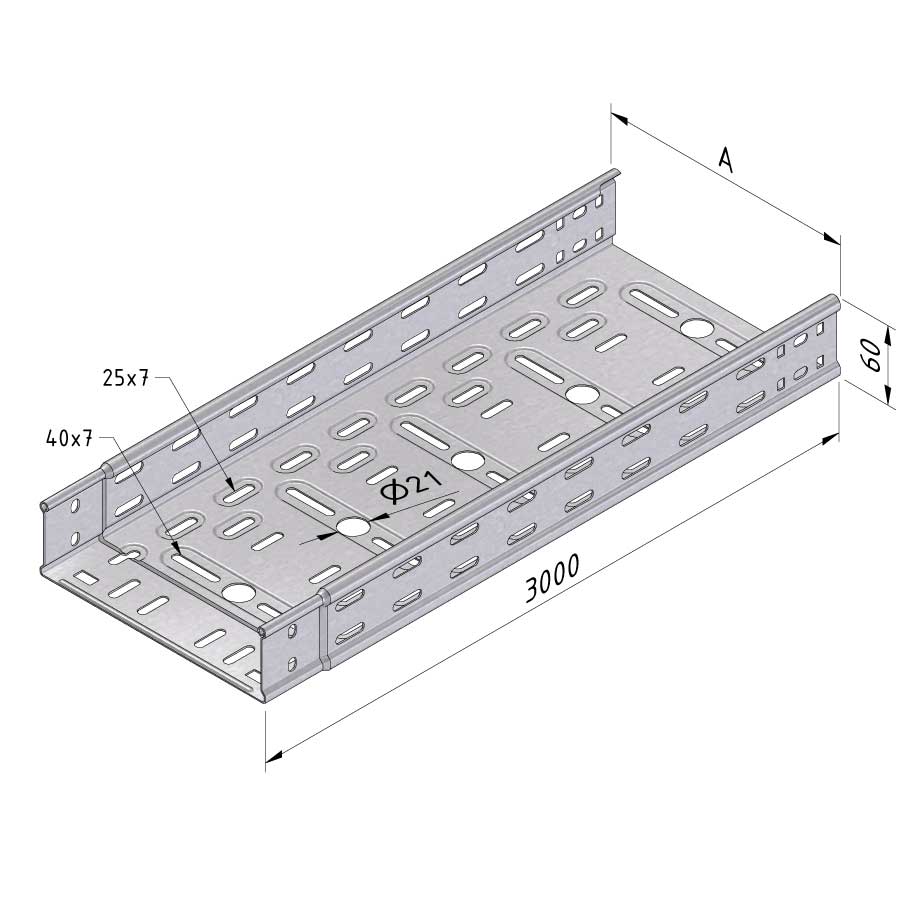
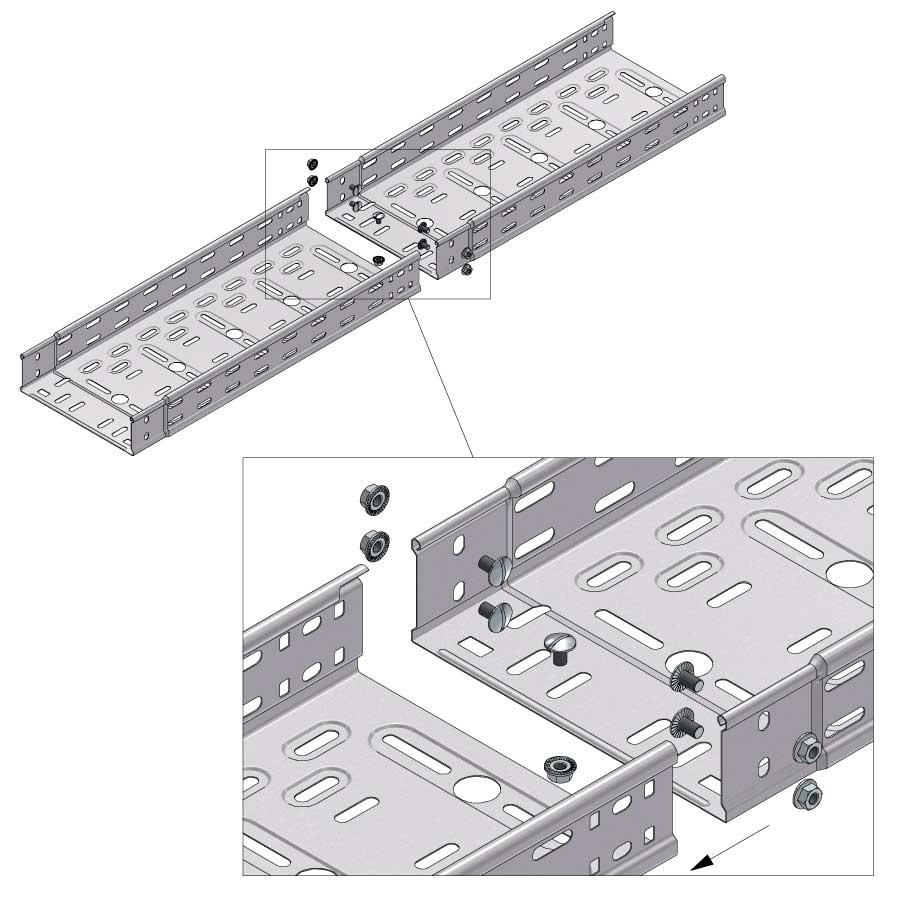
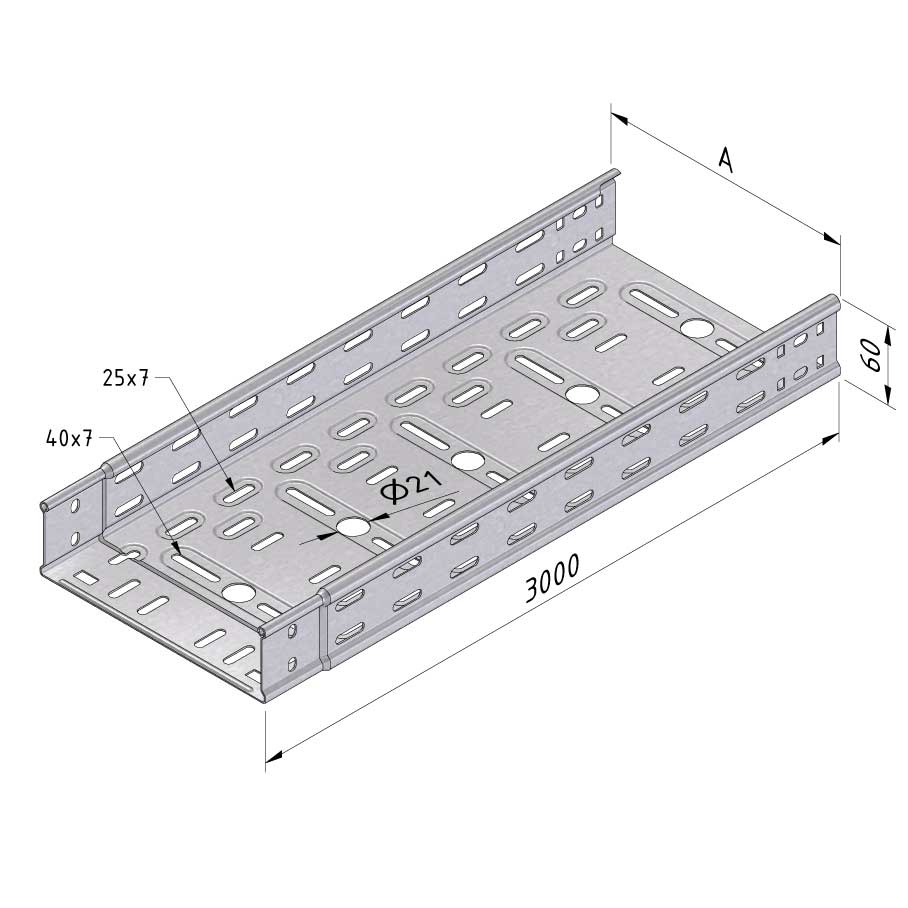
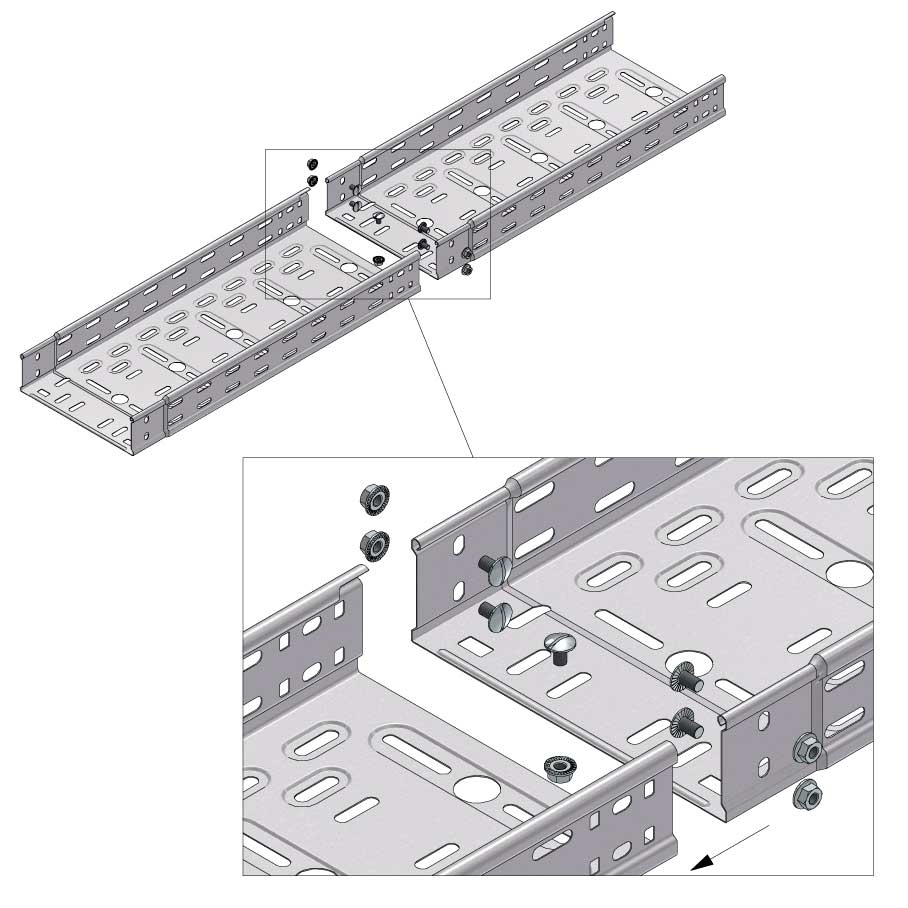
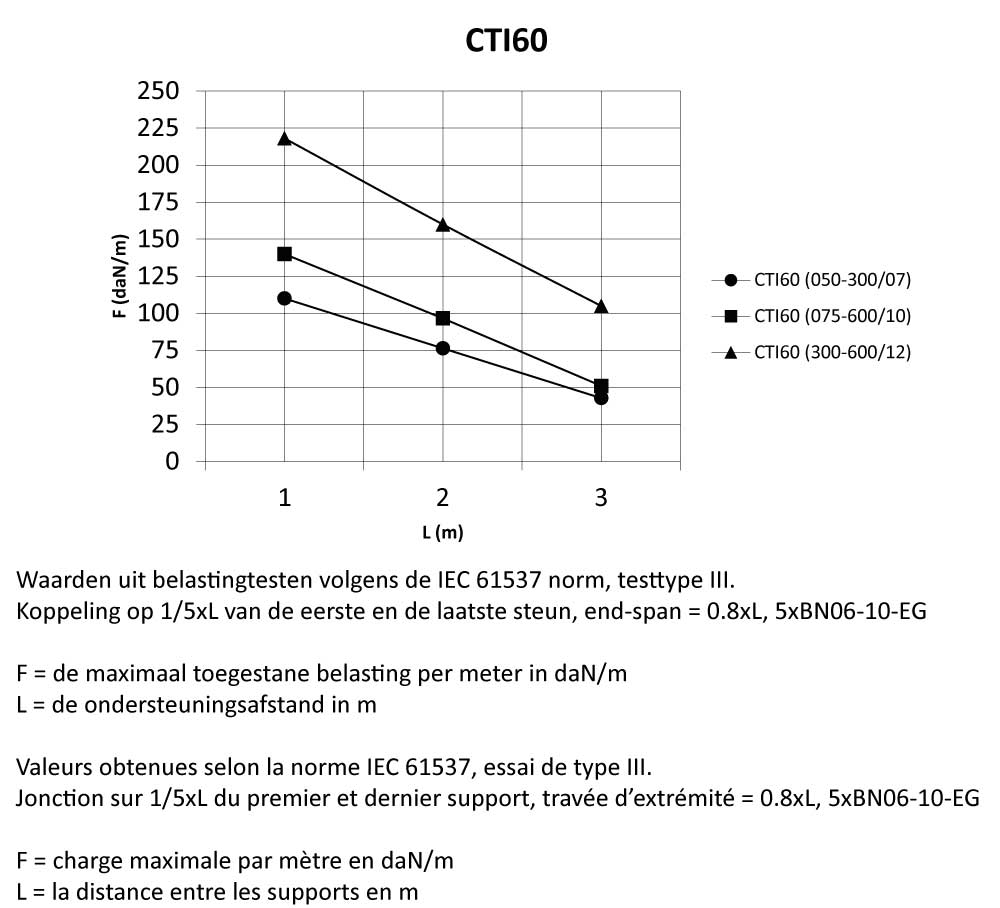
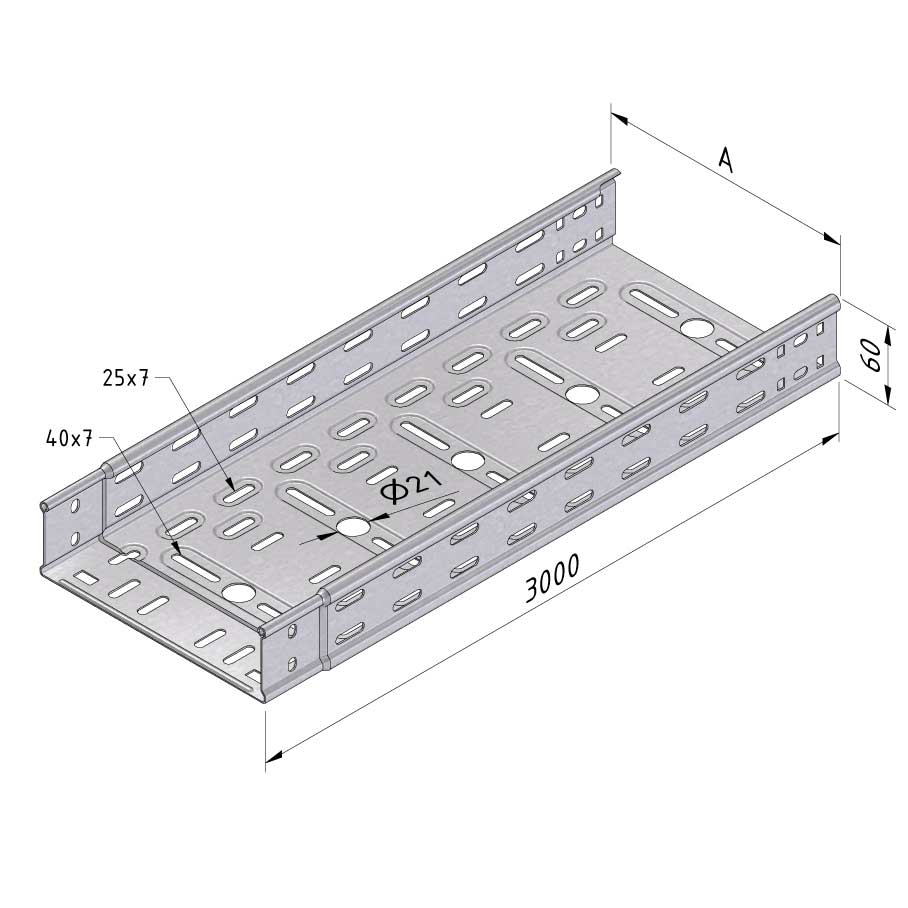
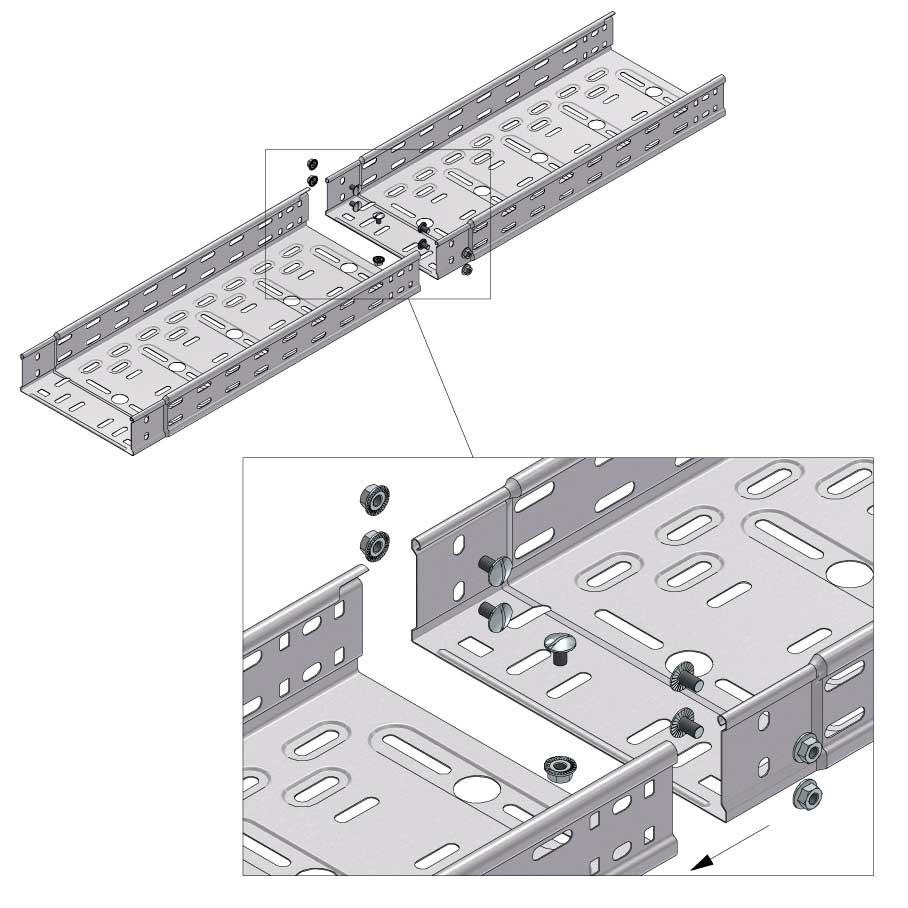
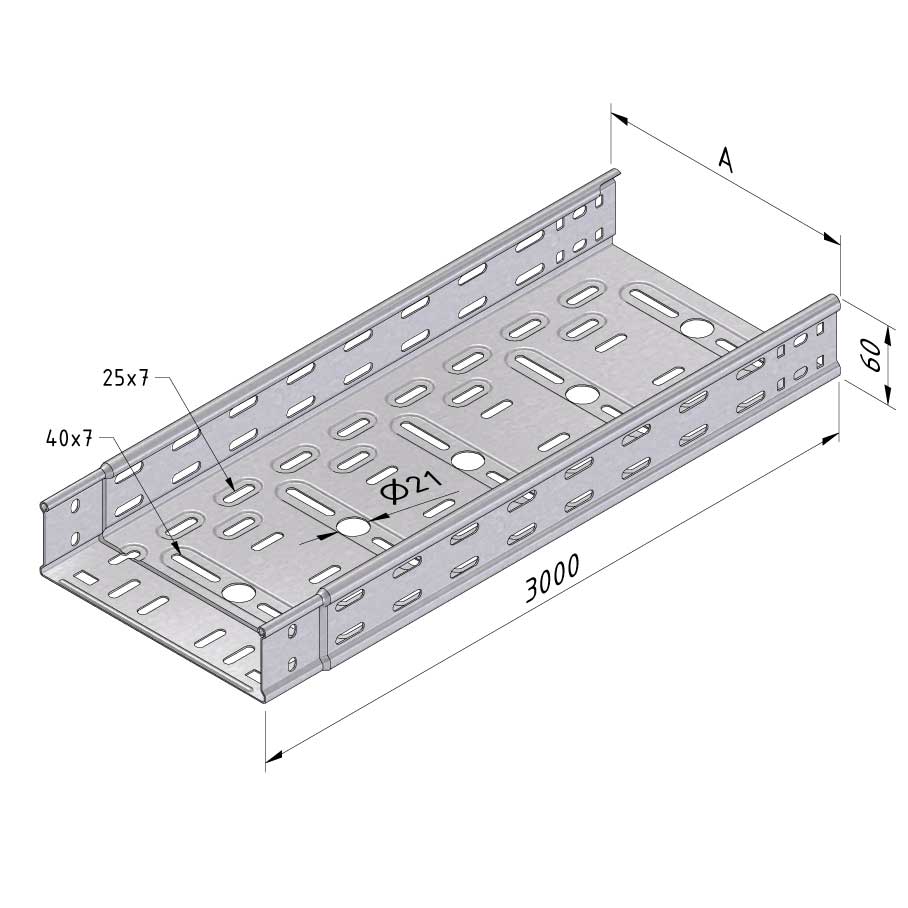
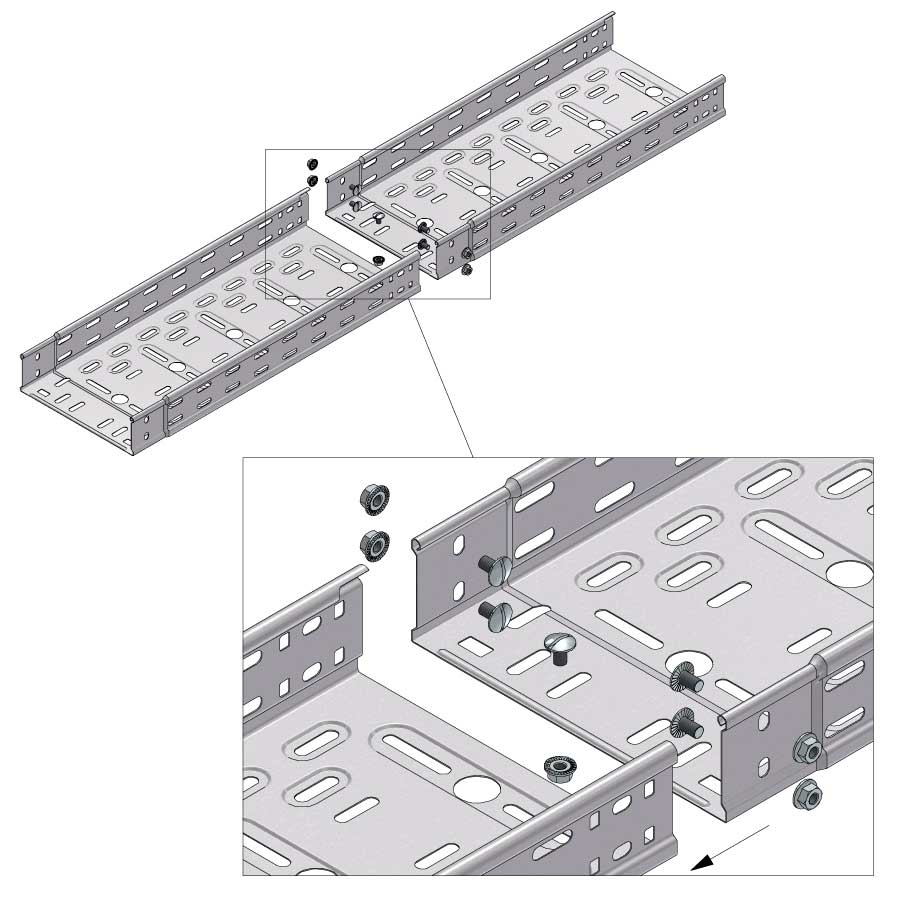
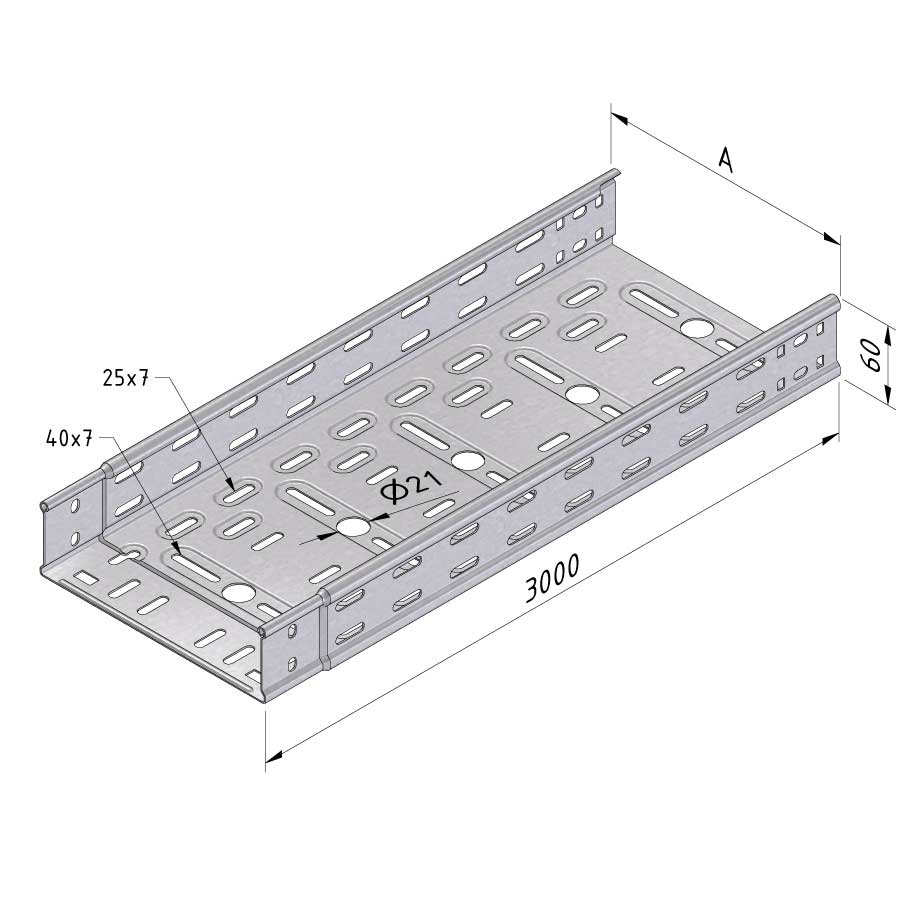
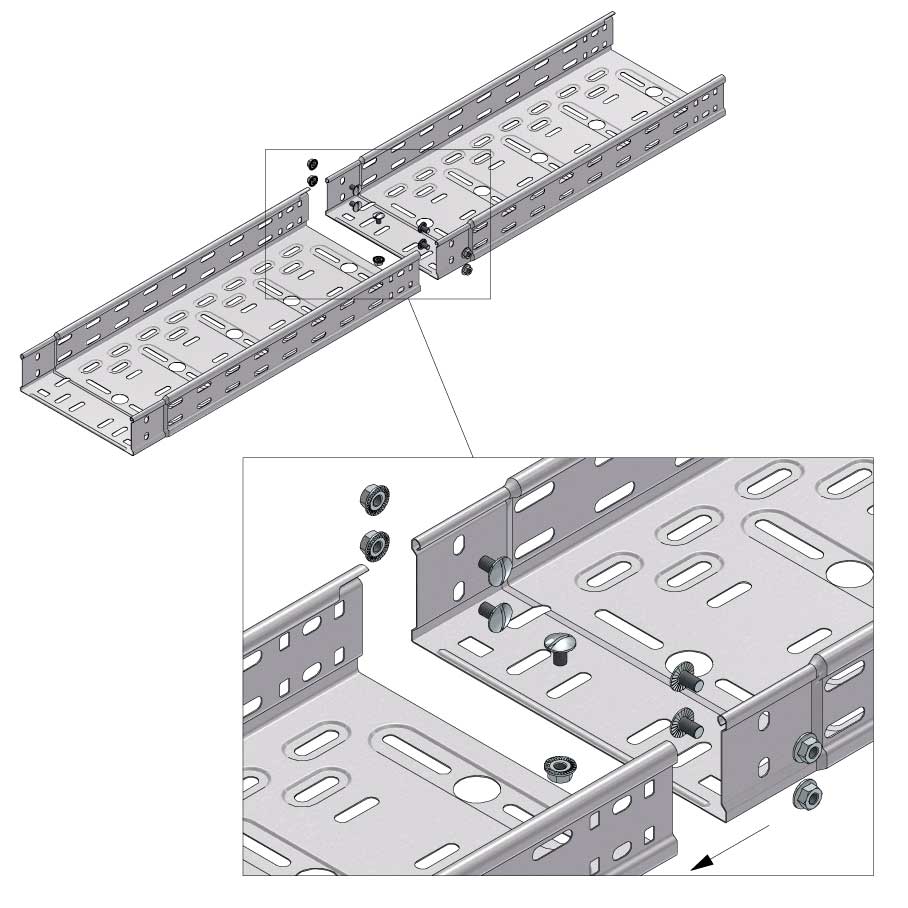
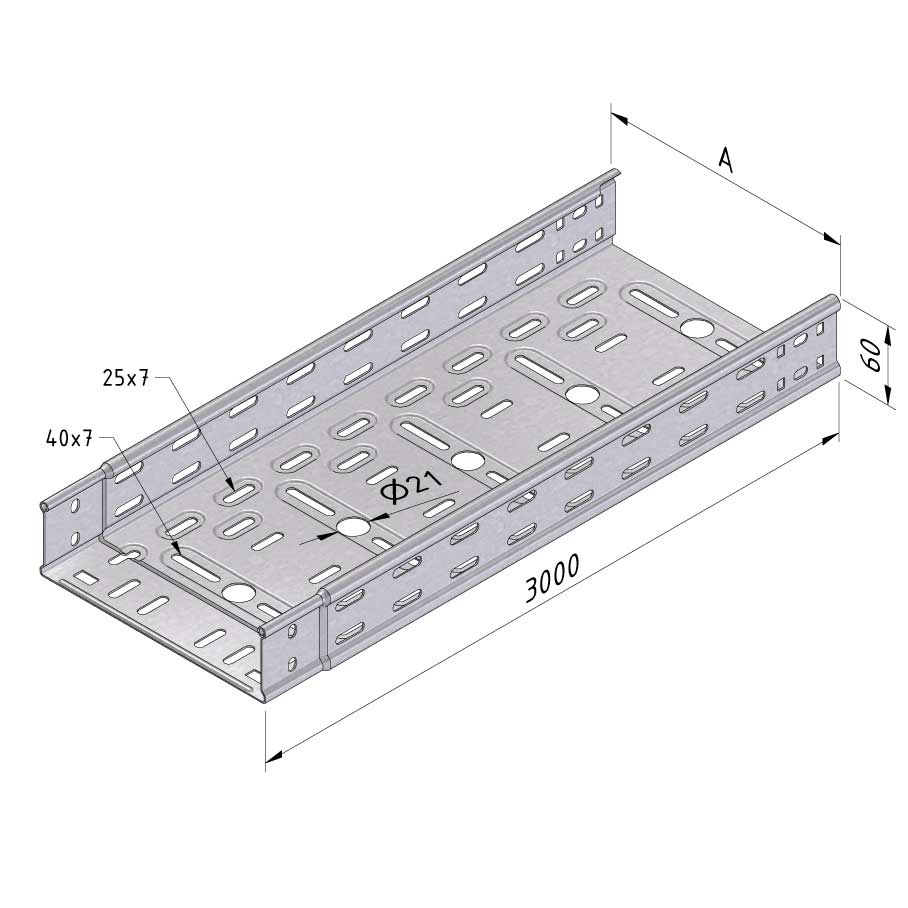
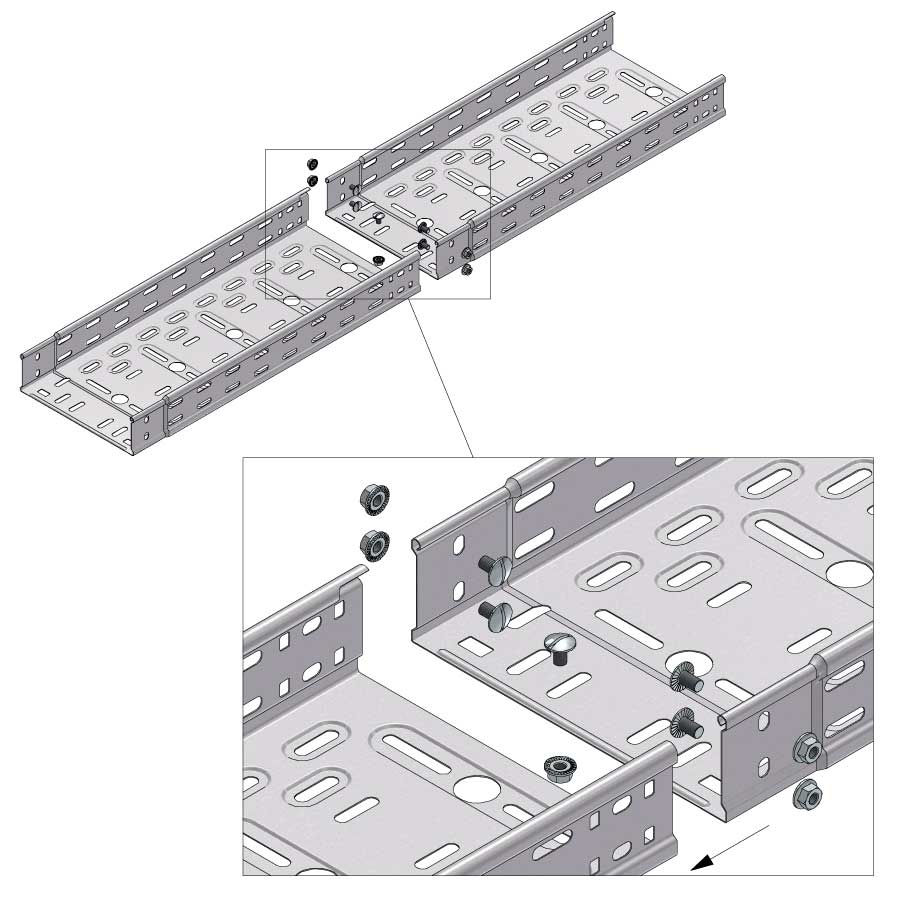
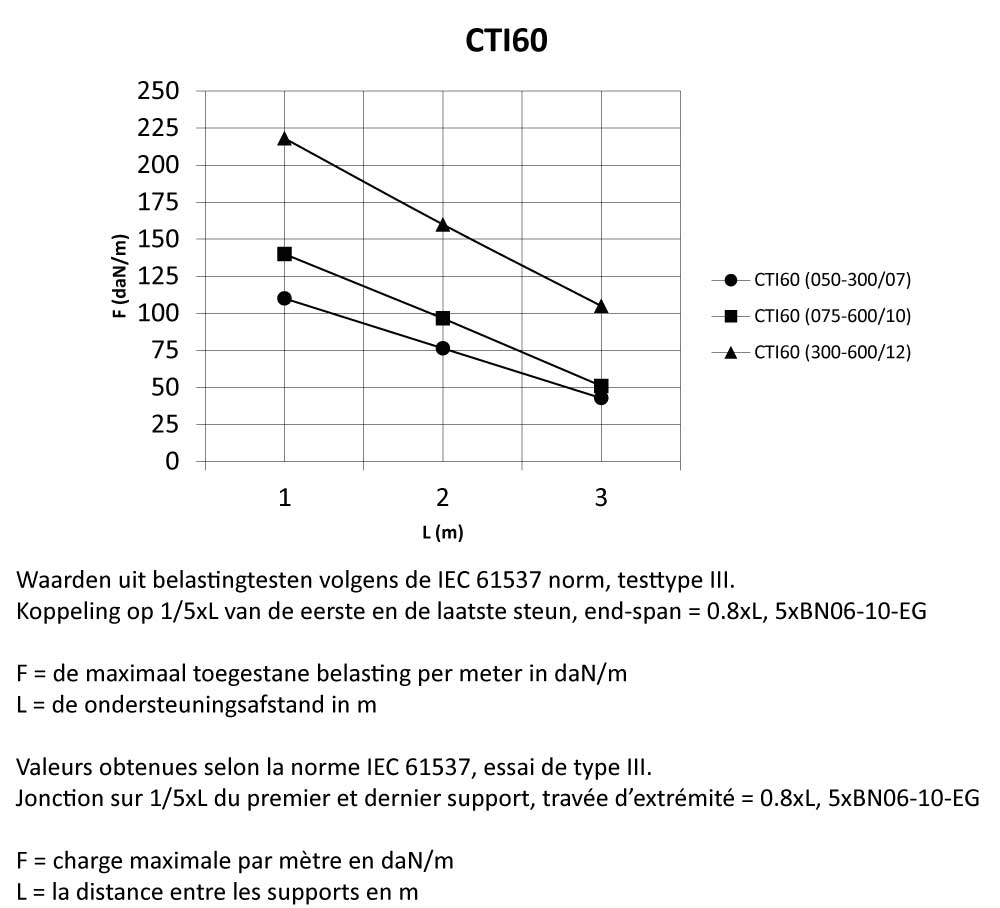
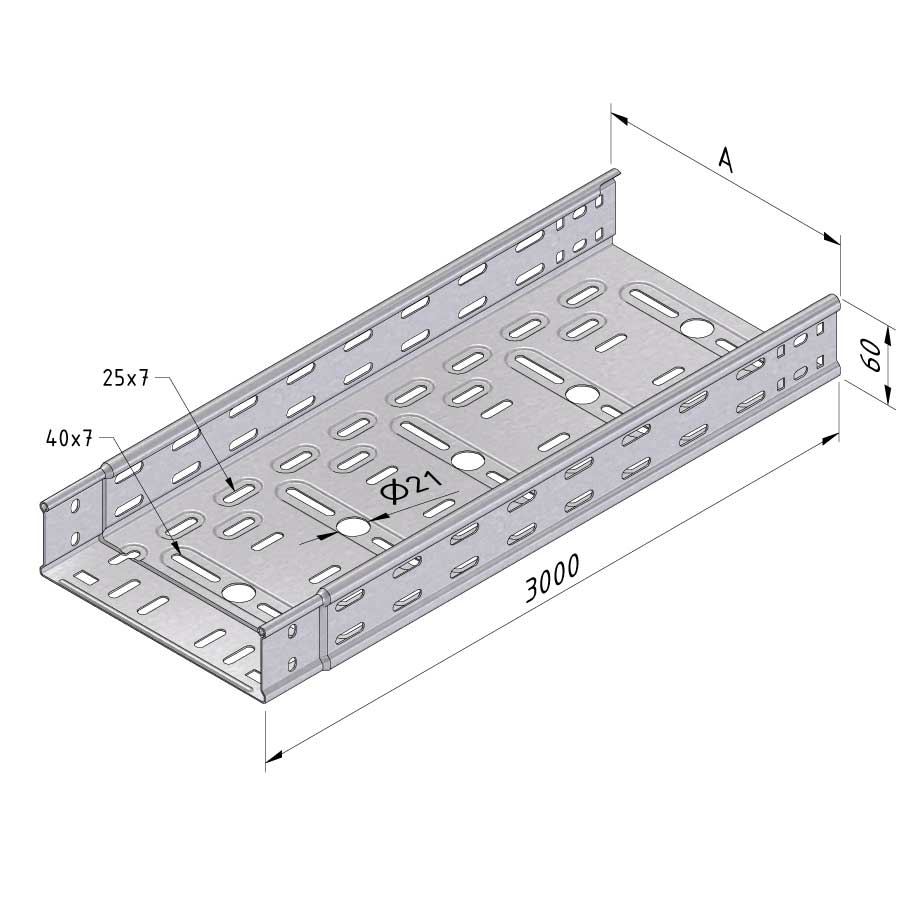
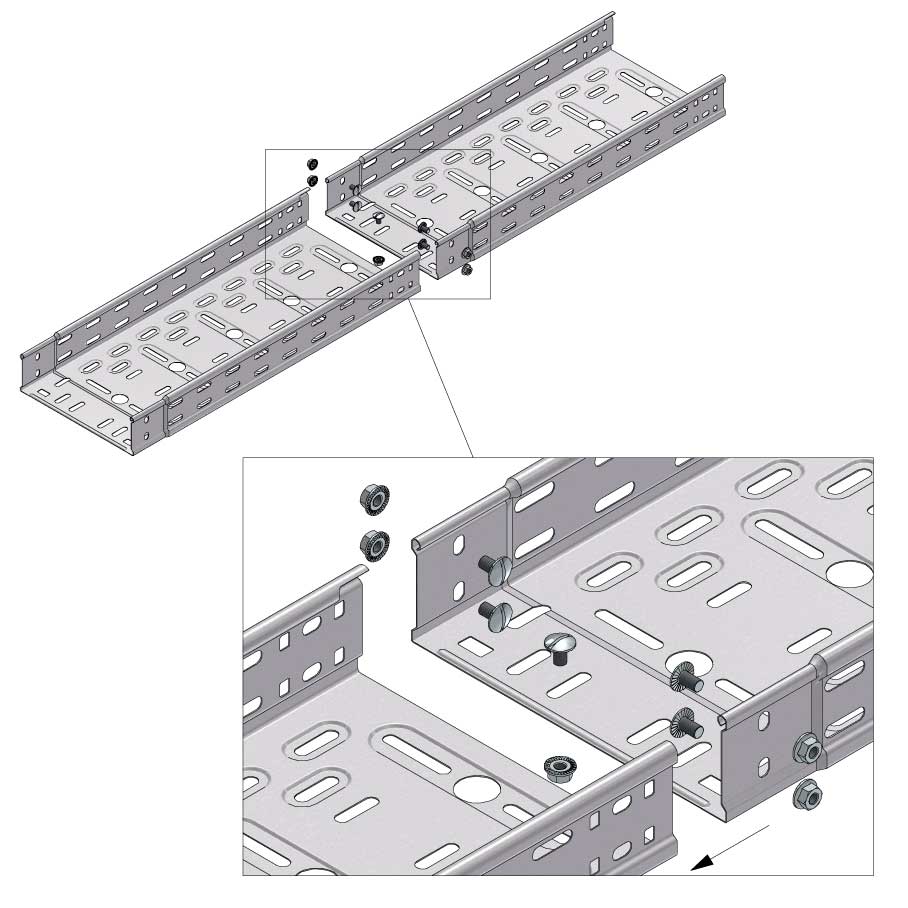
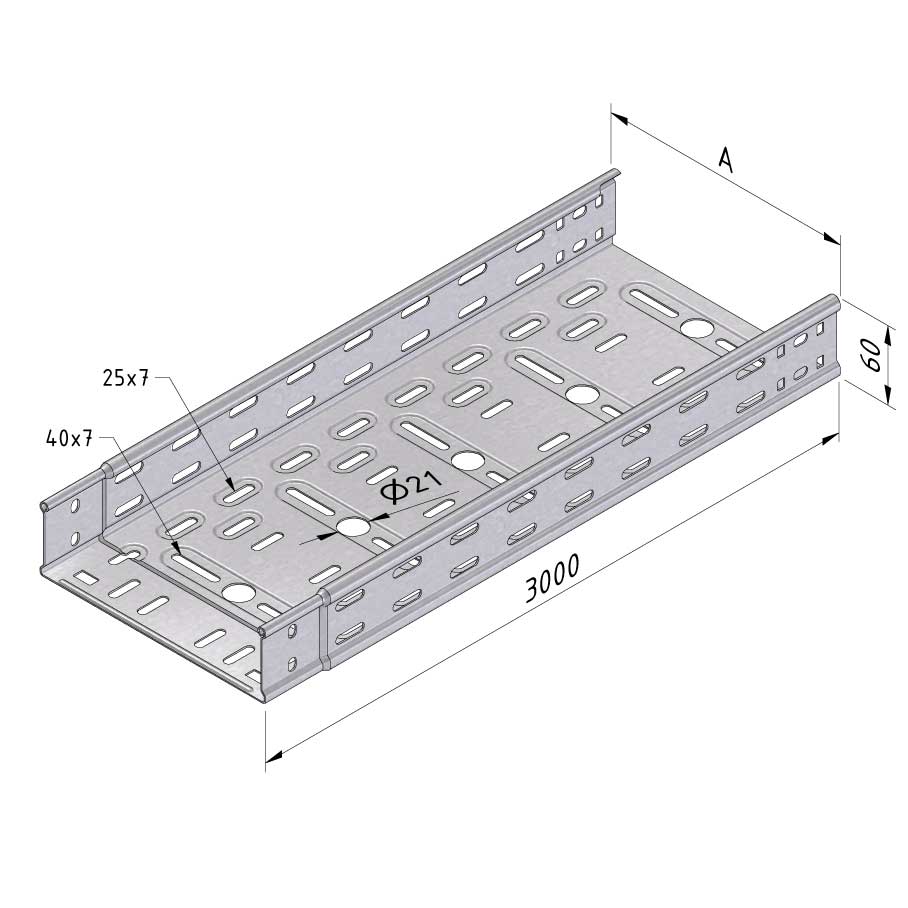
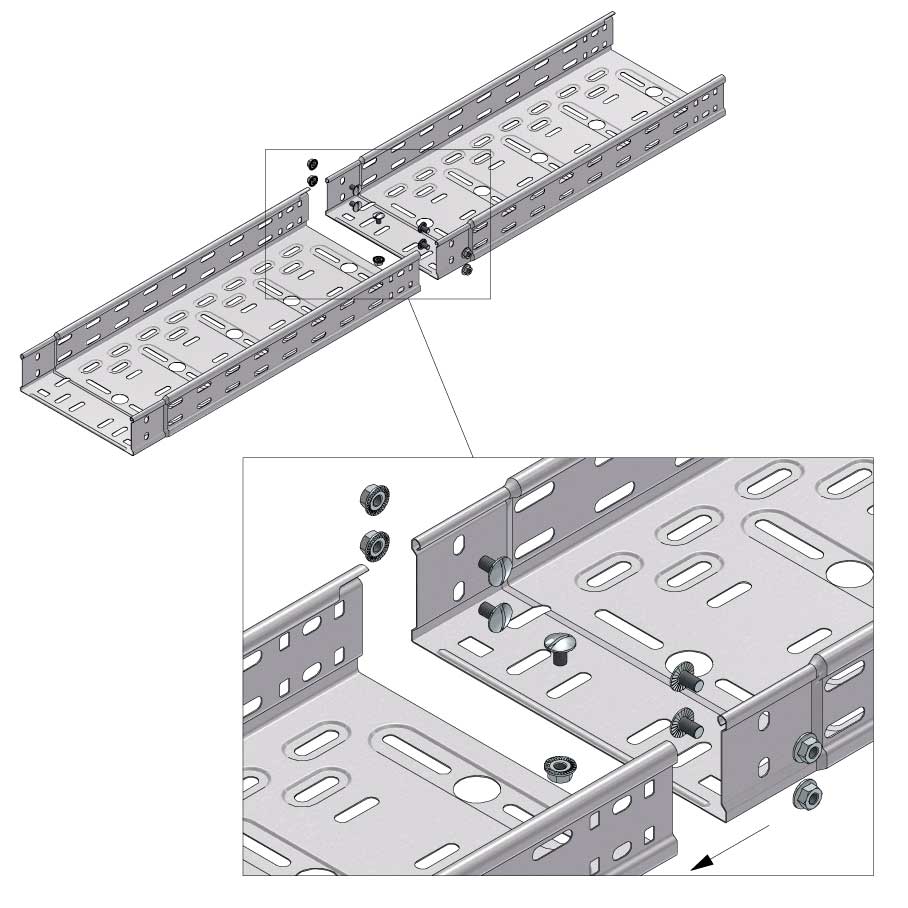
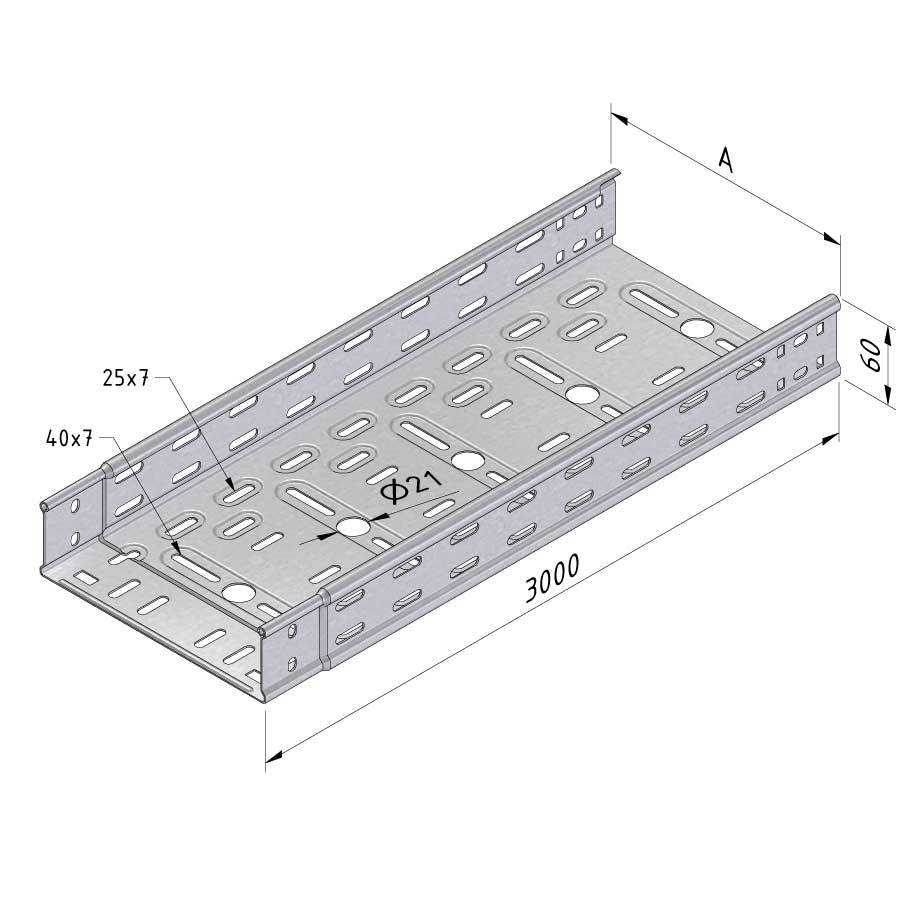
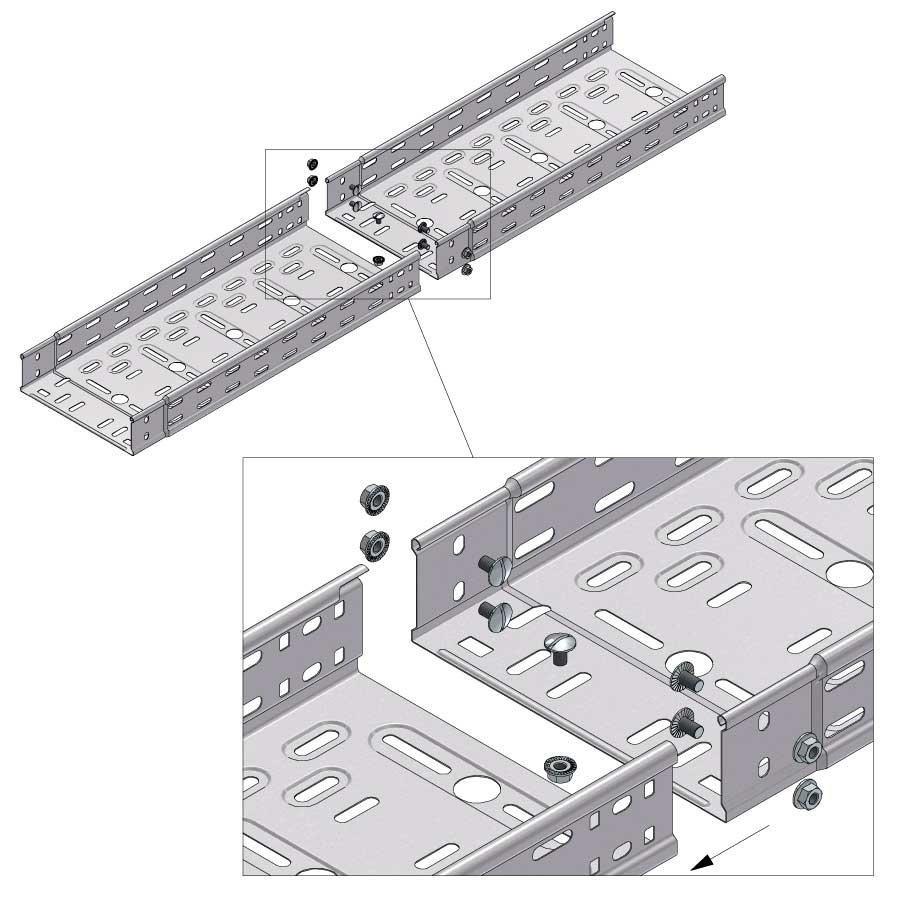
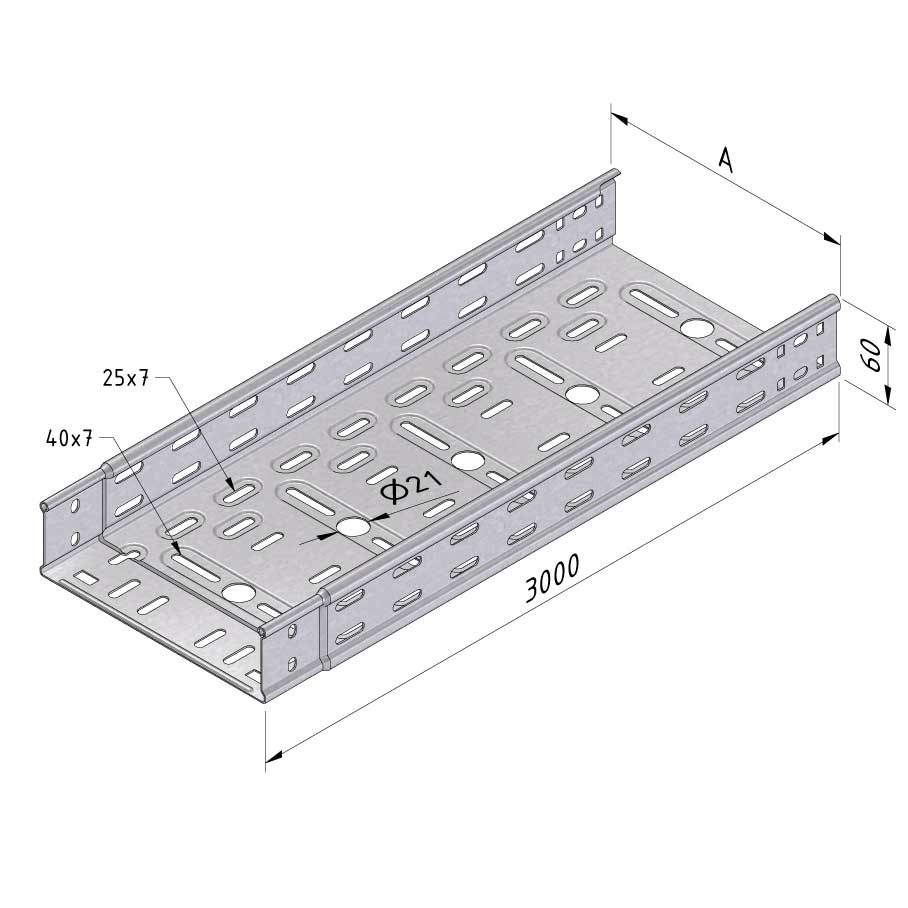
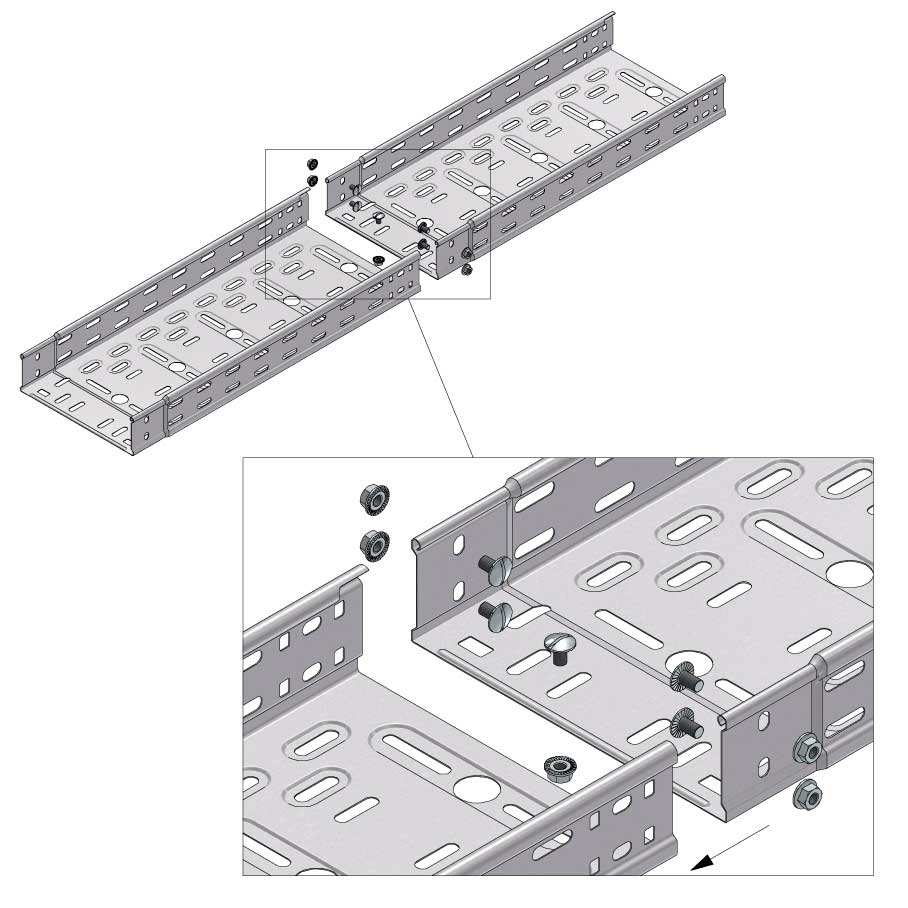
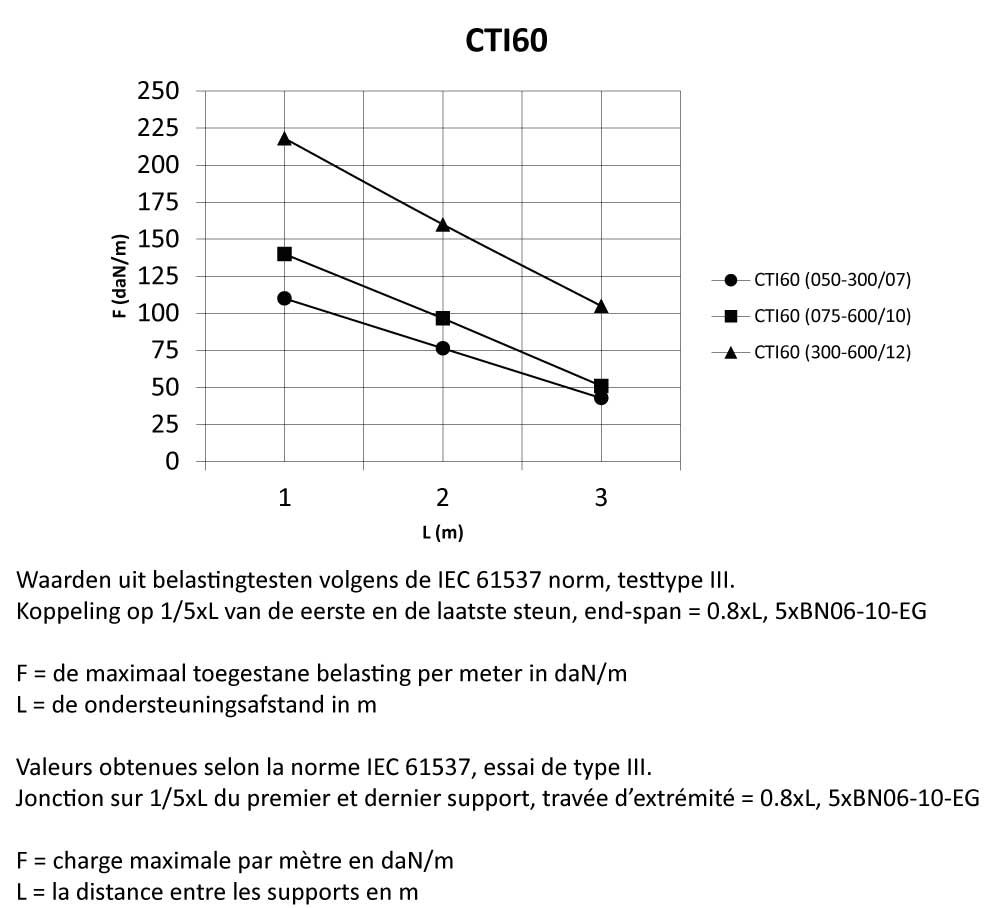
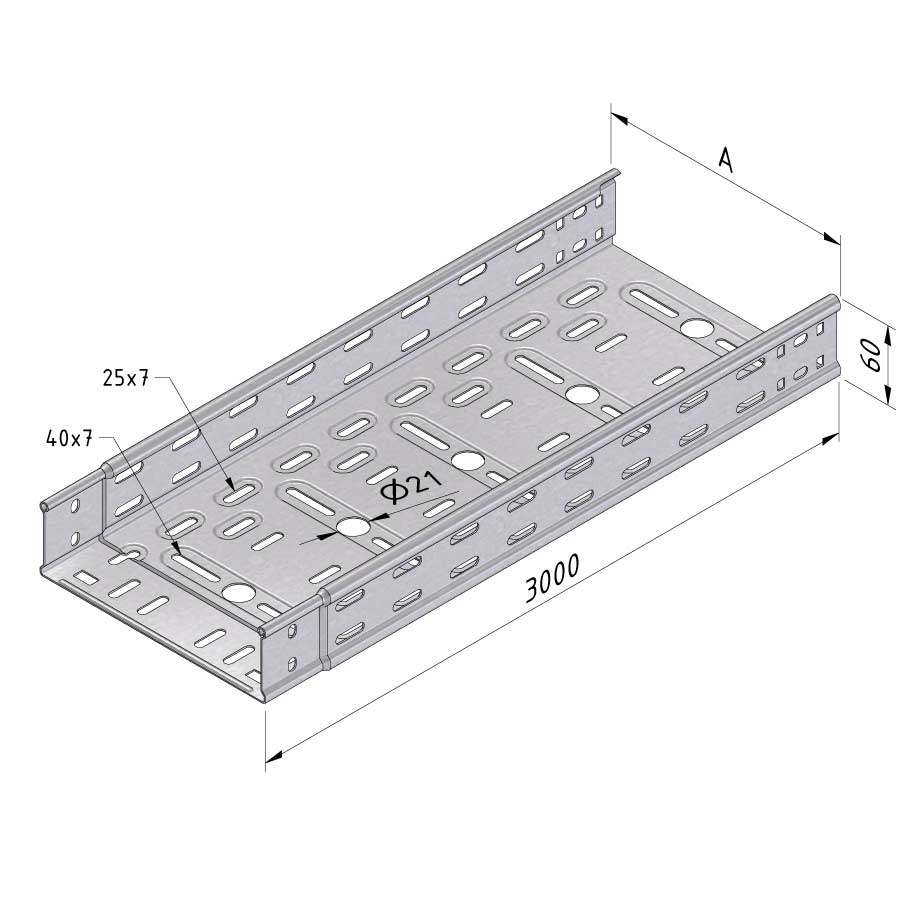
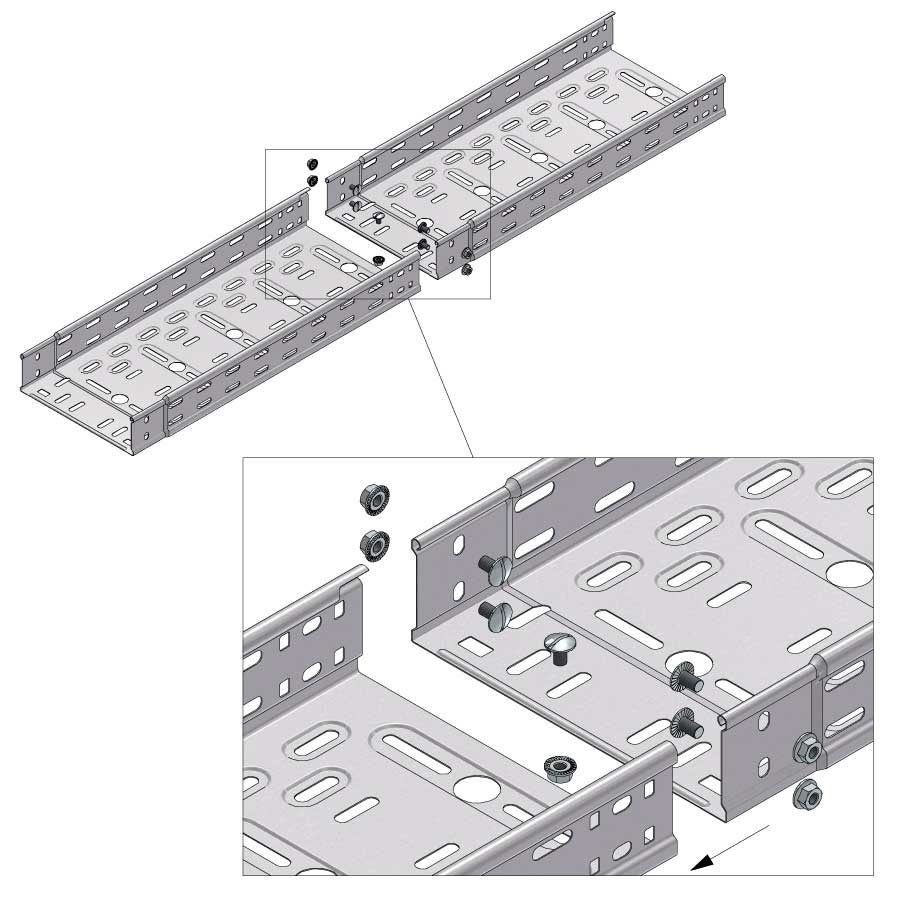
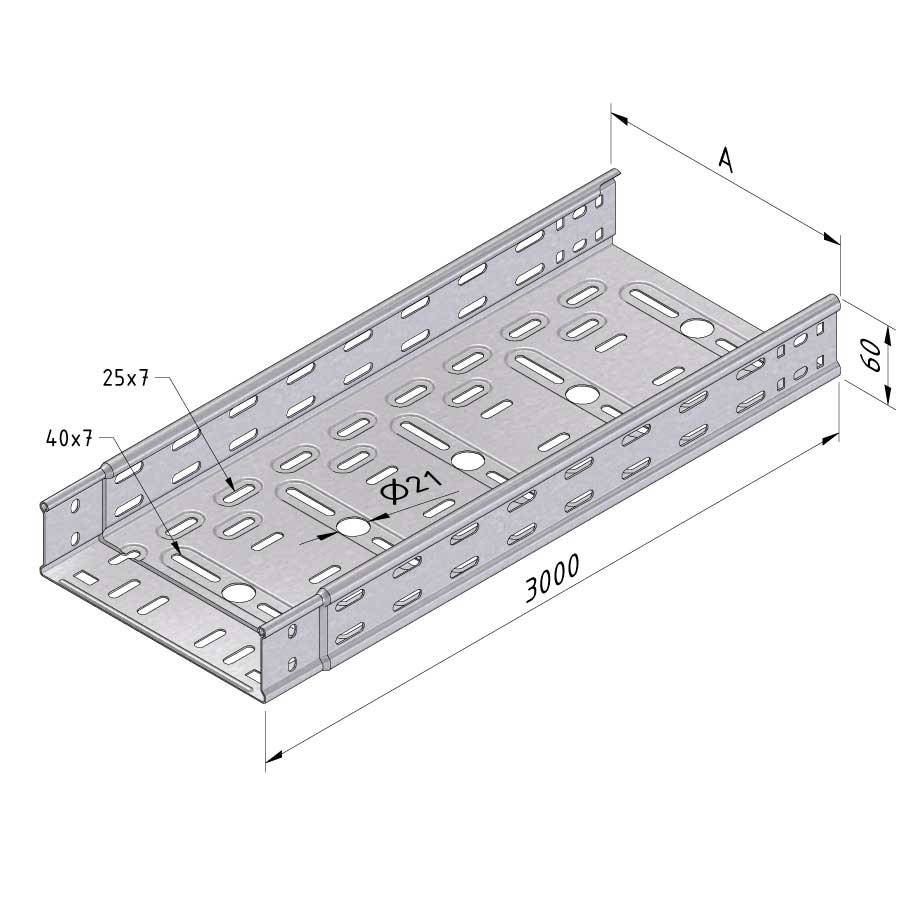
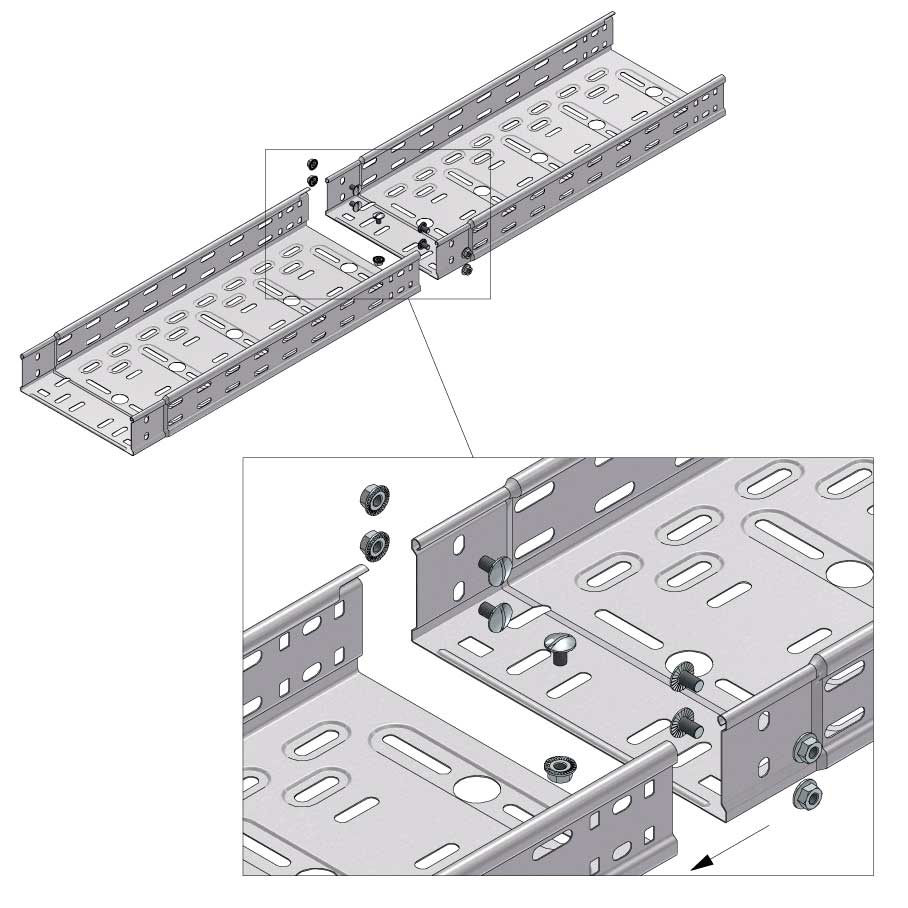
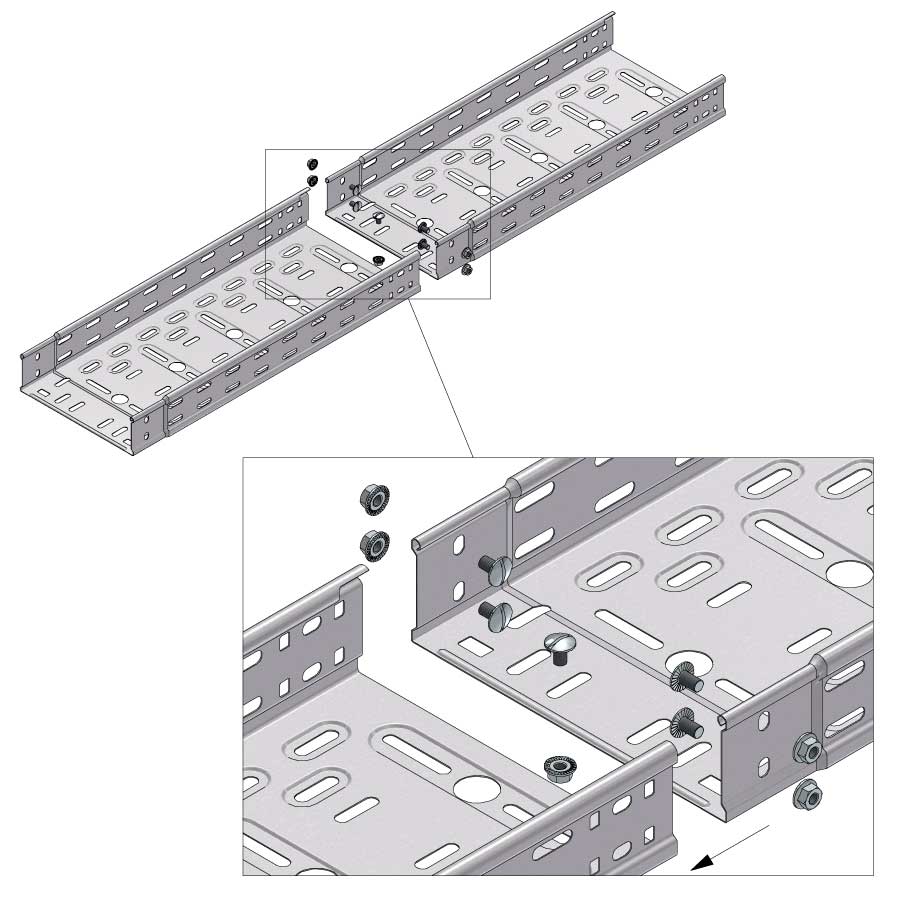
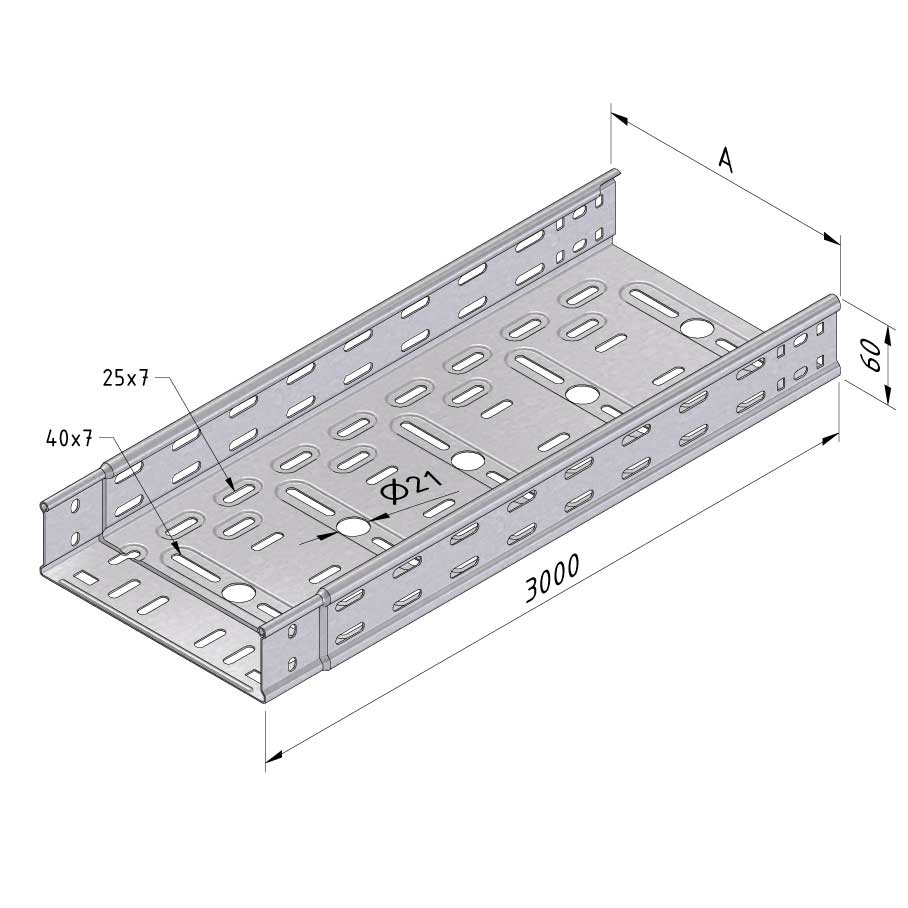
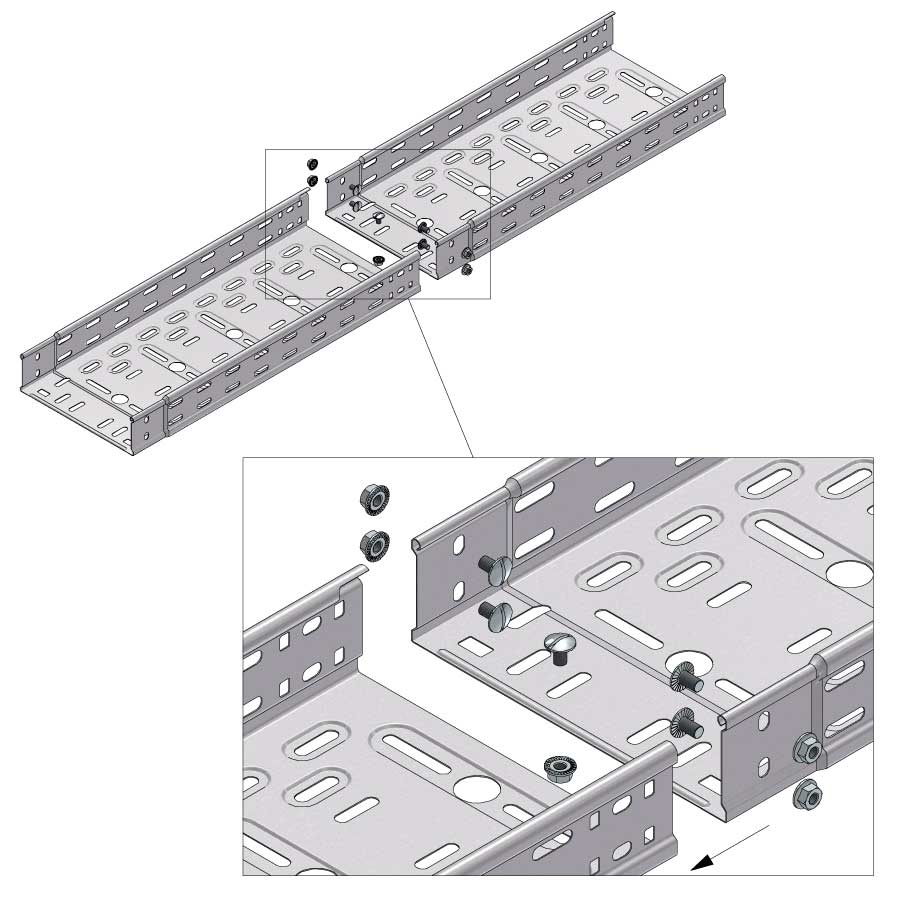
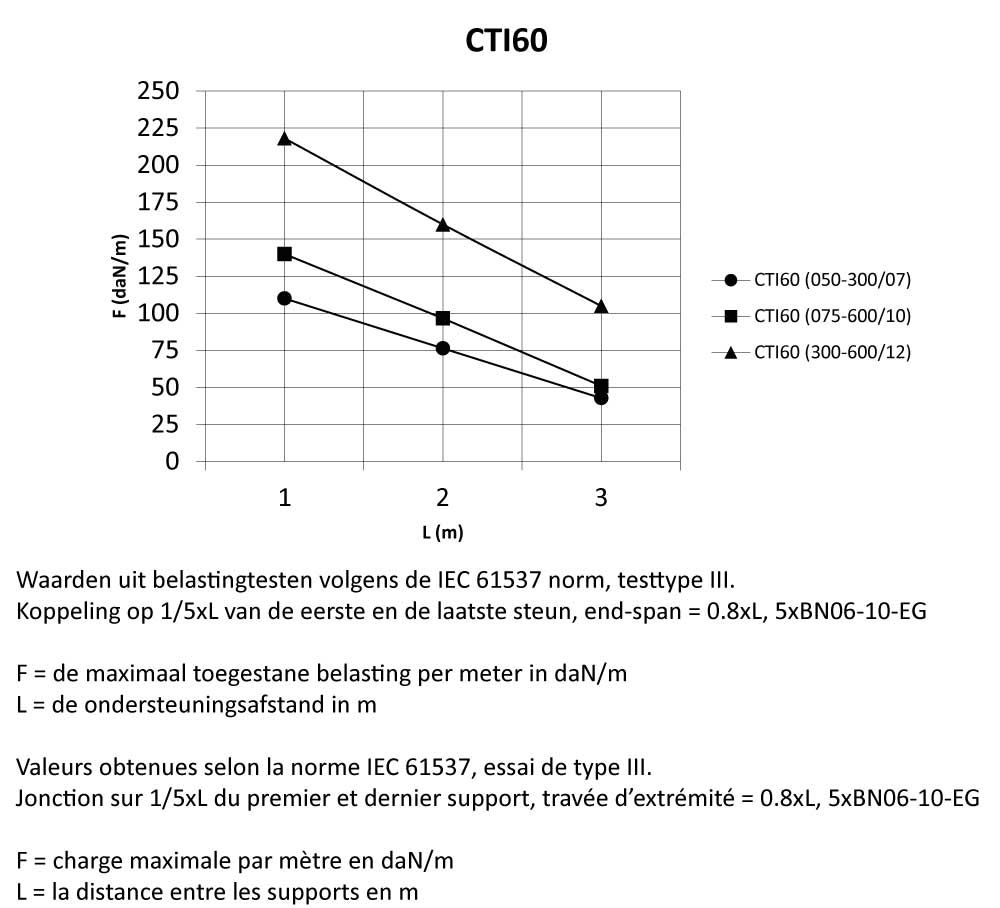
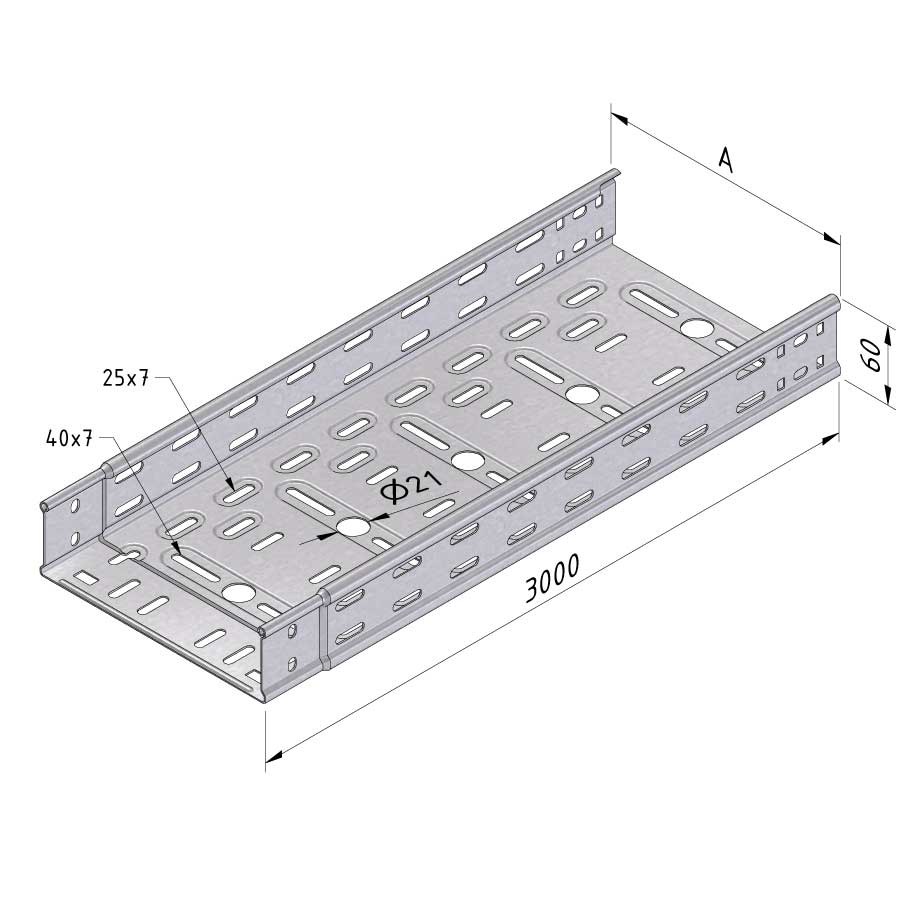
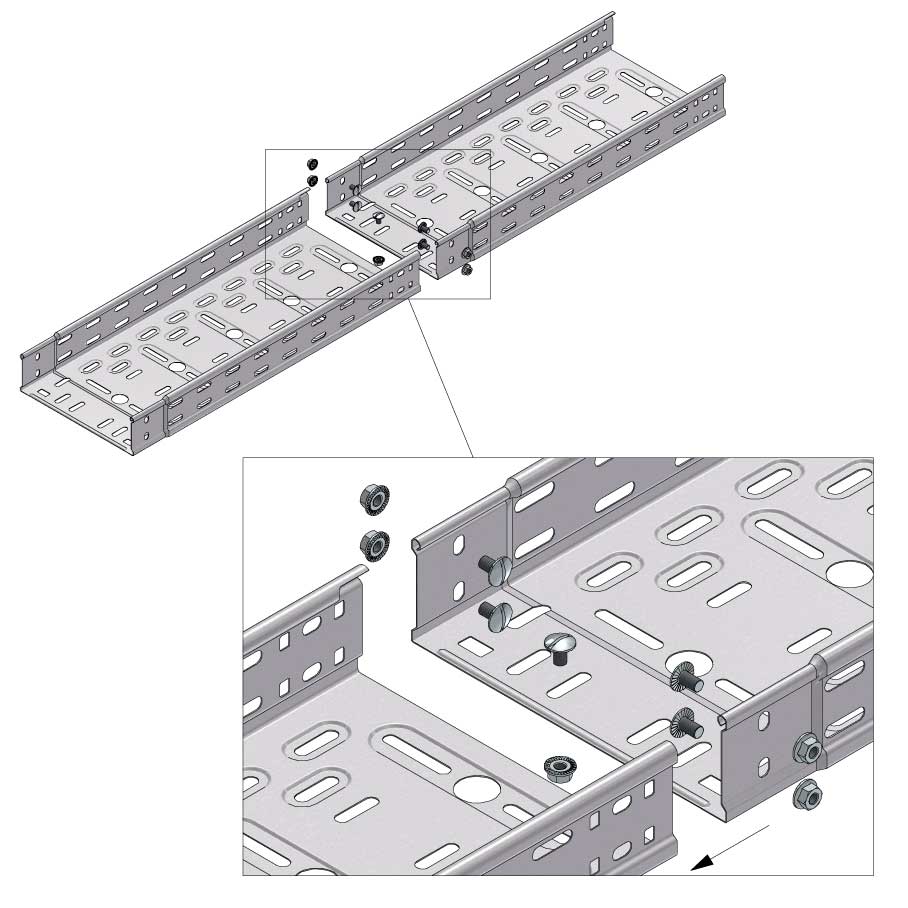
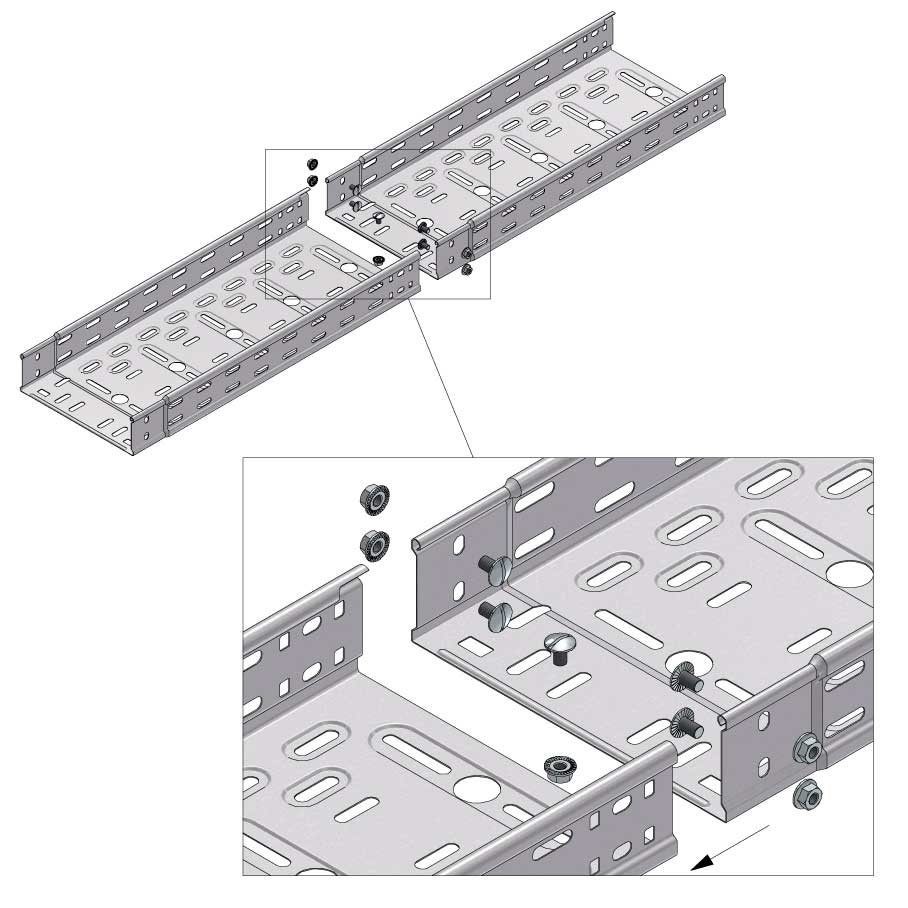
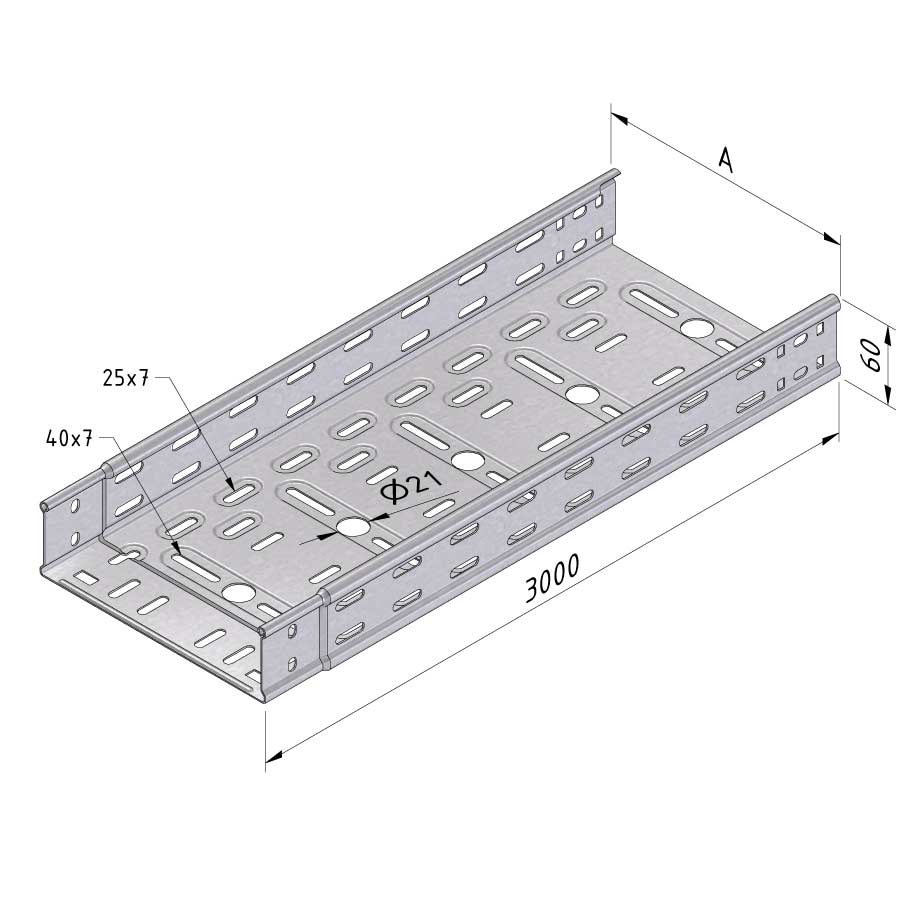
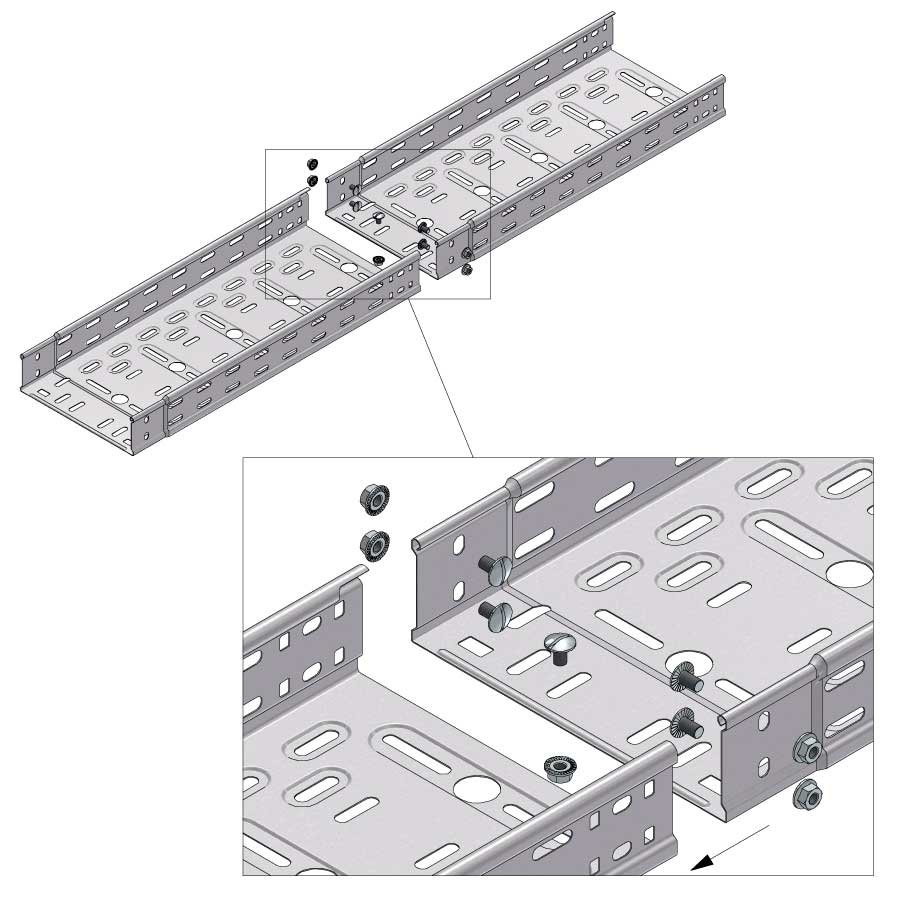
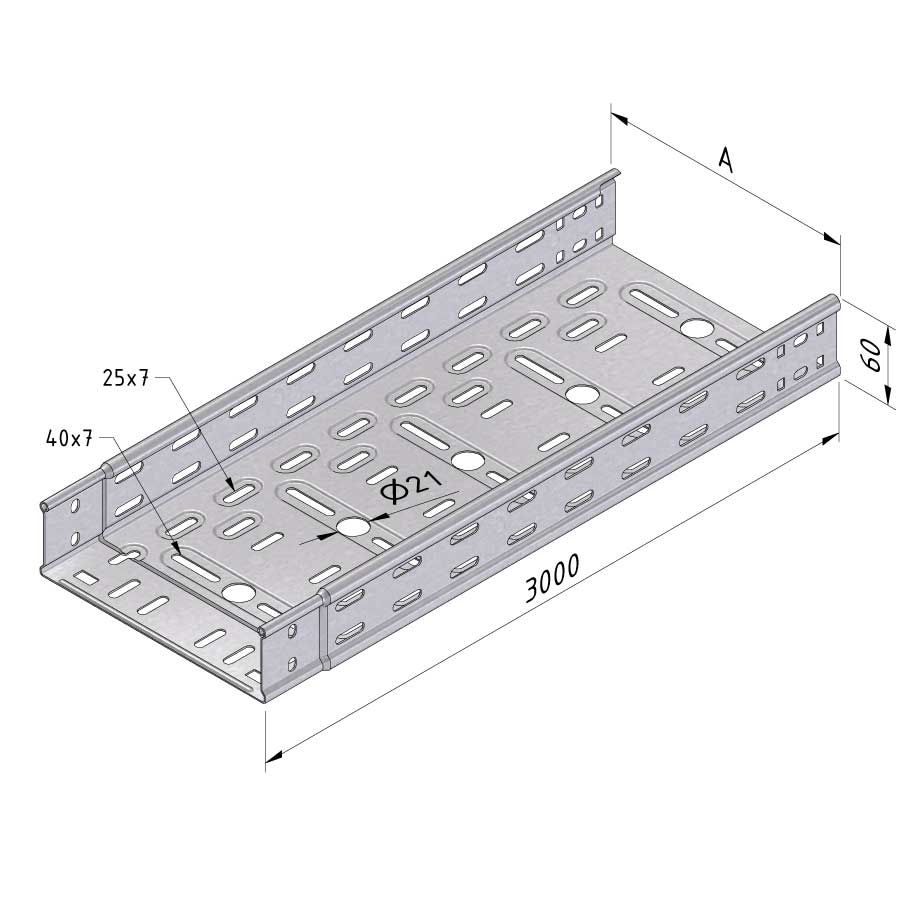
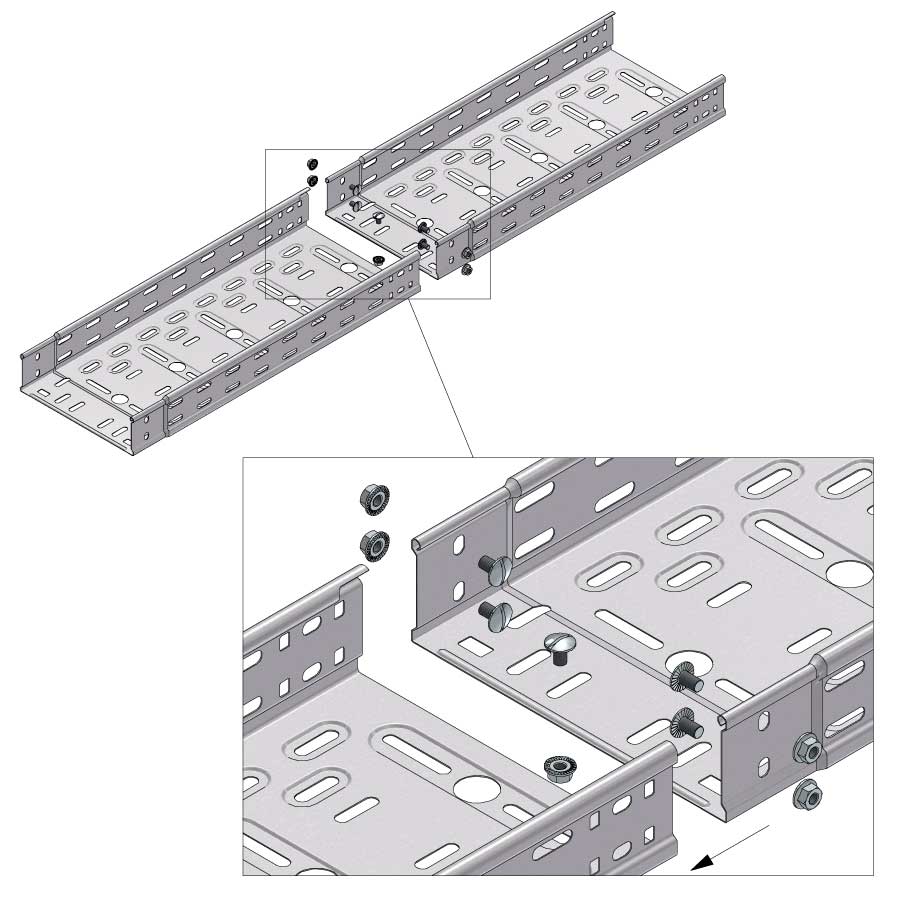
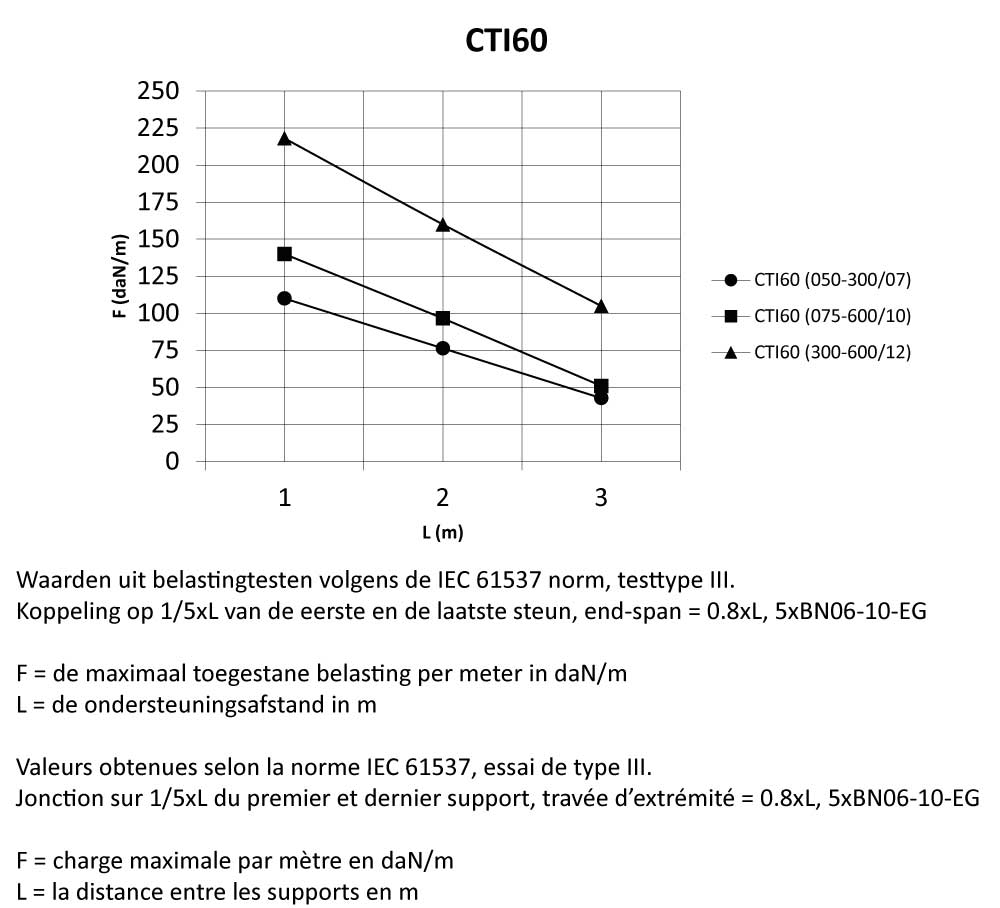
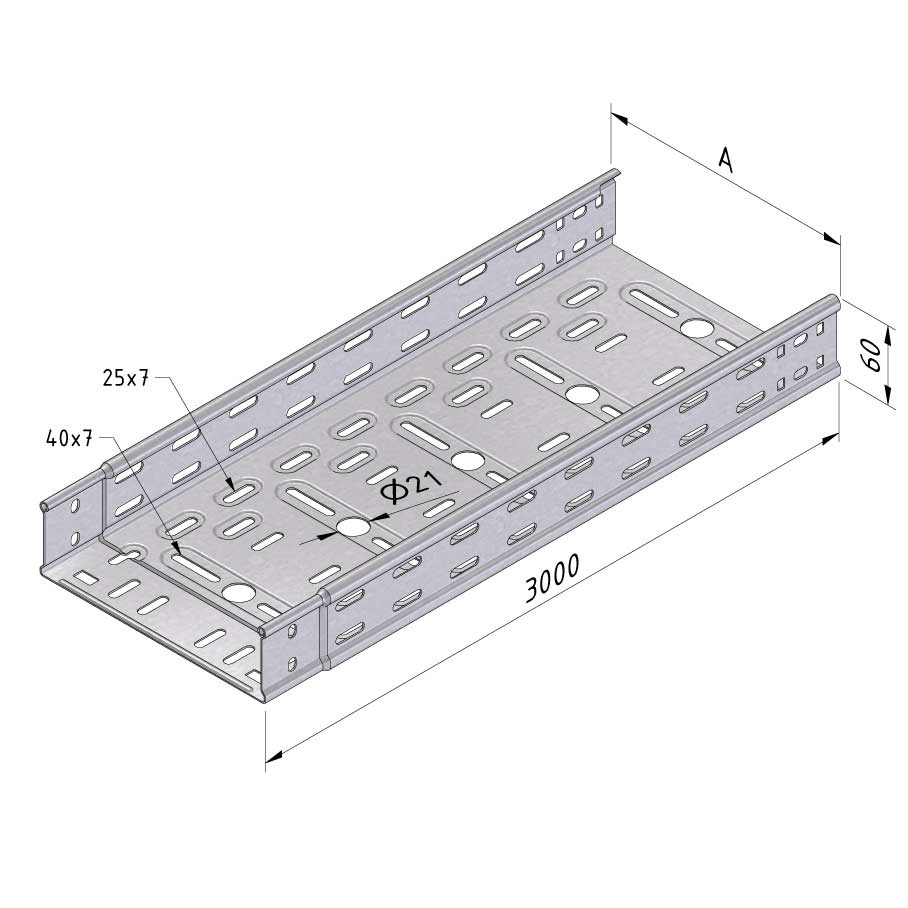
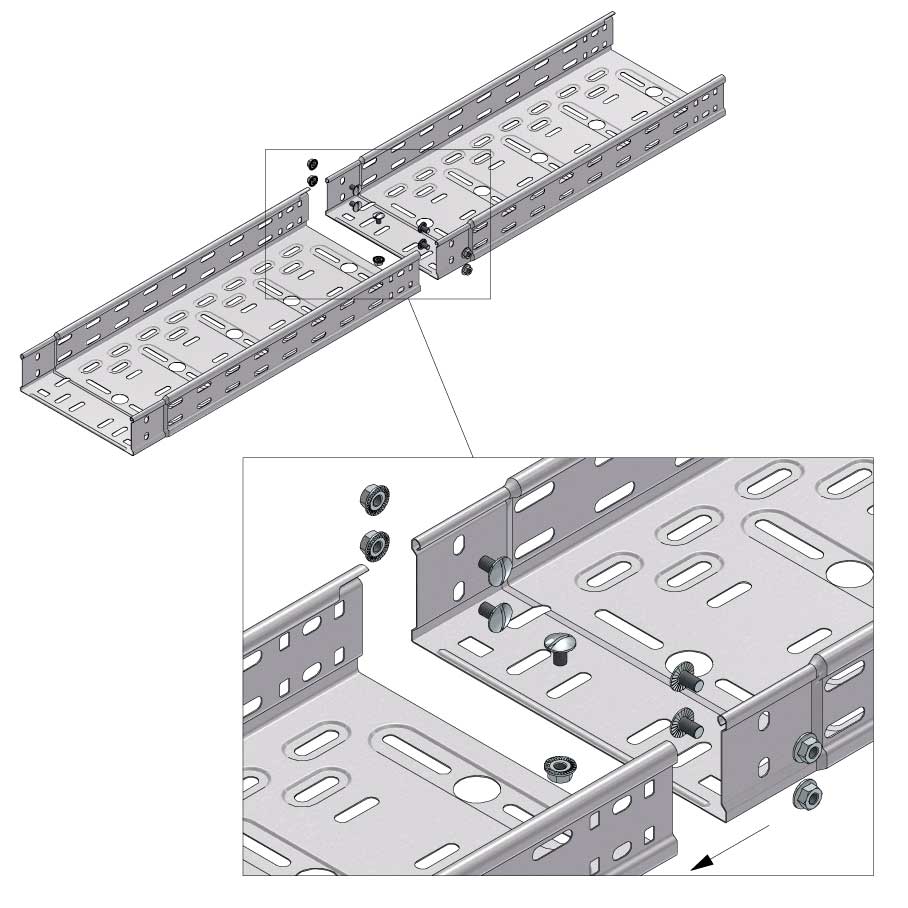
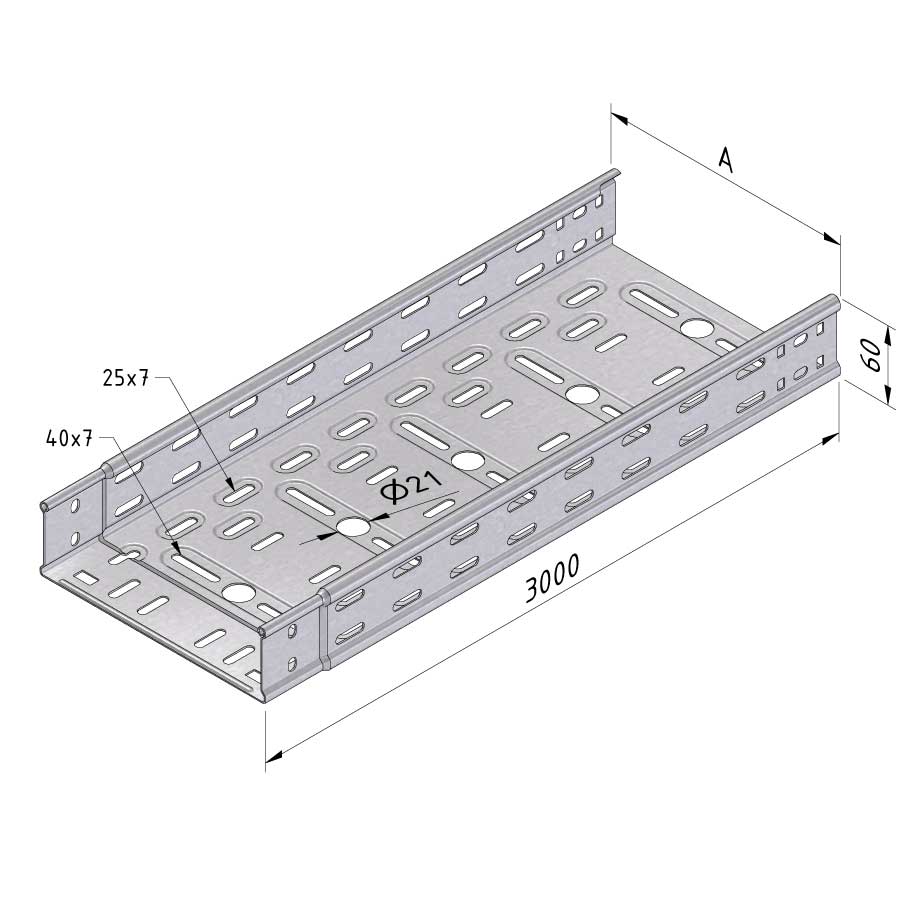
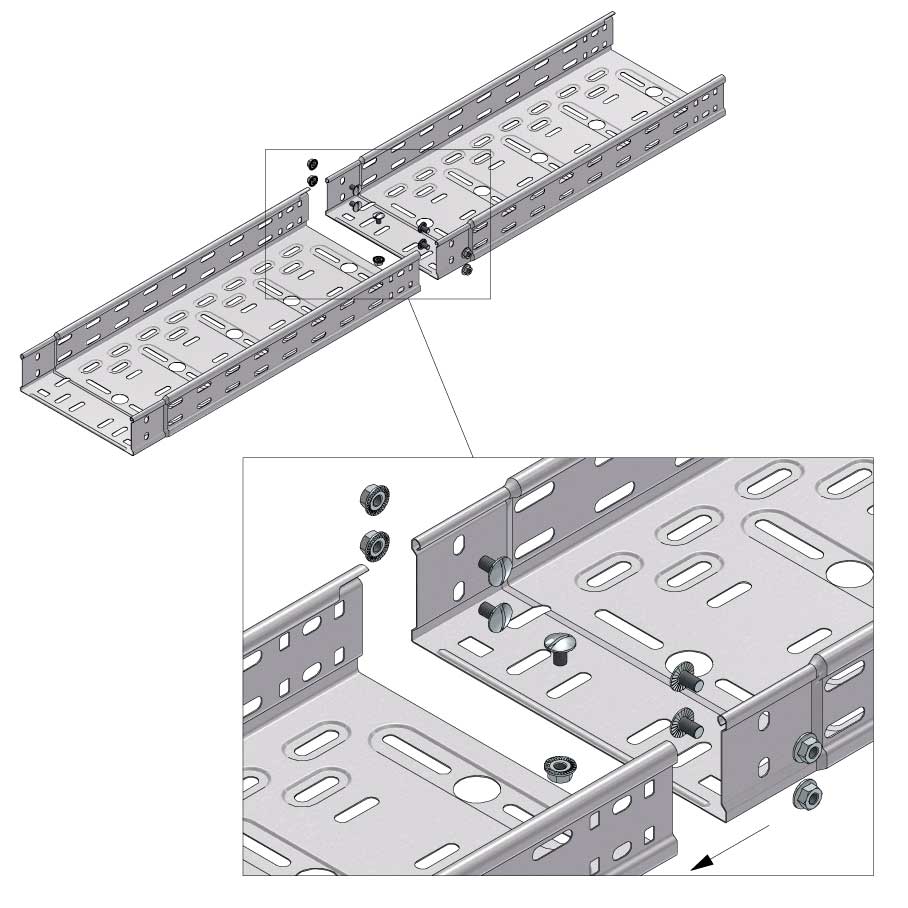
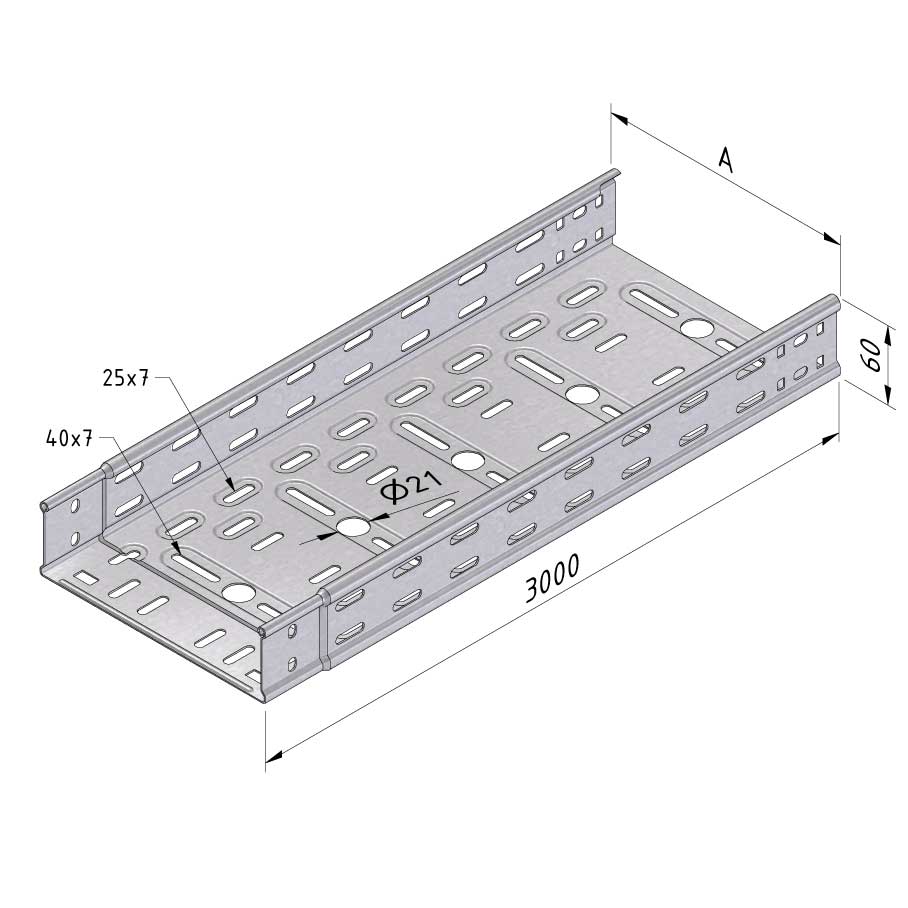
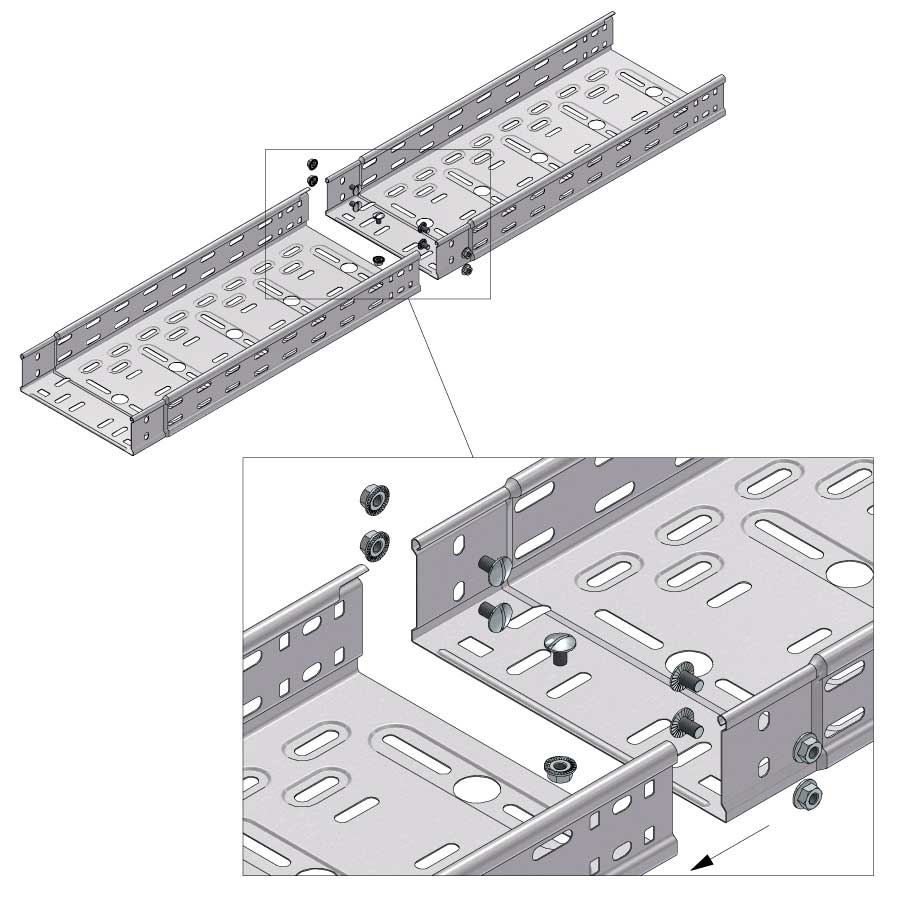
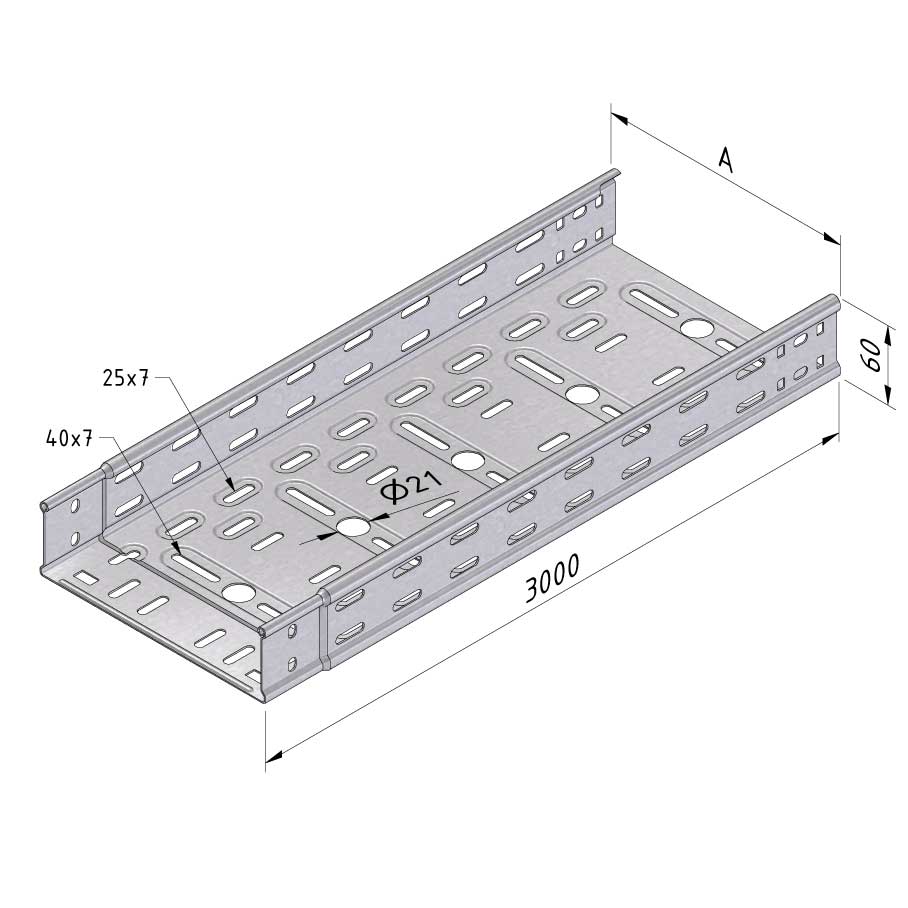
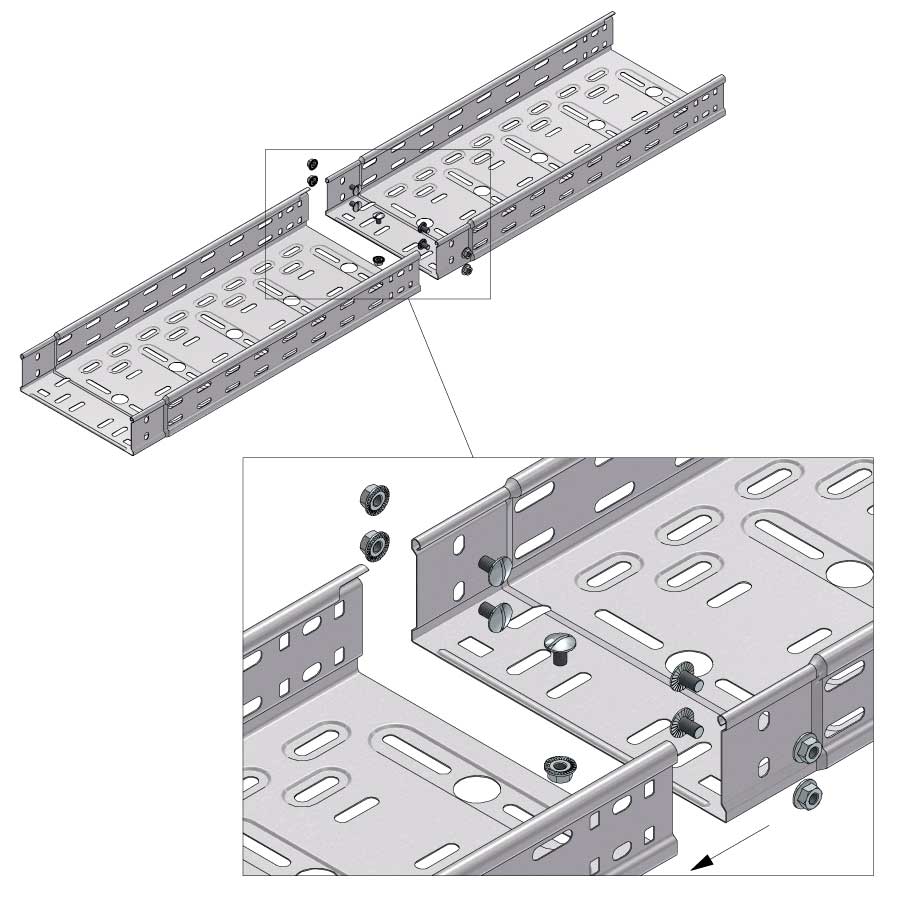
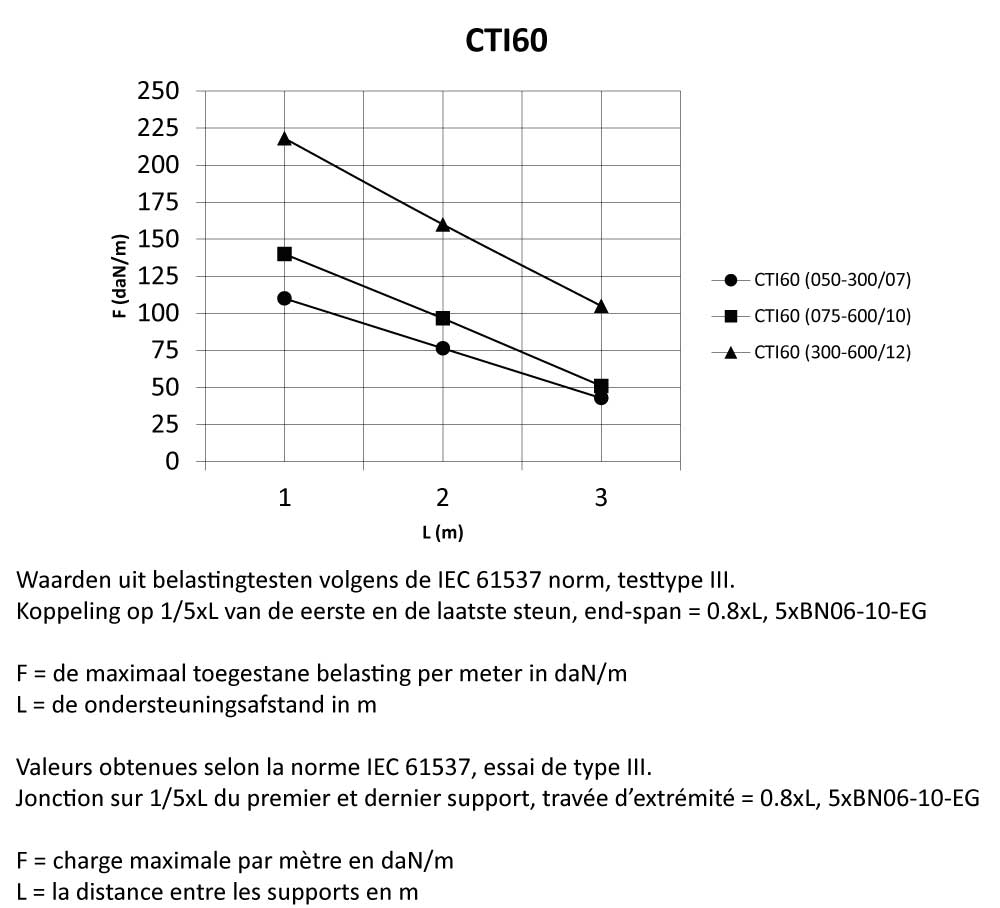
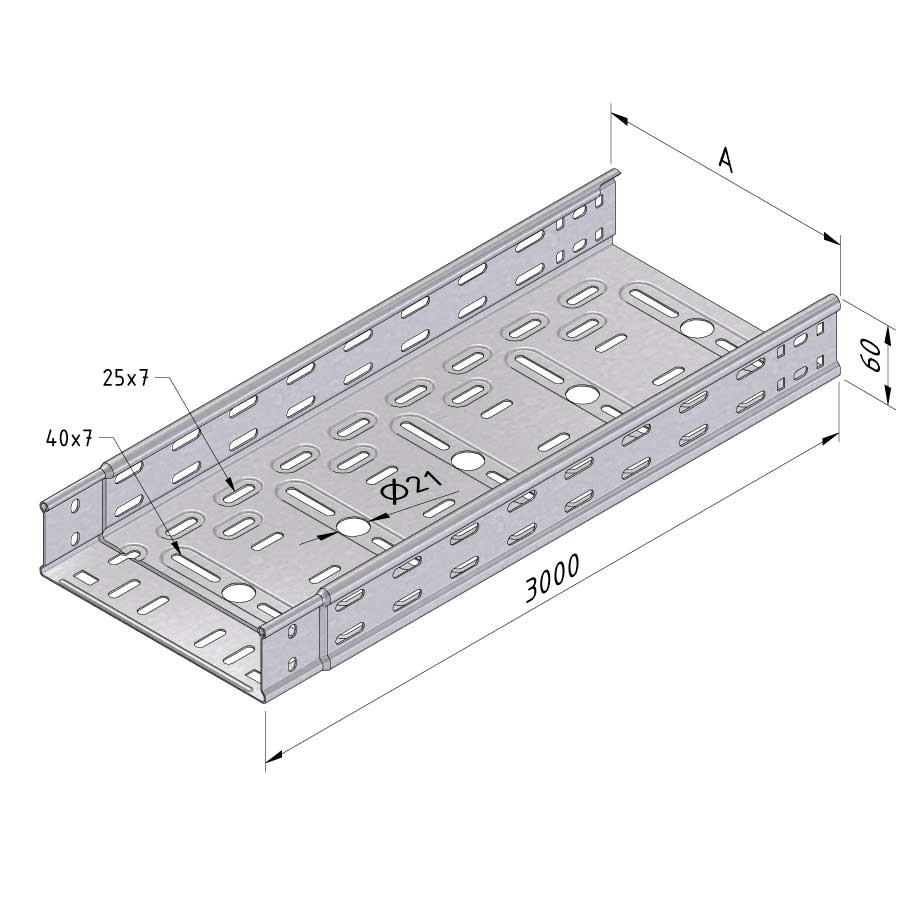
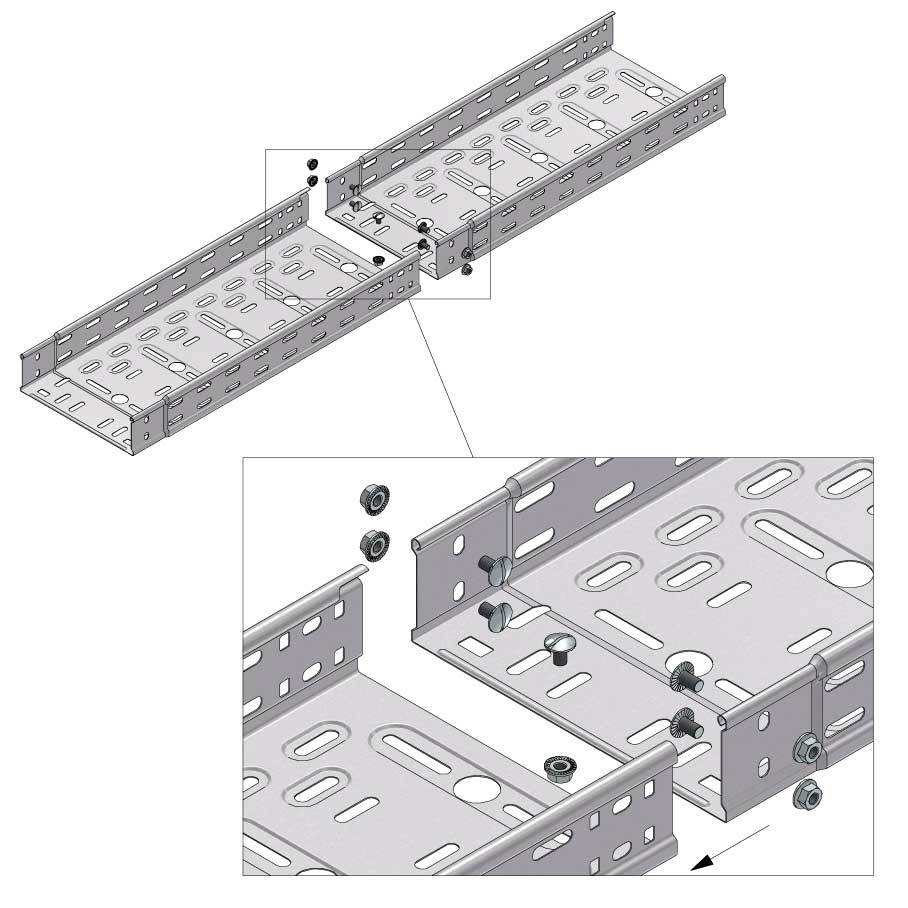
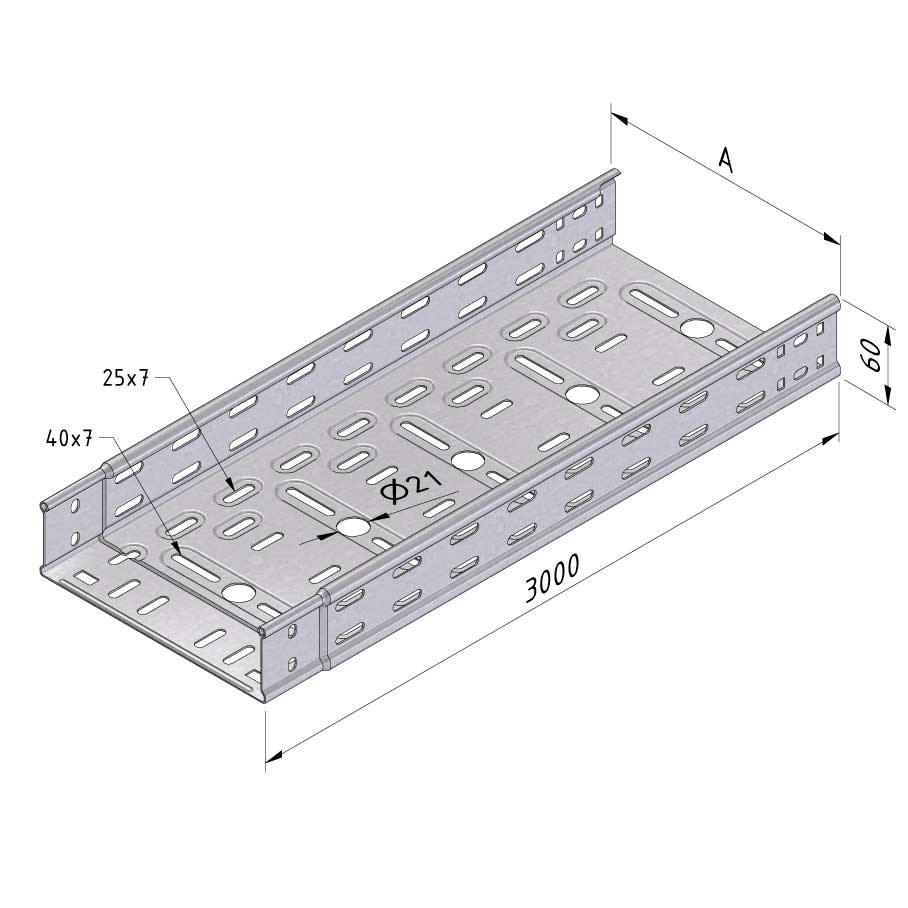
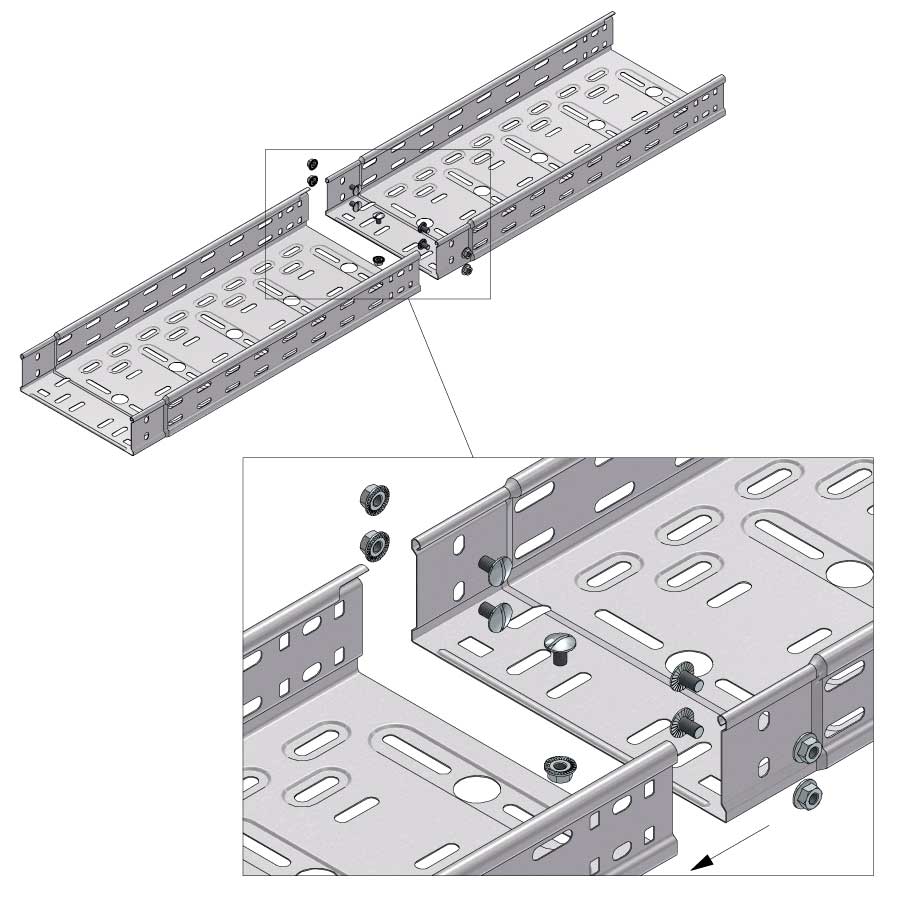
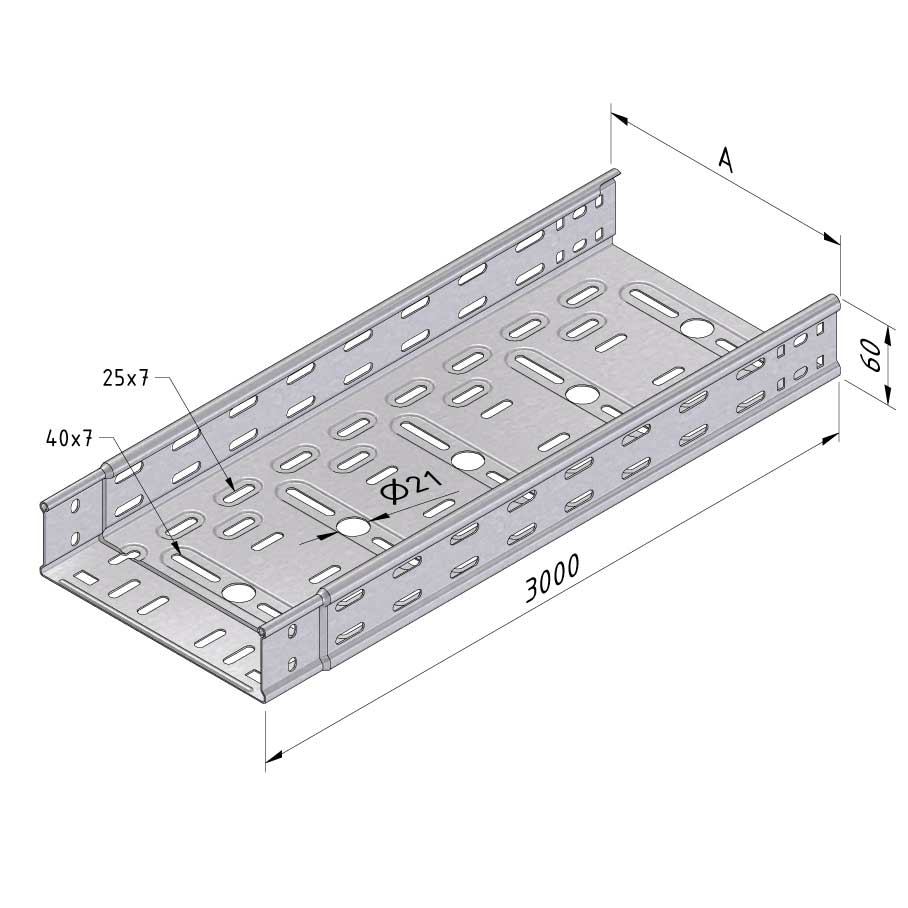
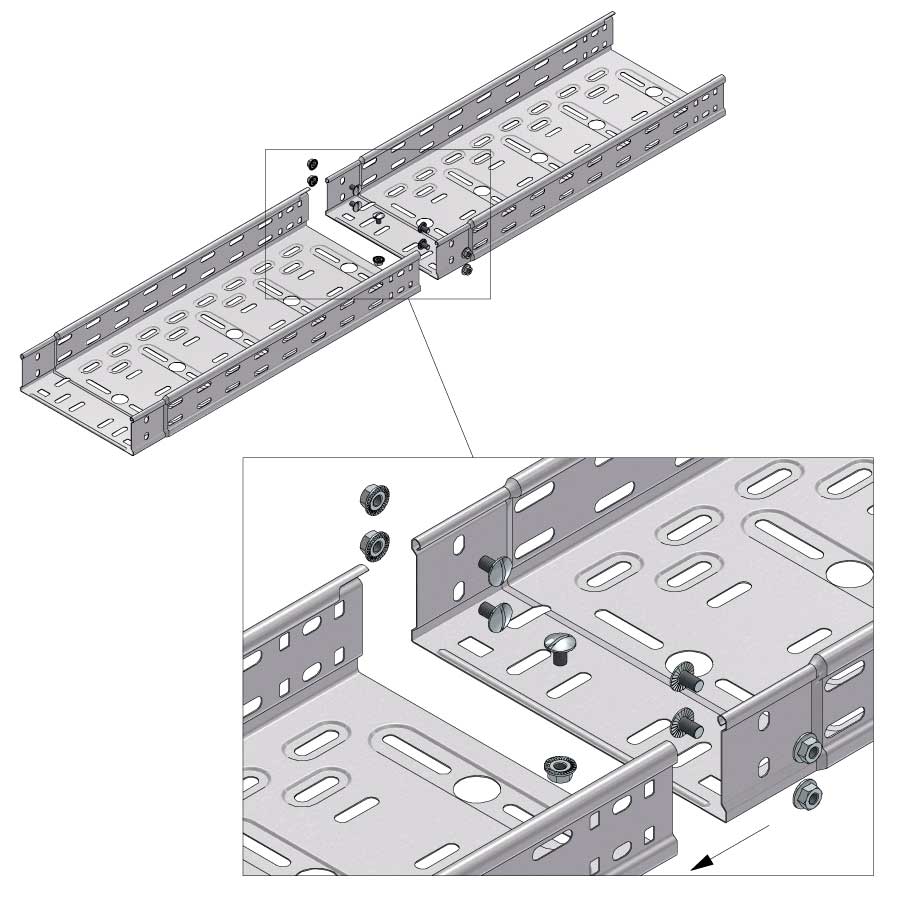
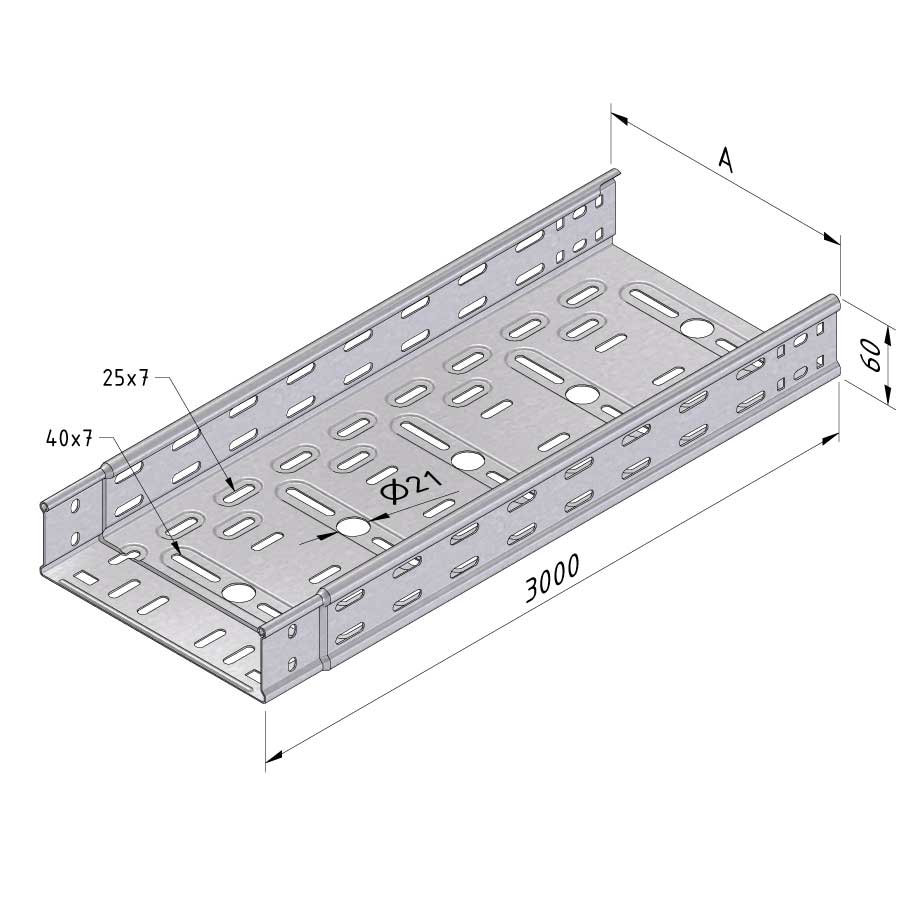
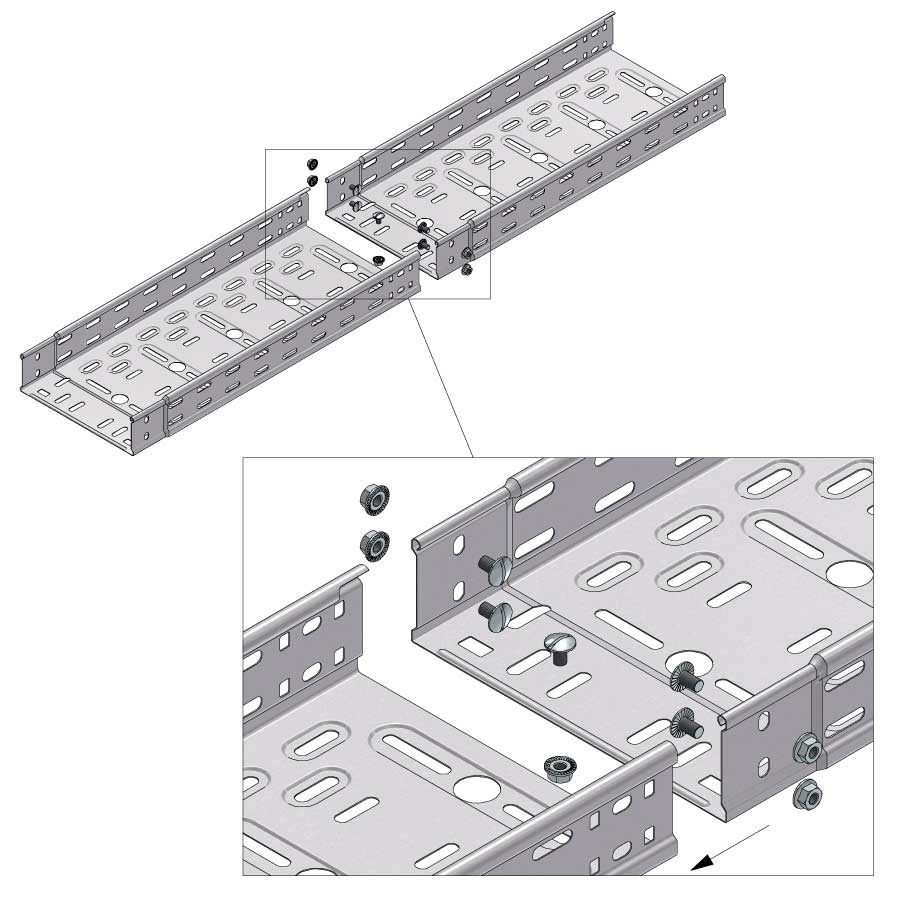
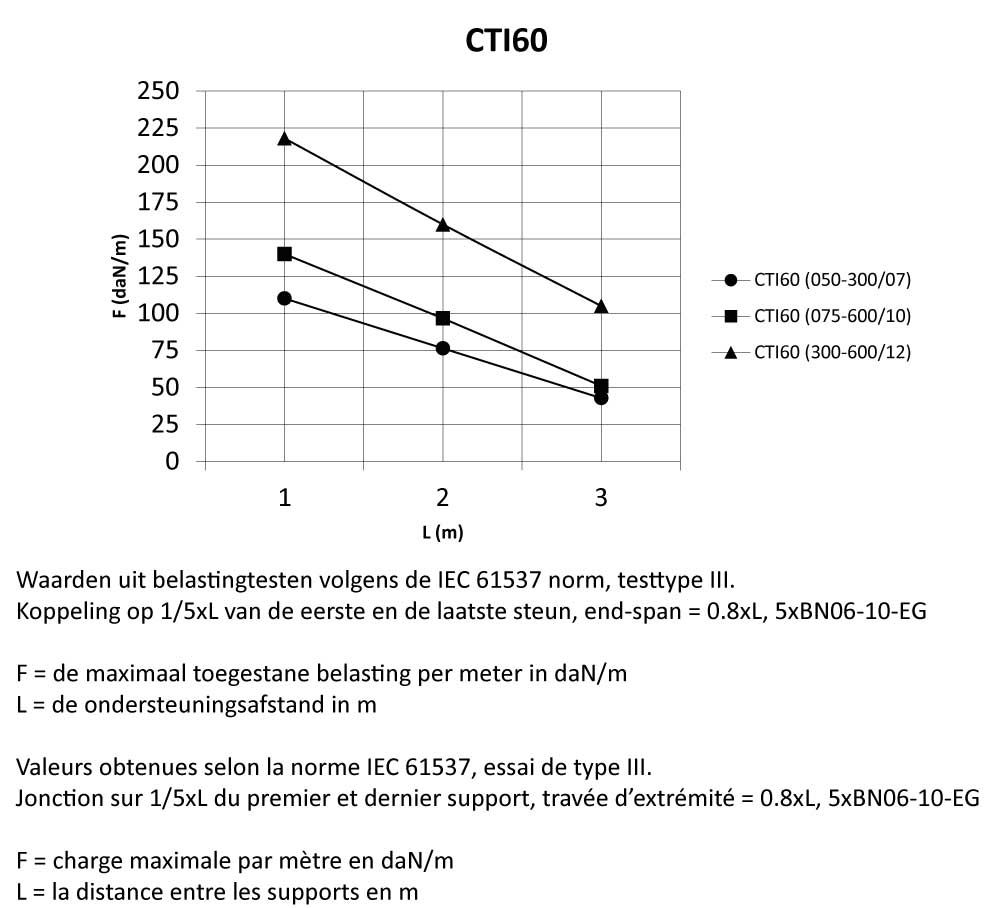
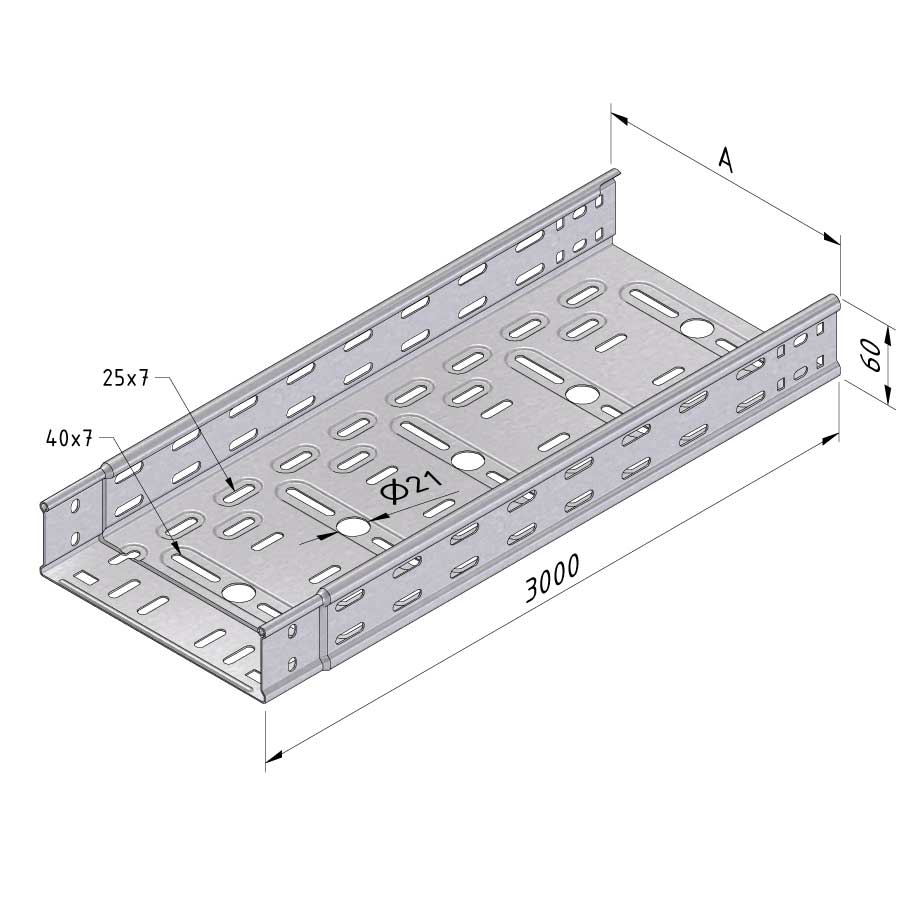
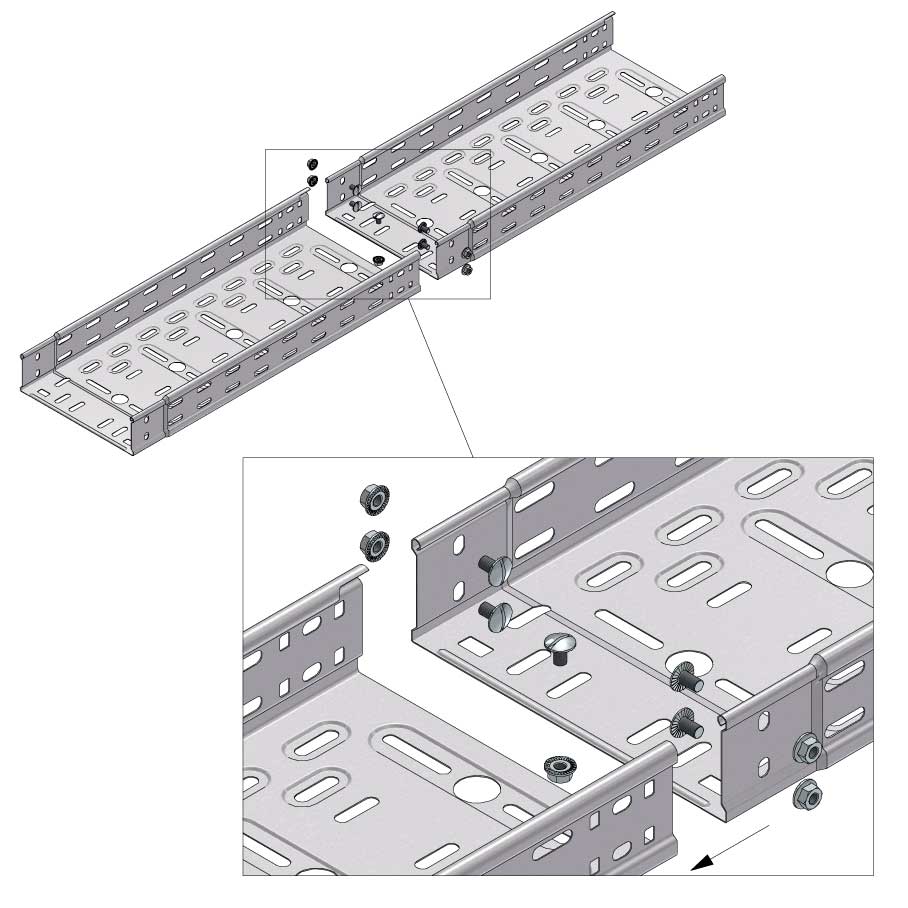
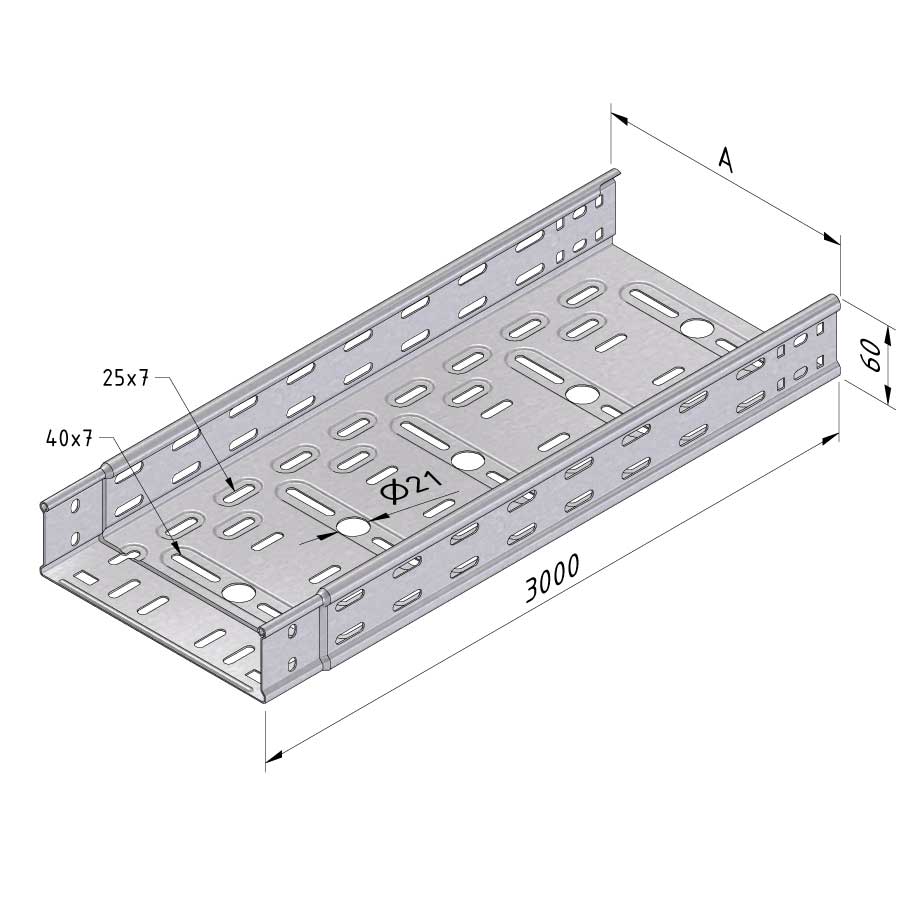
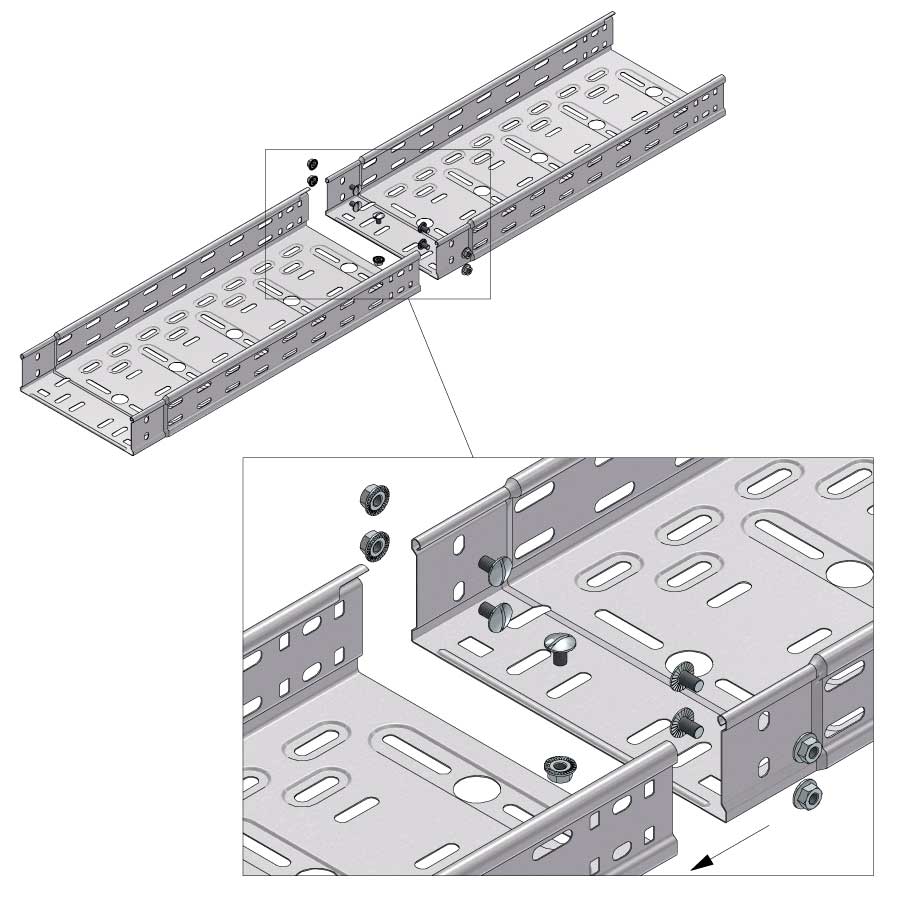
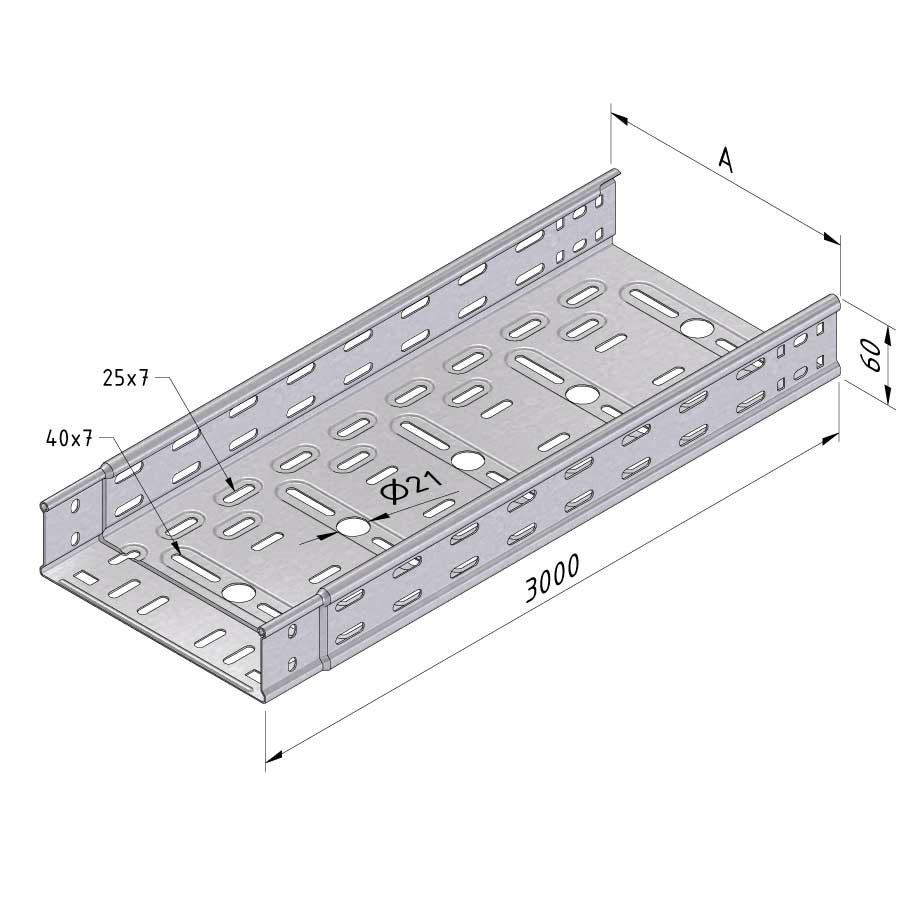
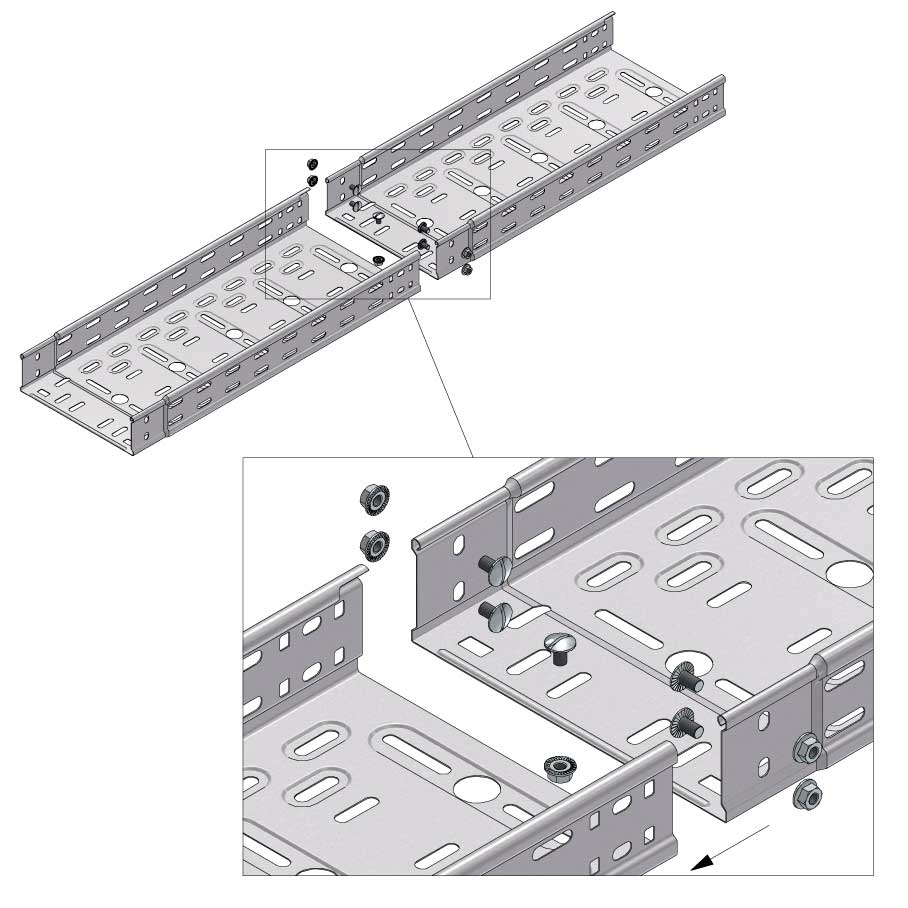
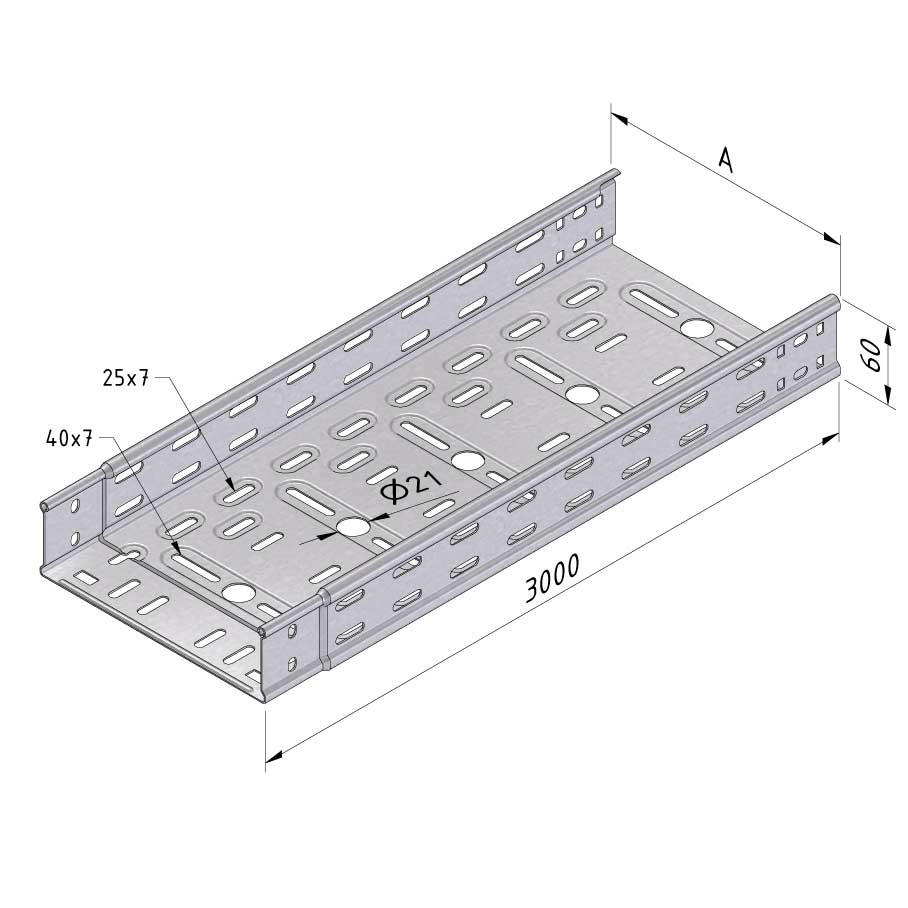
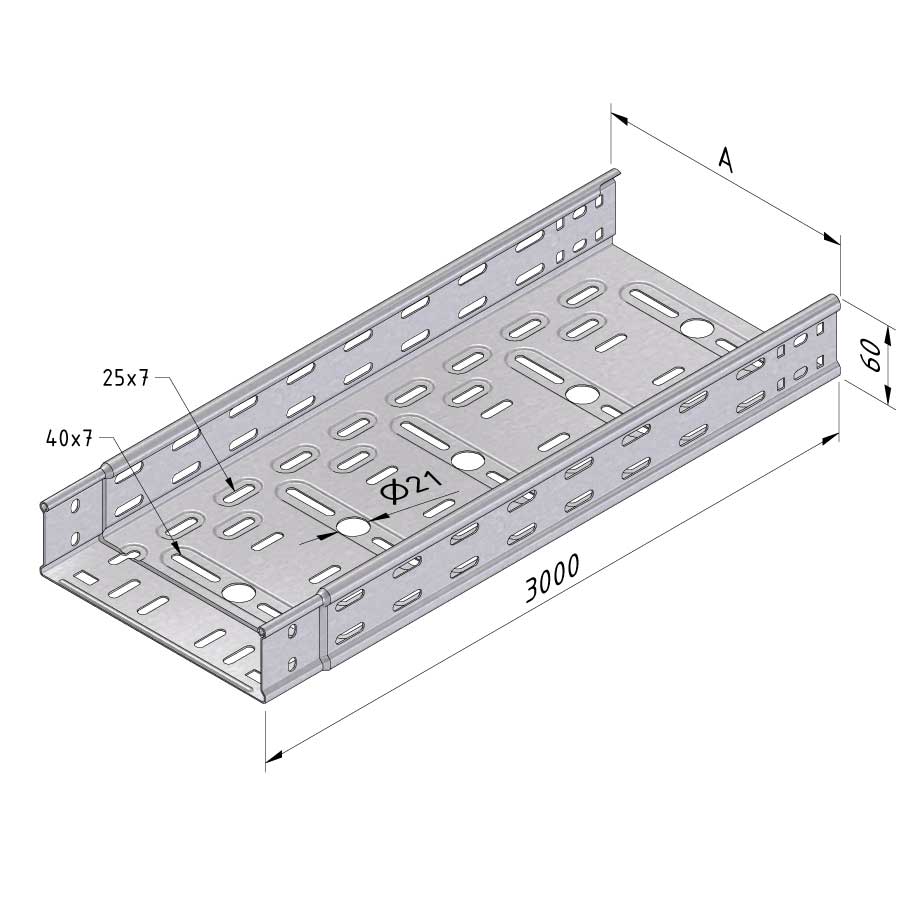
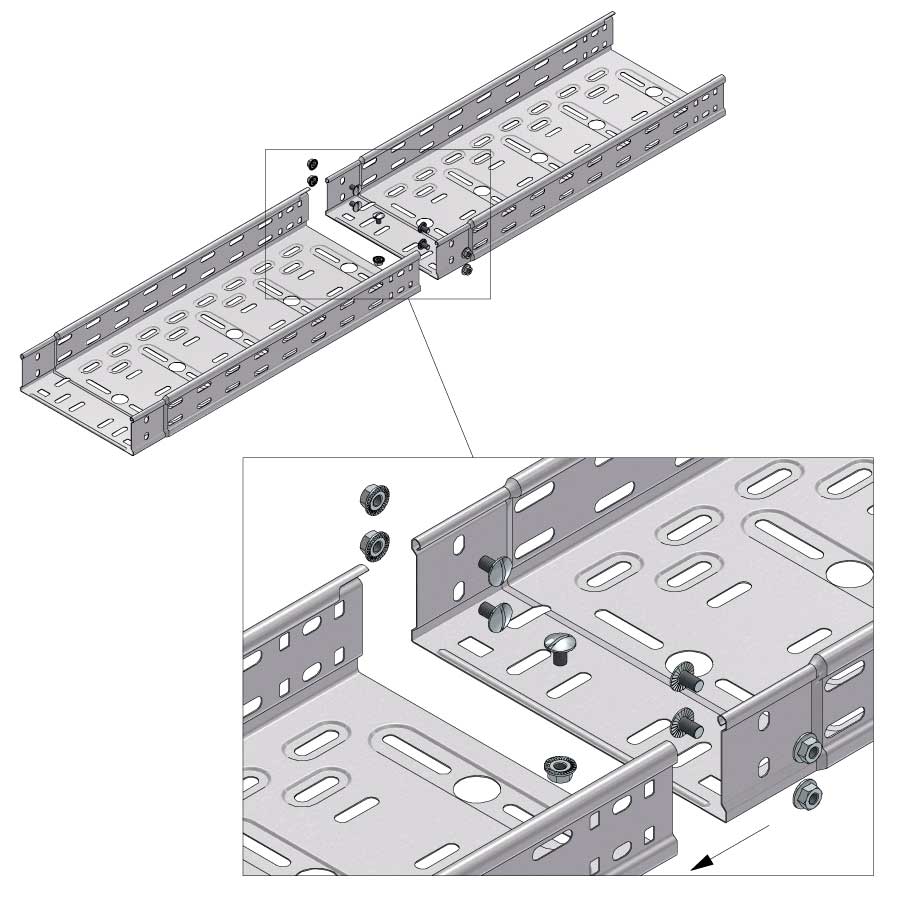
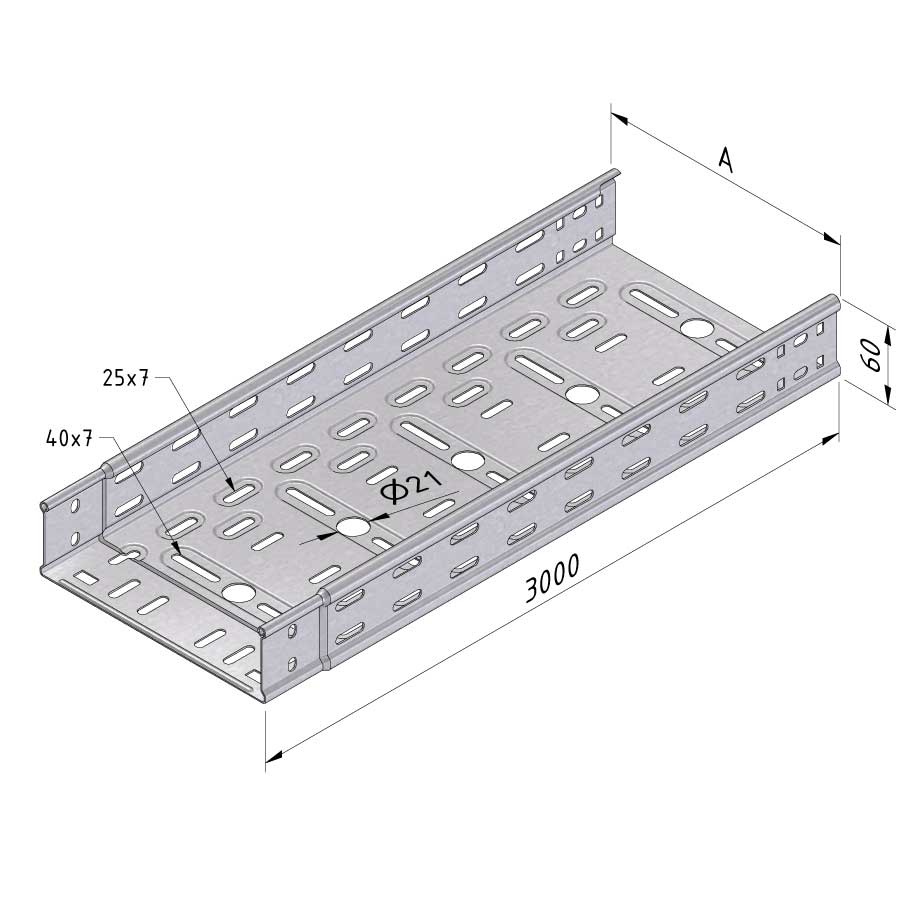
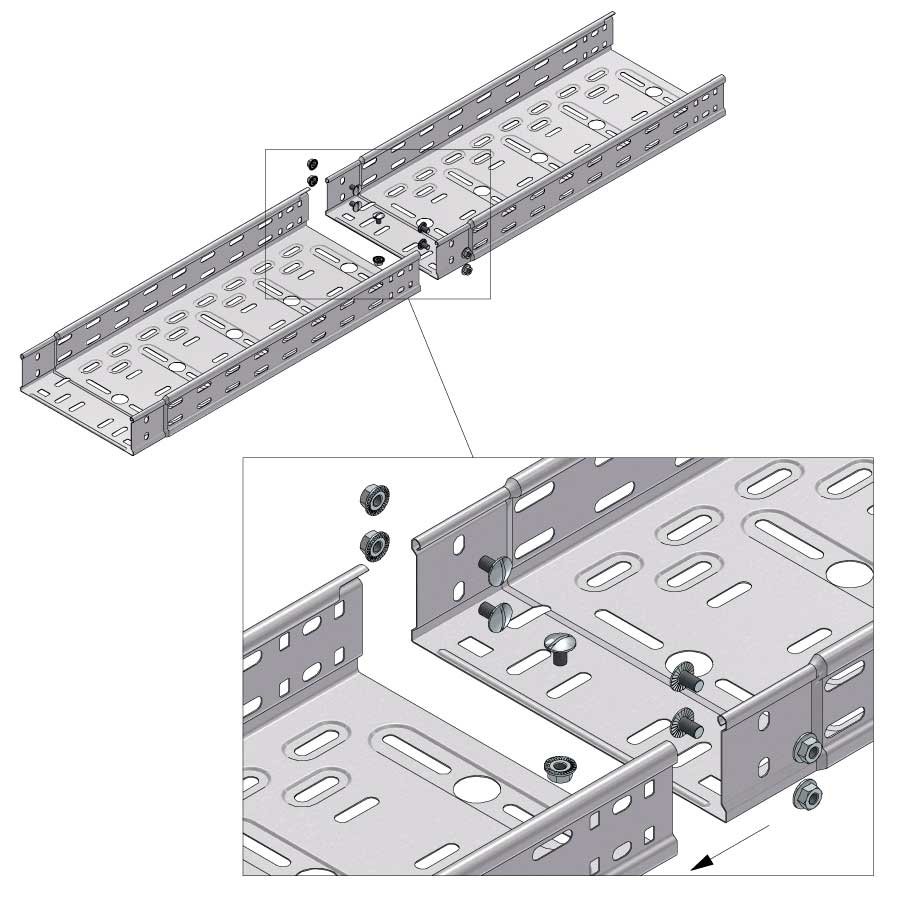
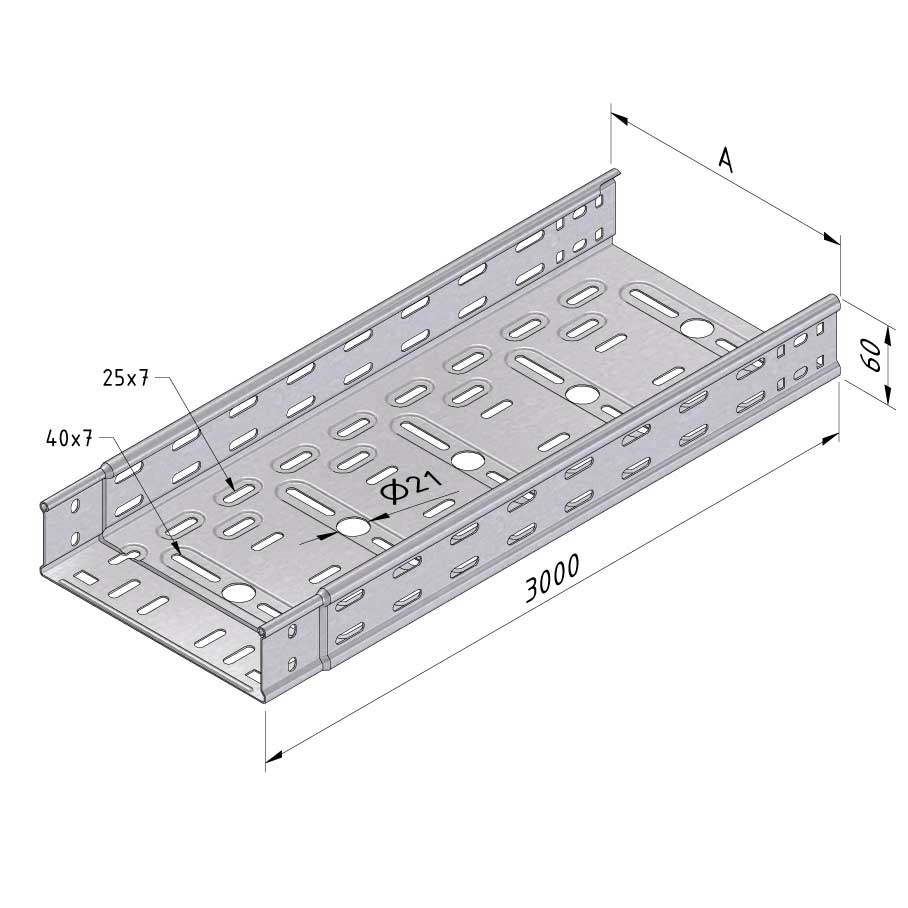
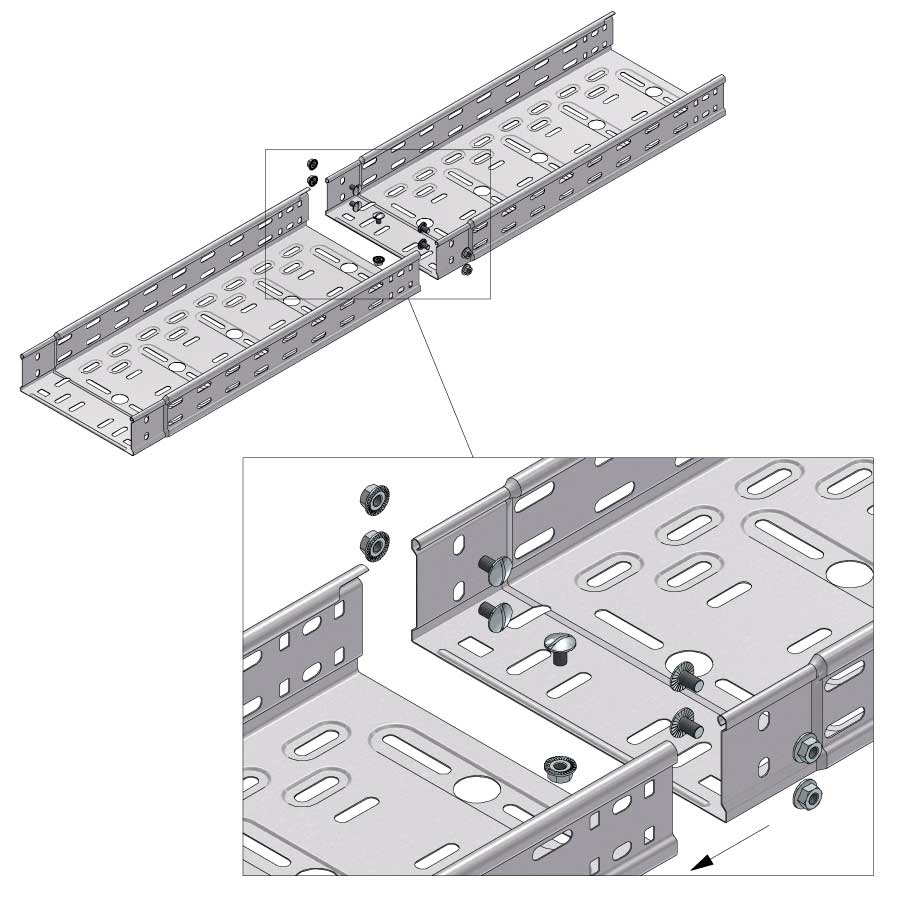
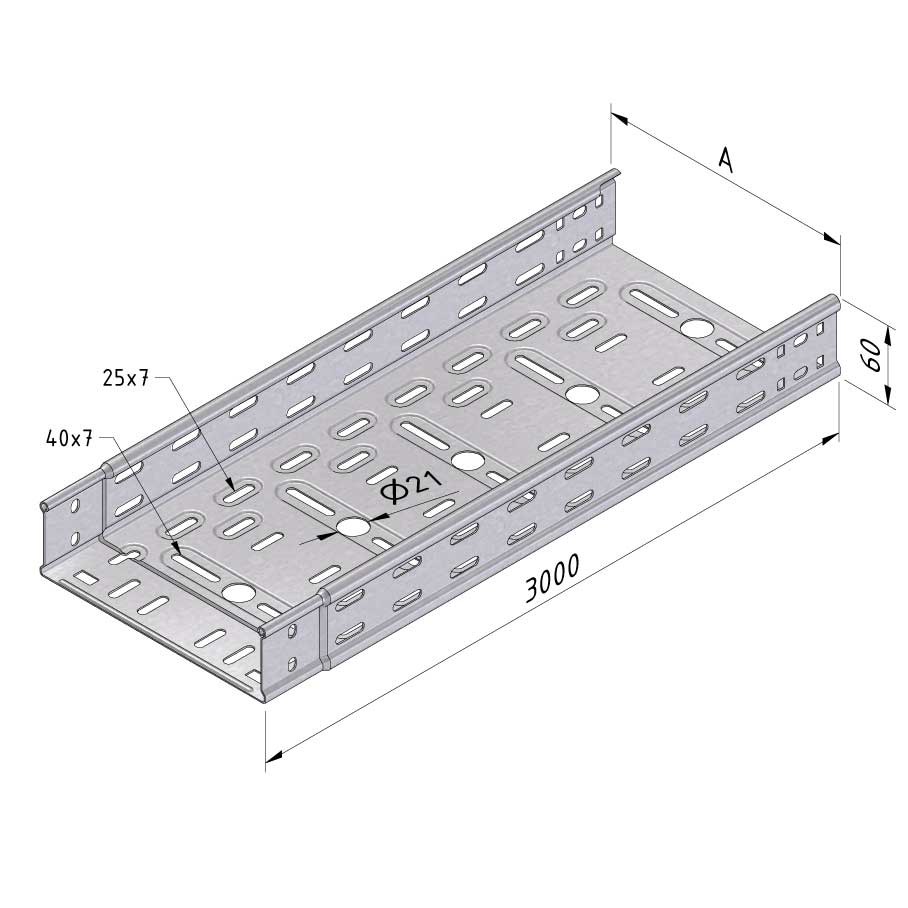
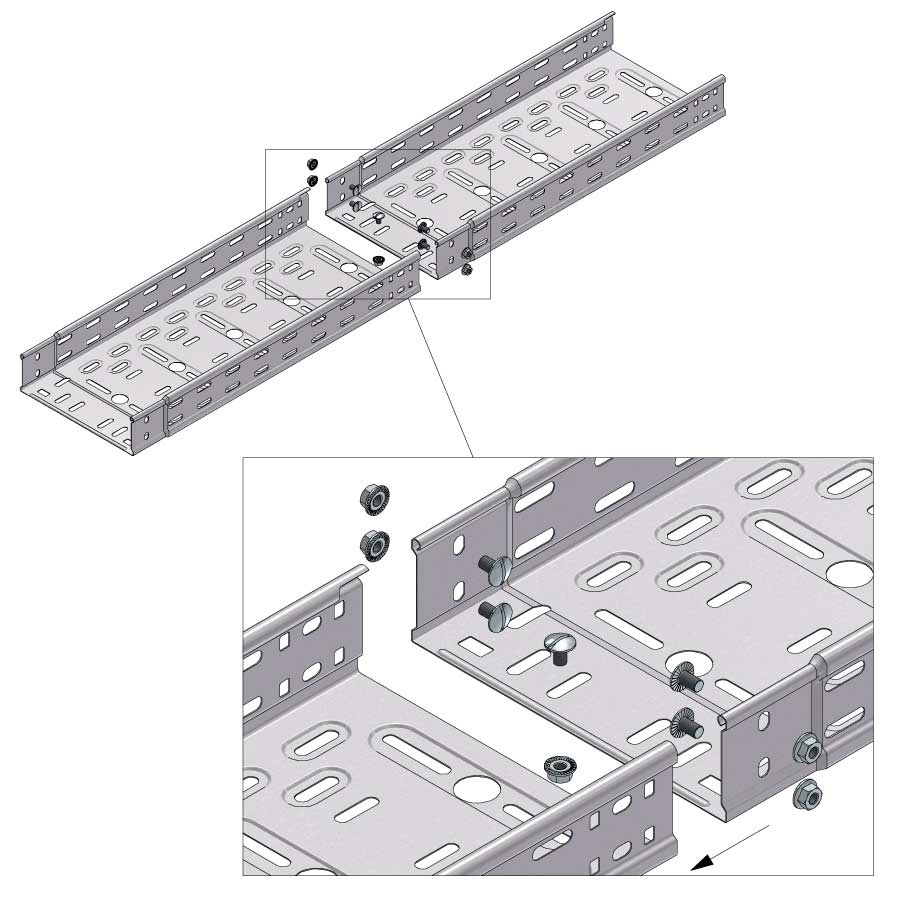
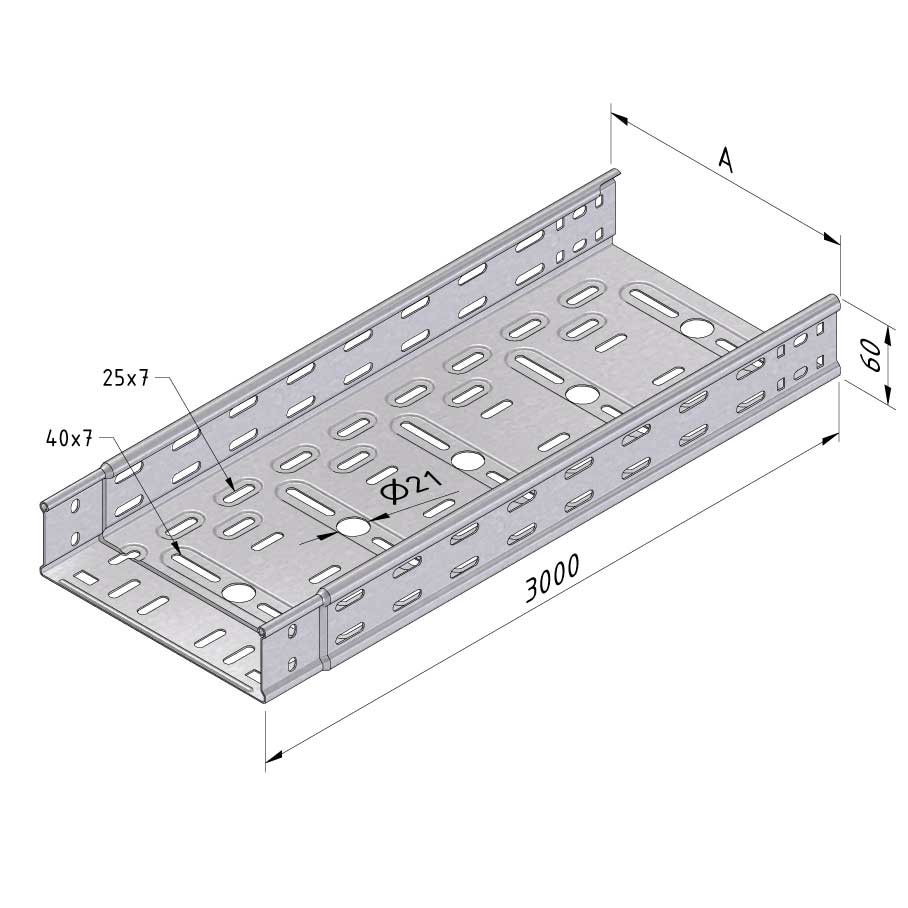
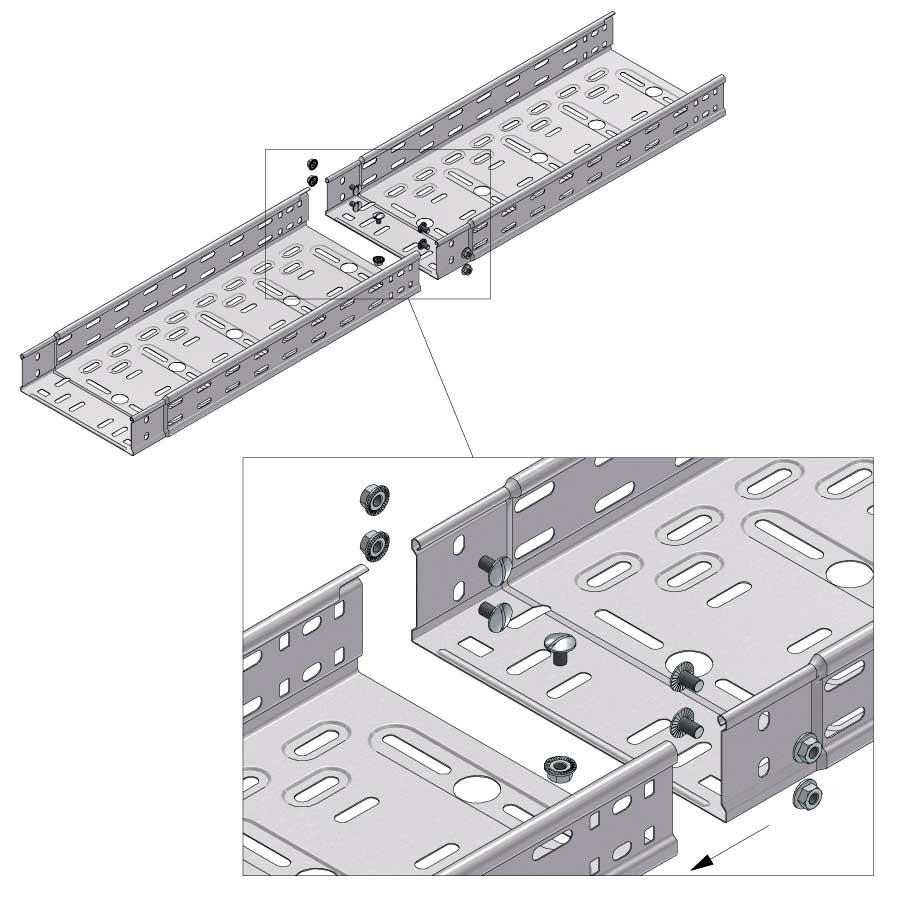
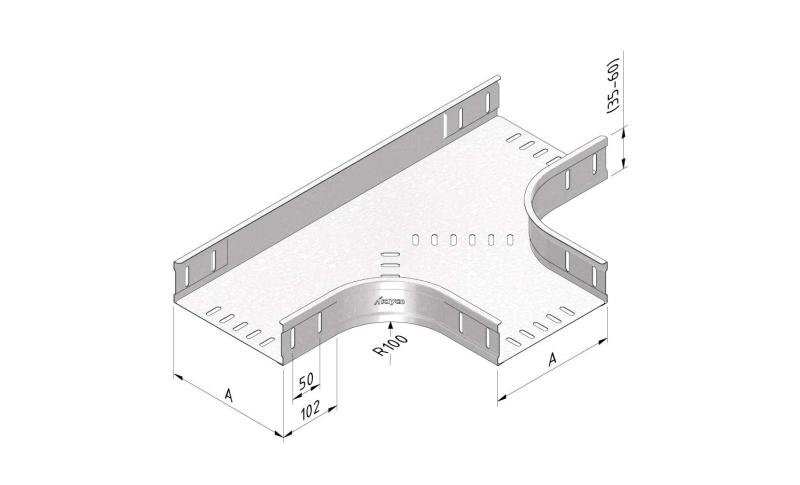
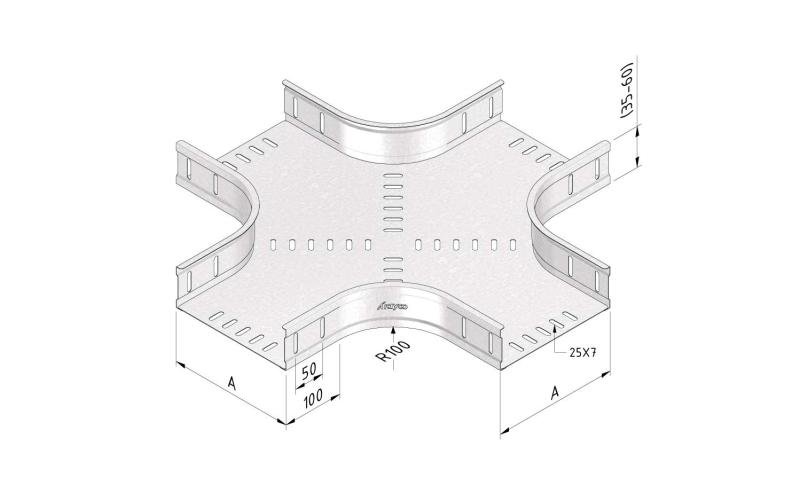
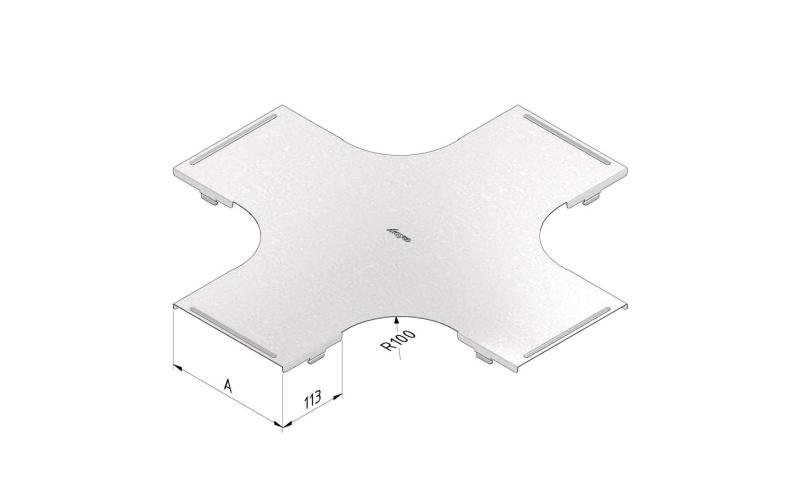
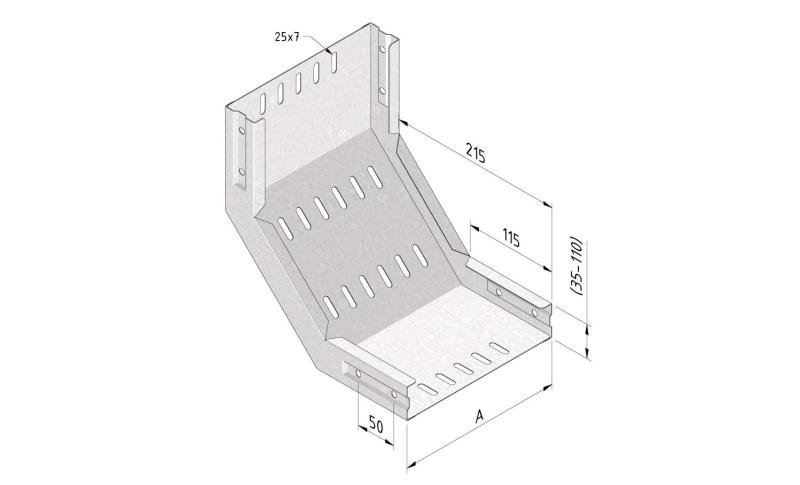
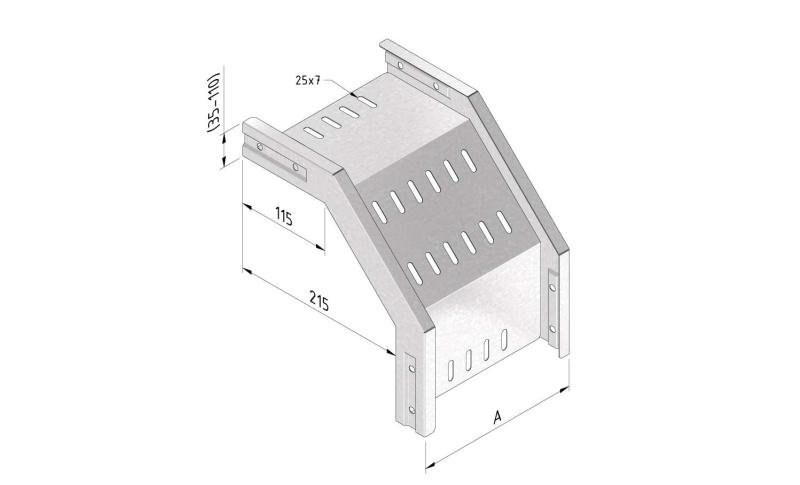
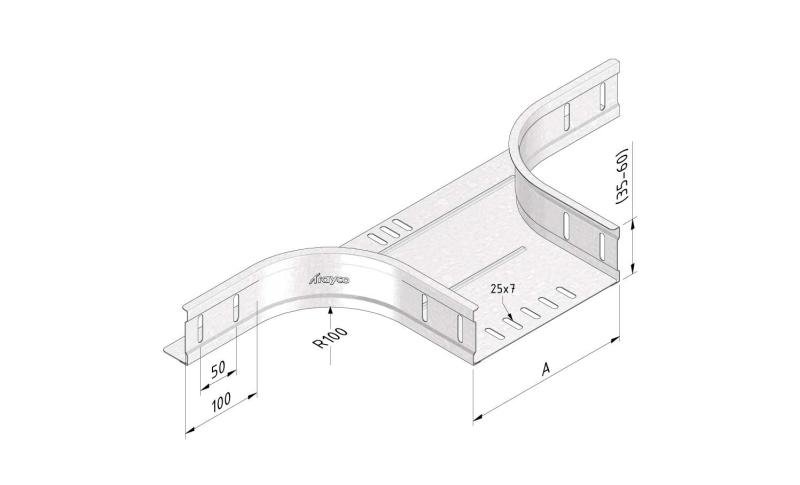
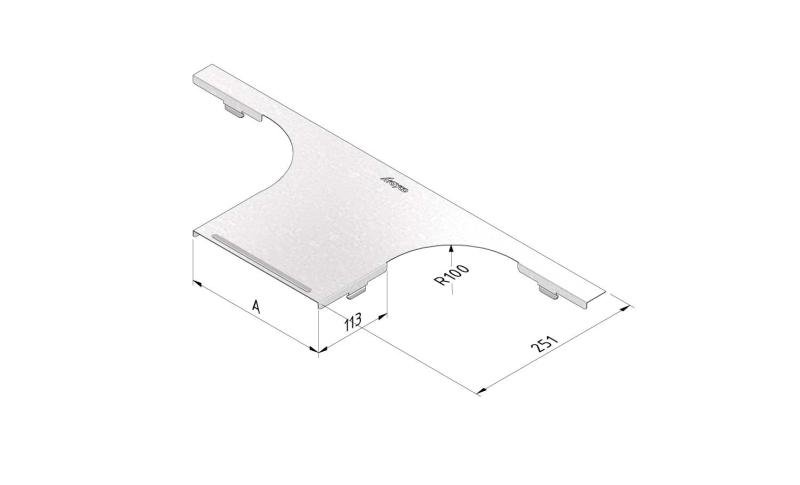
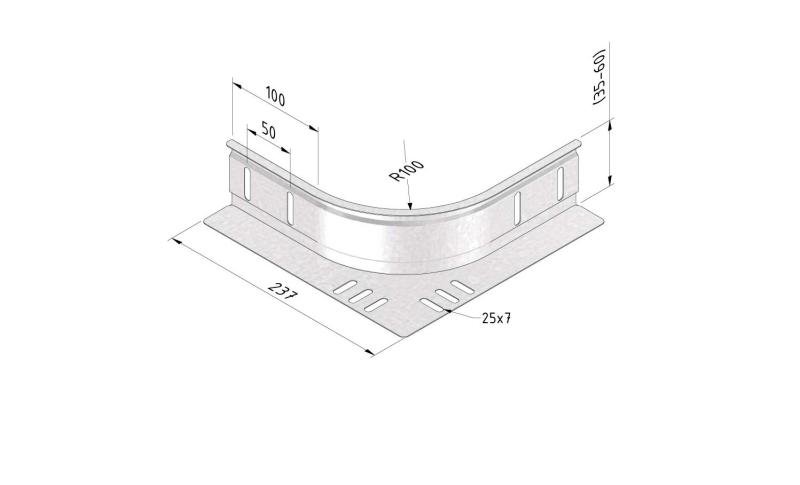
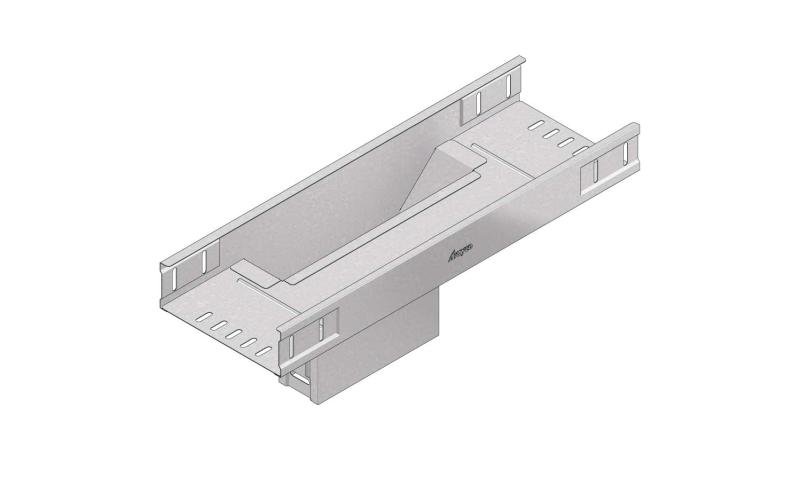
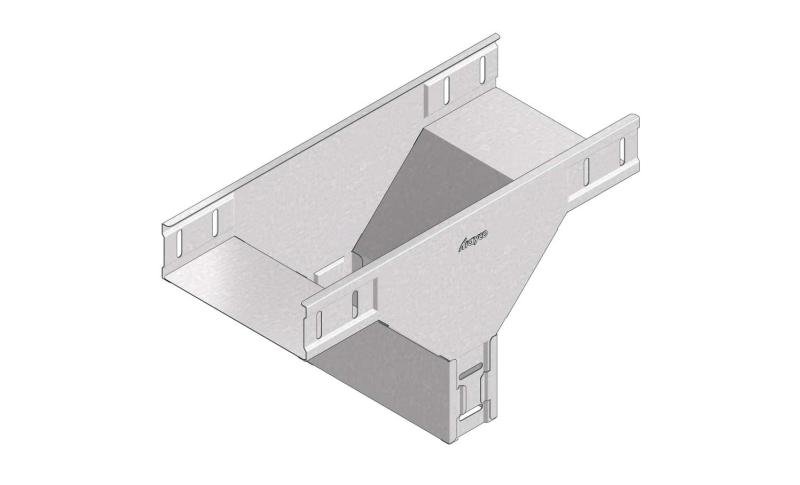
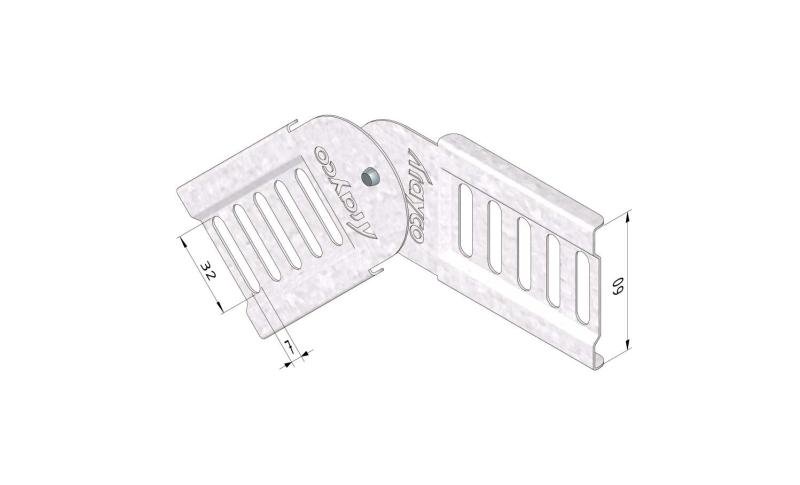
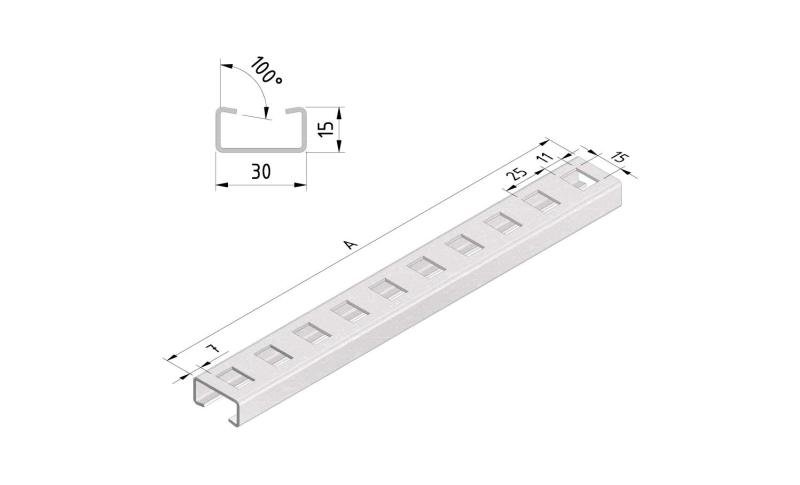
Cable Tray Interlocking ends
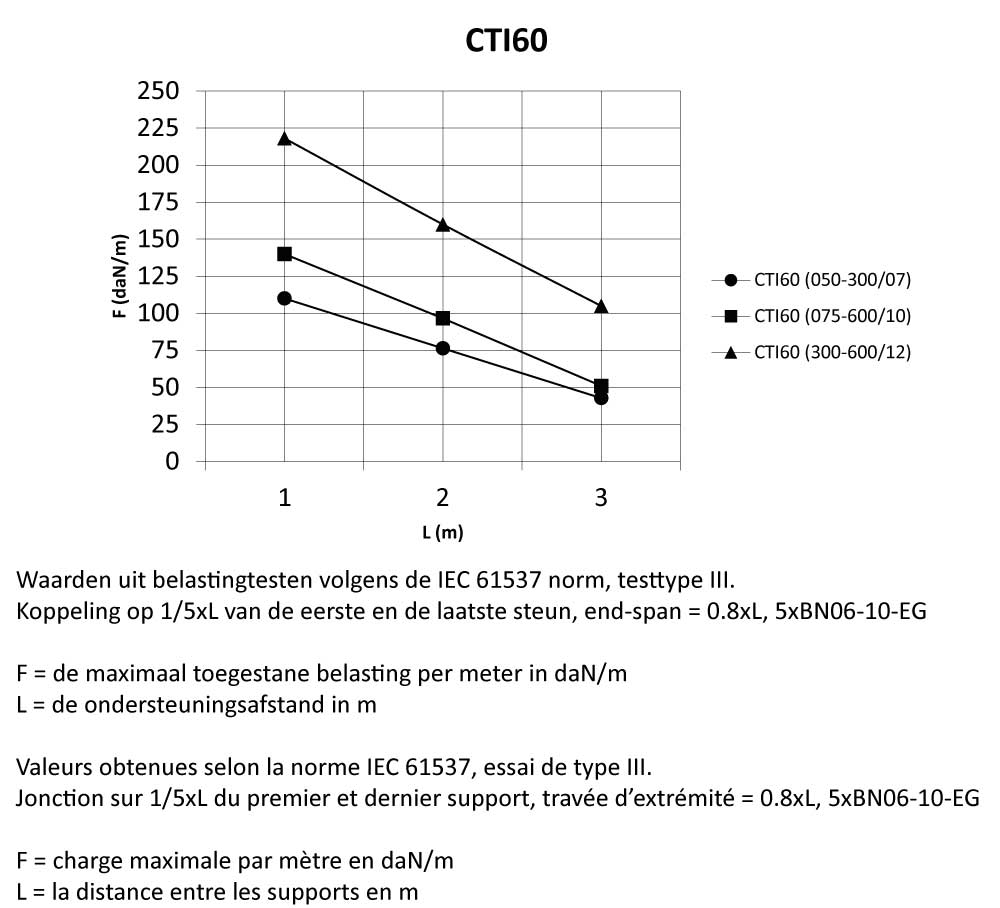
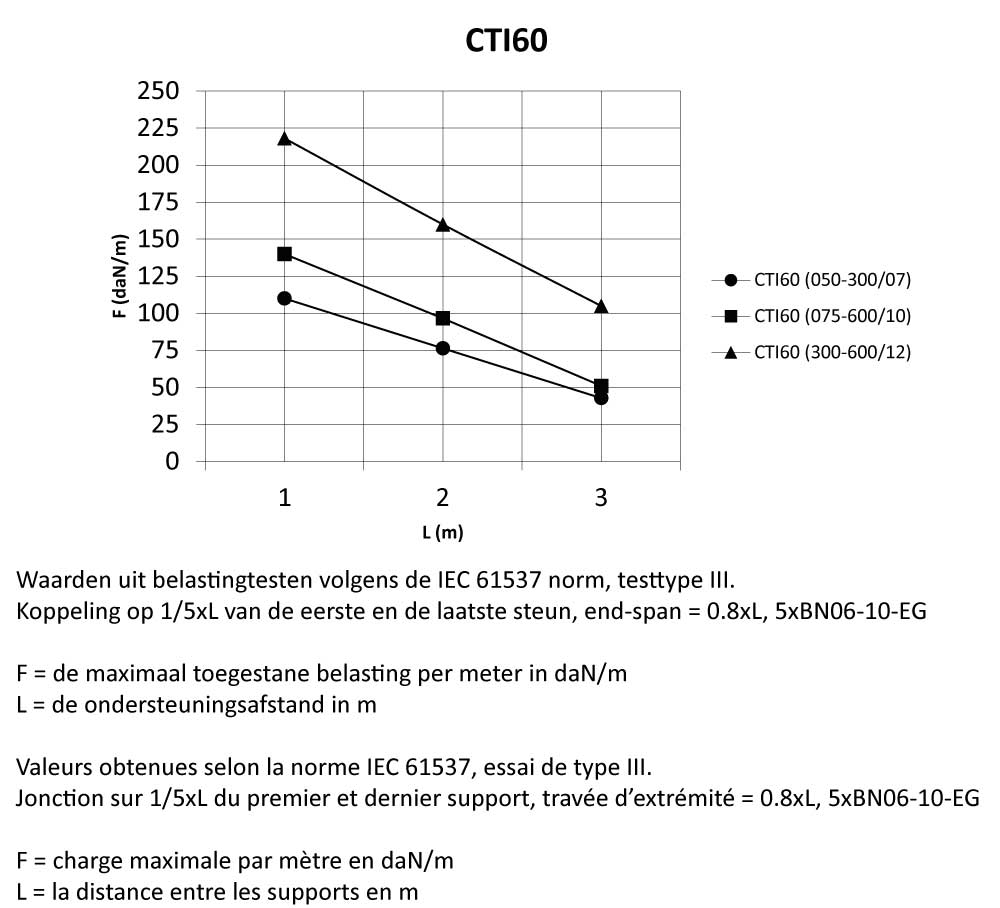
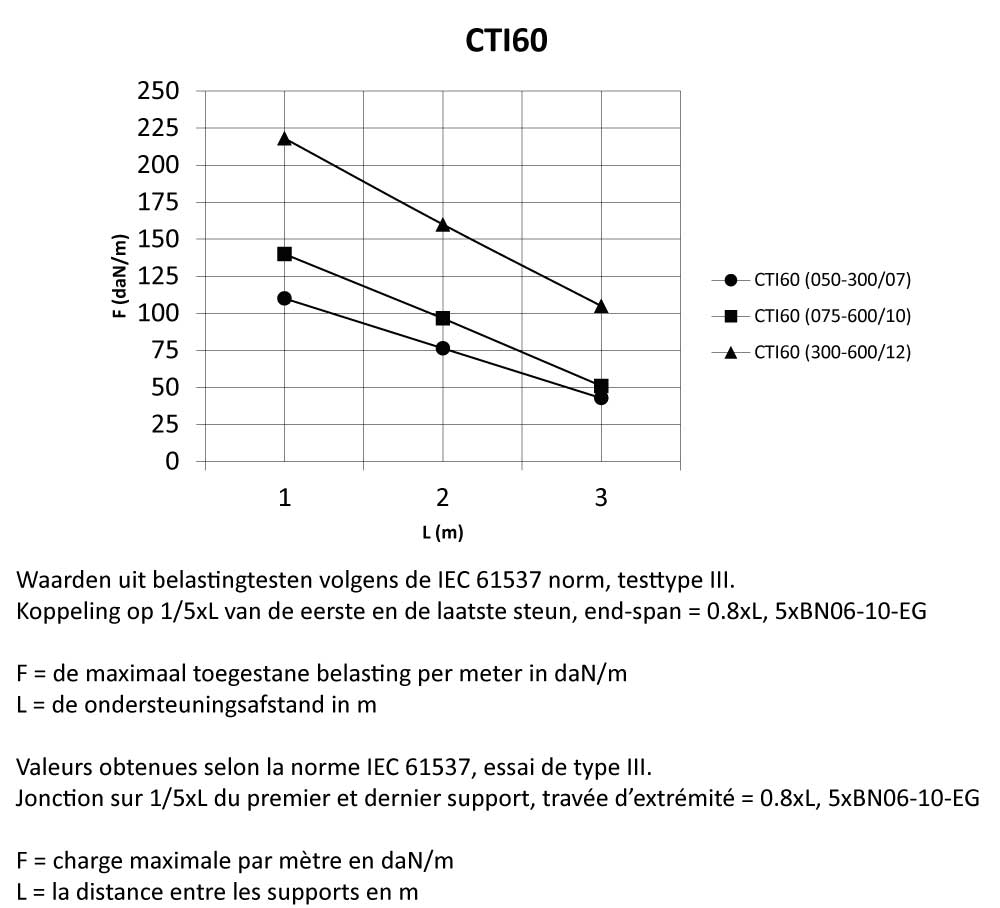
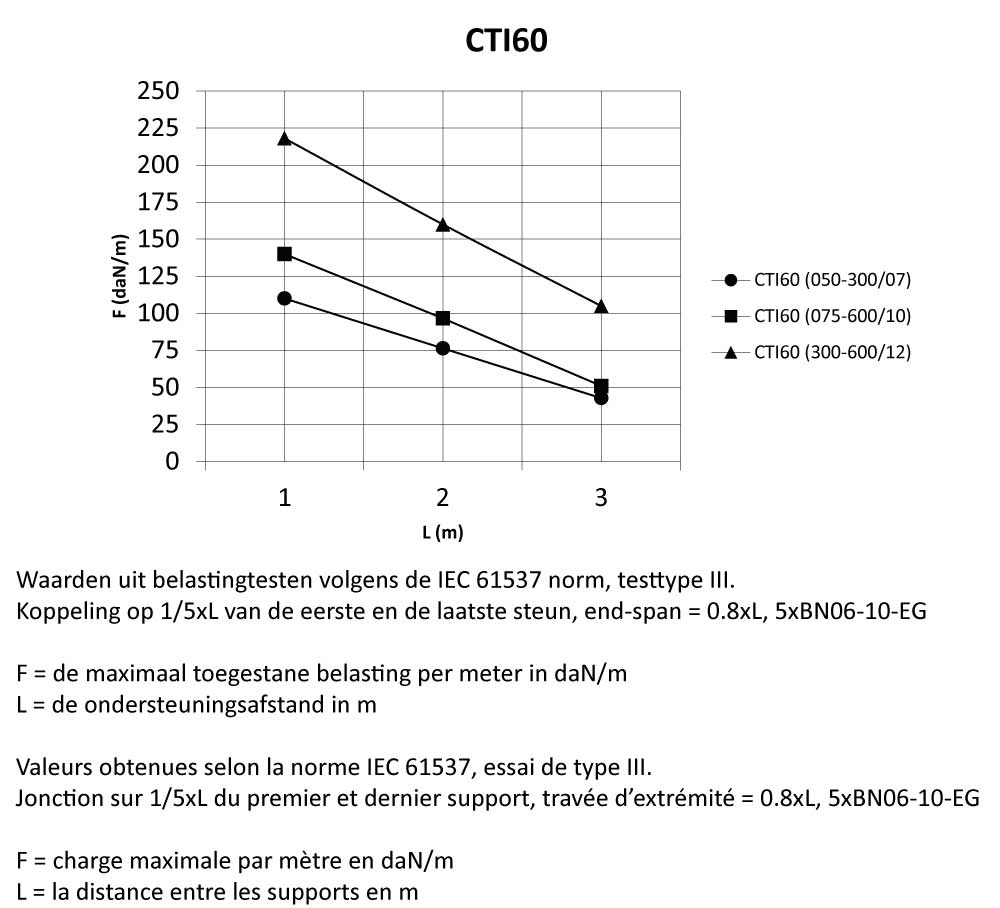
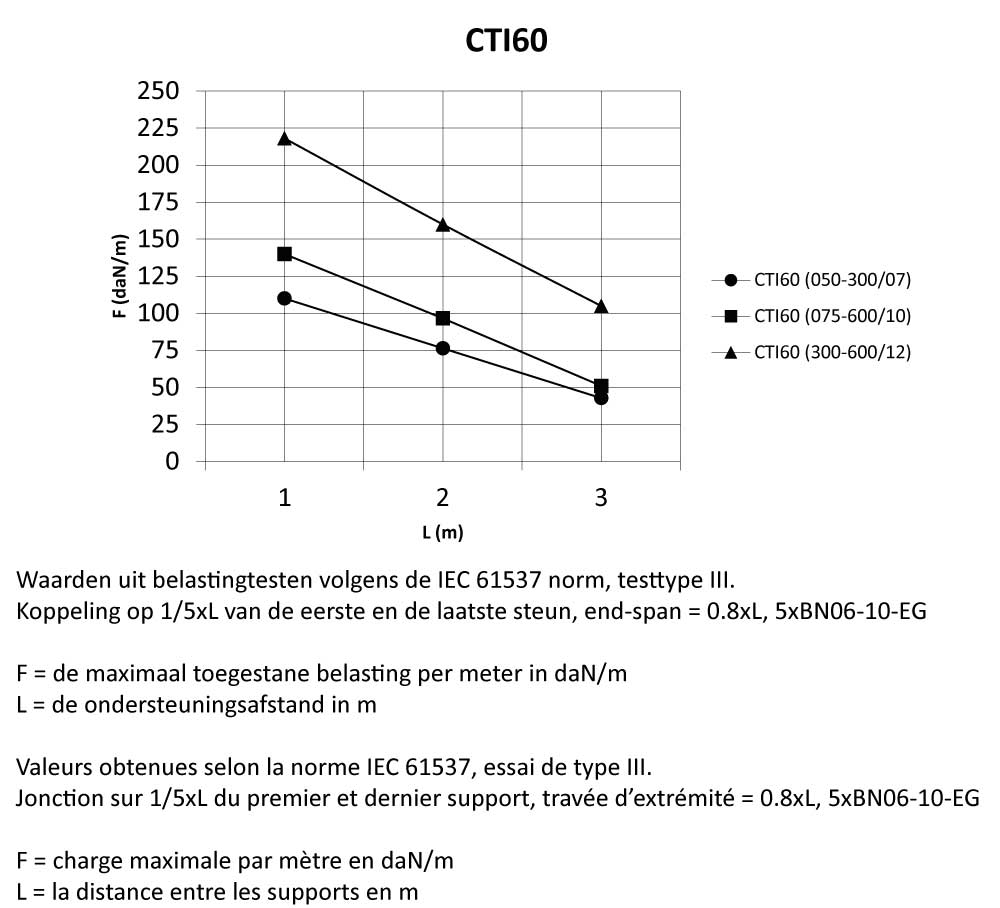
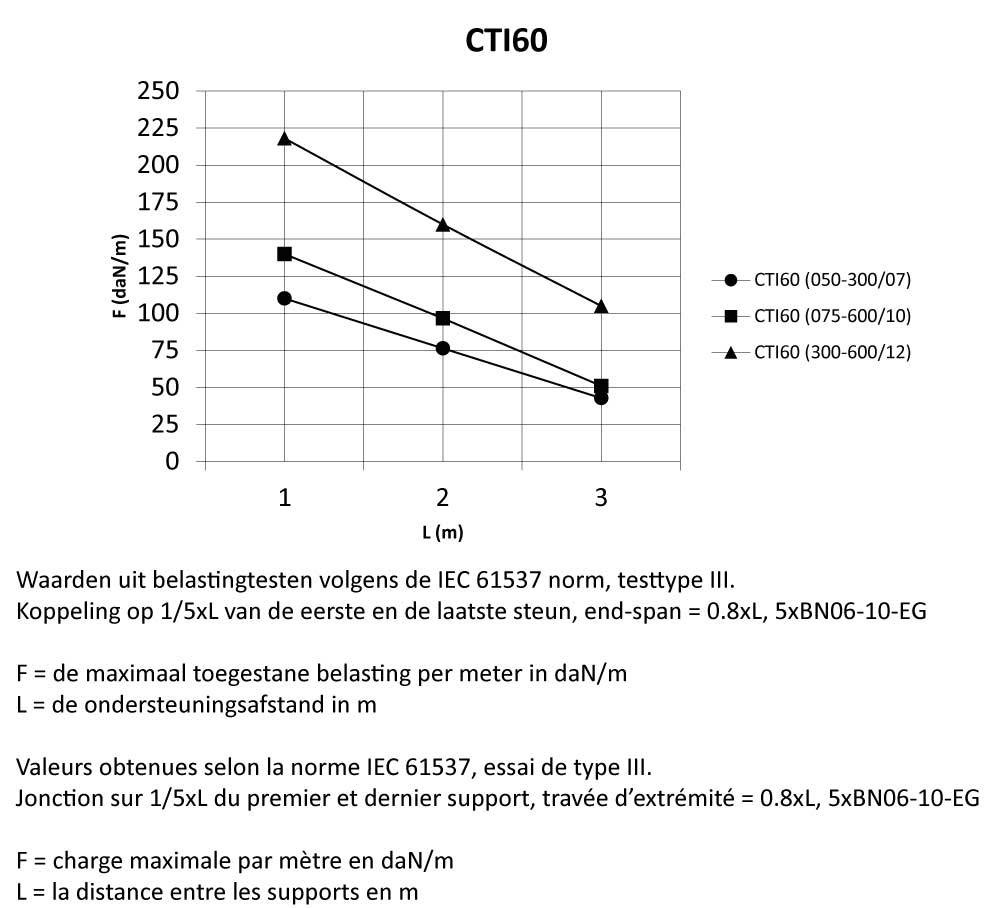
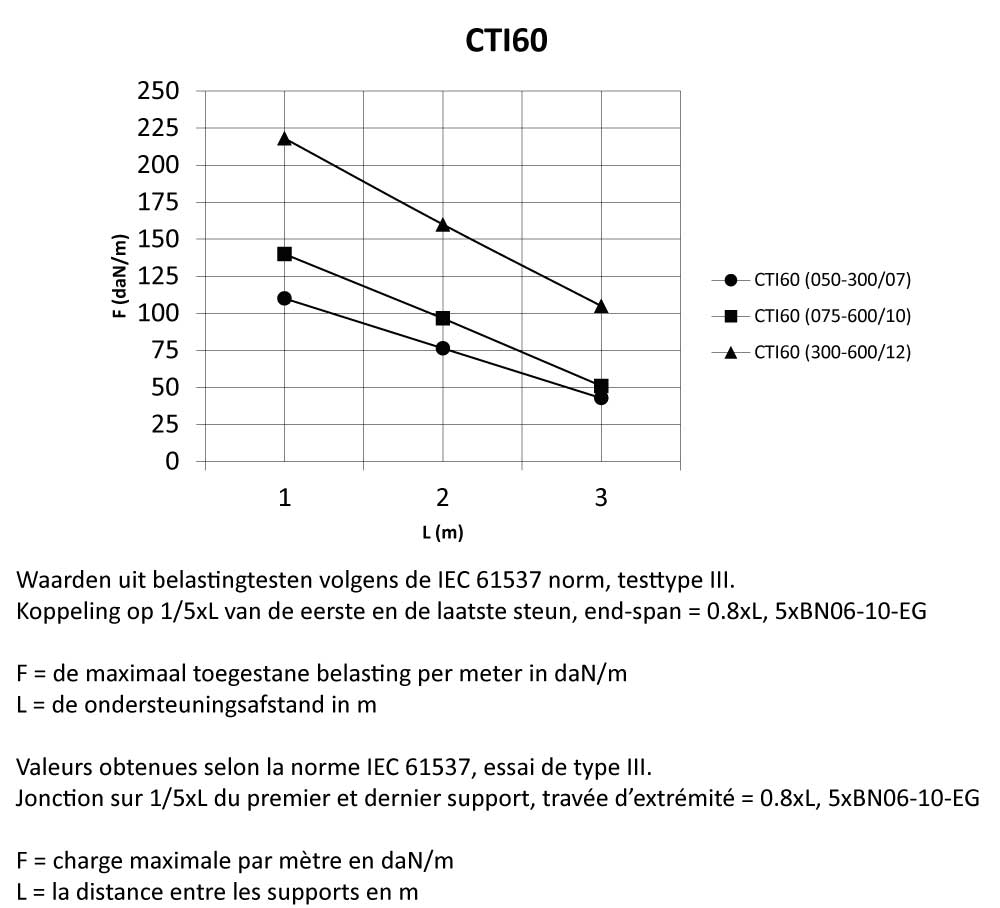
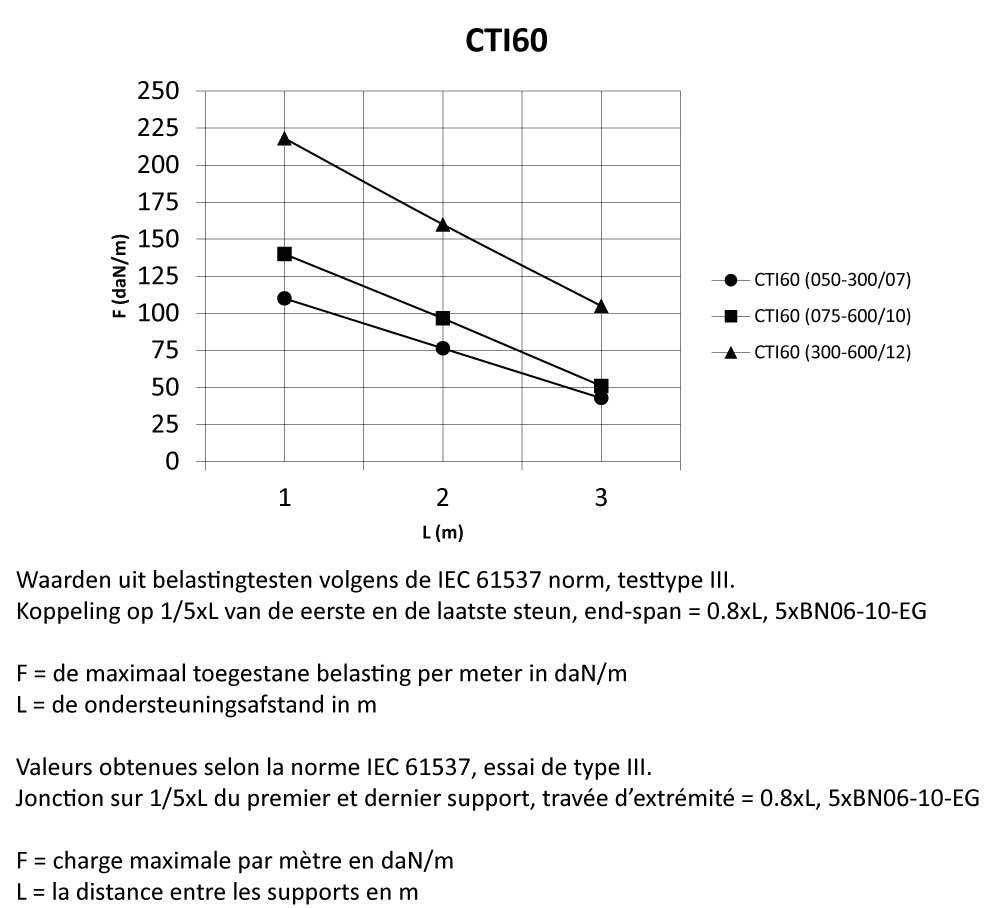
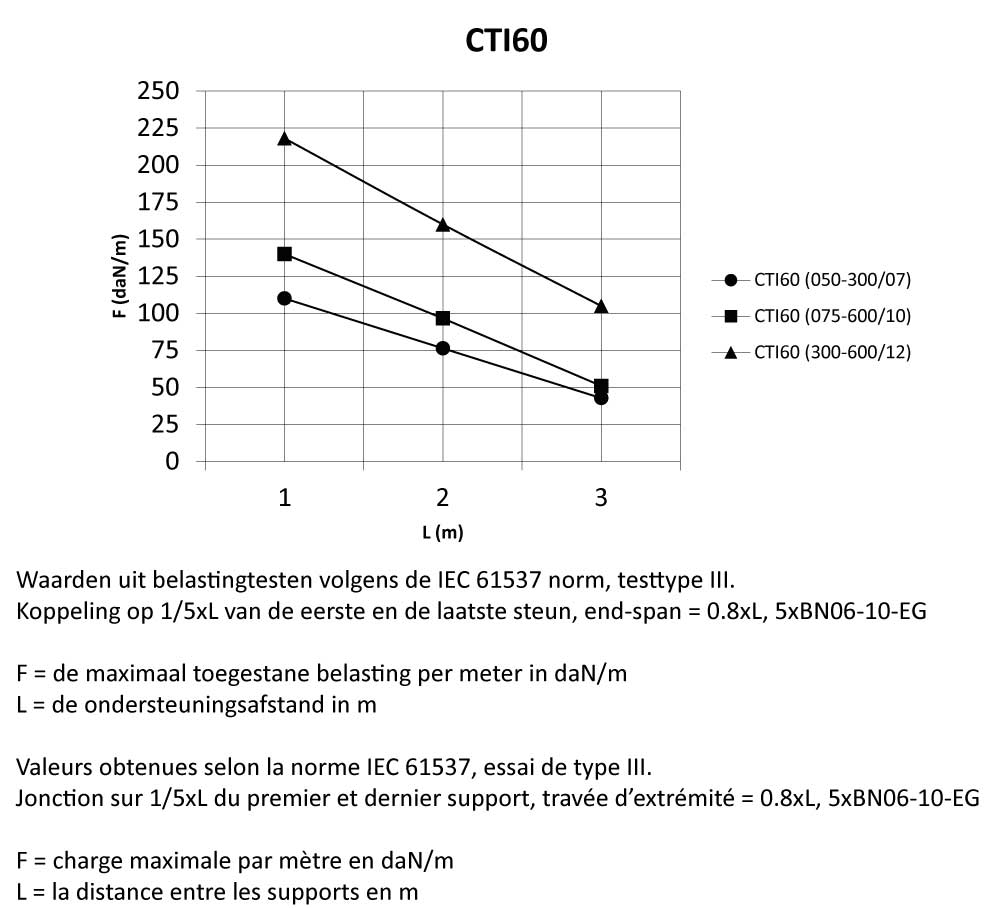
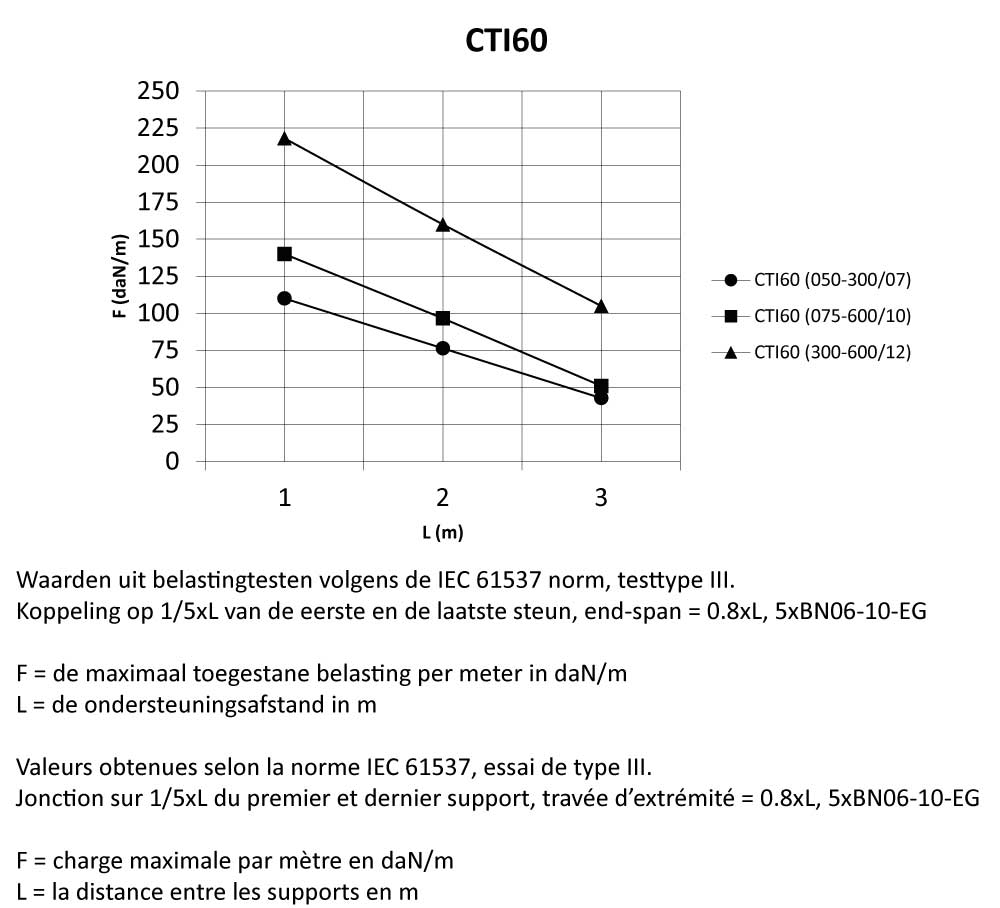
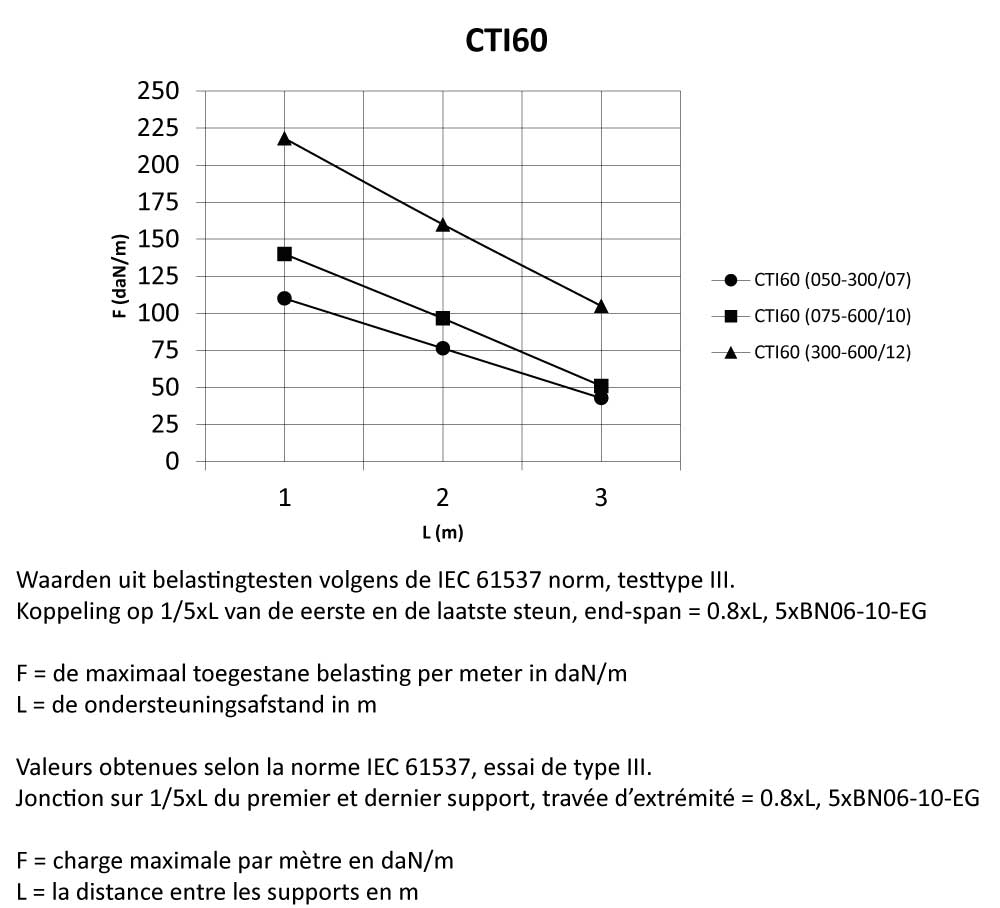
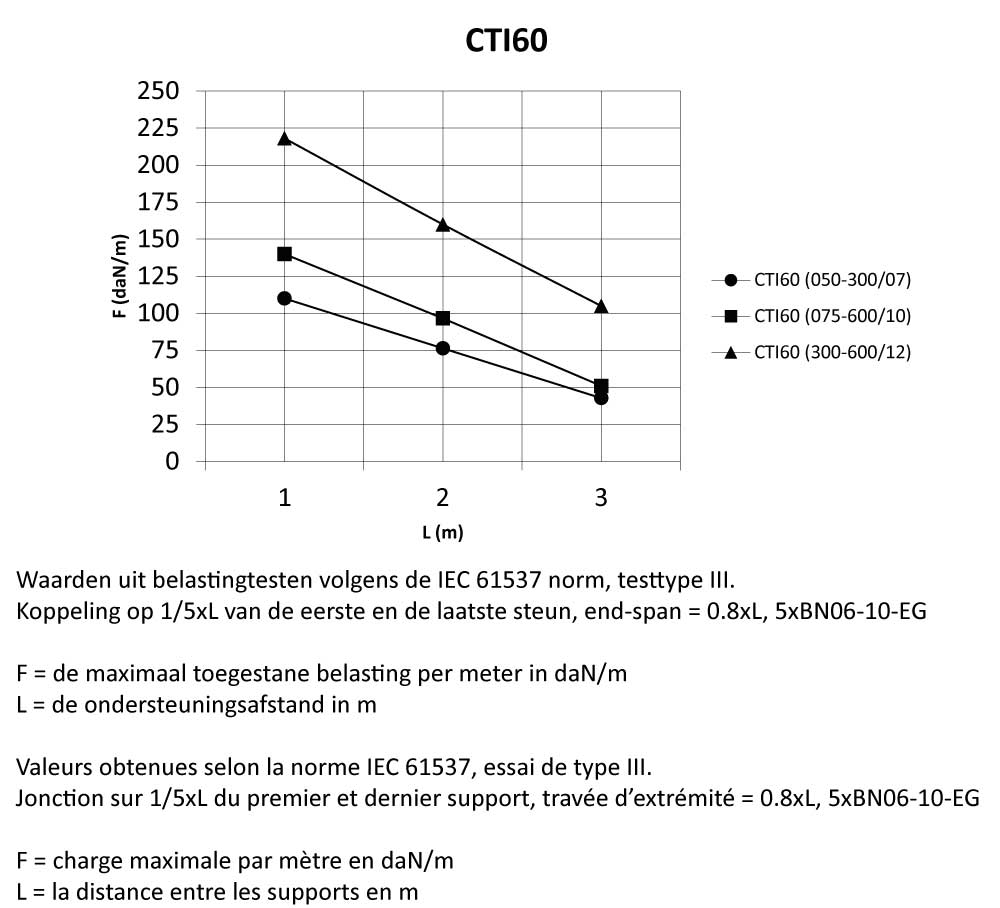
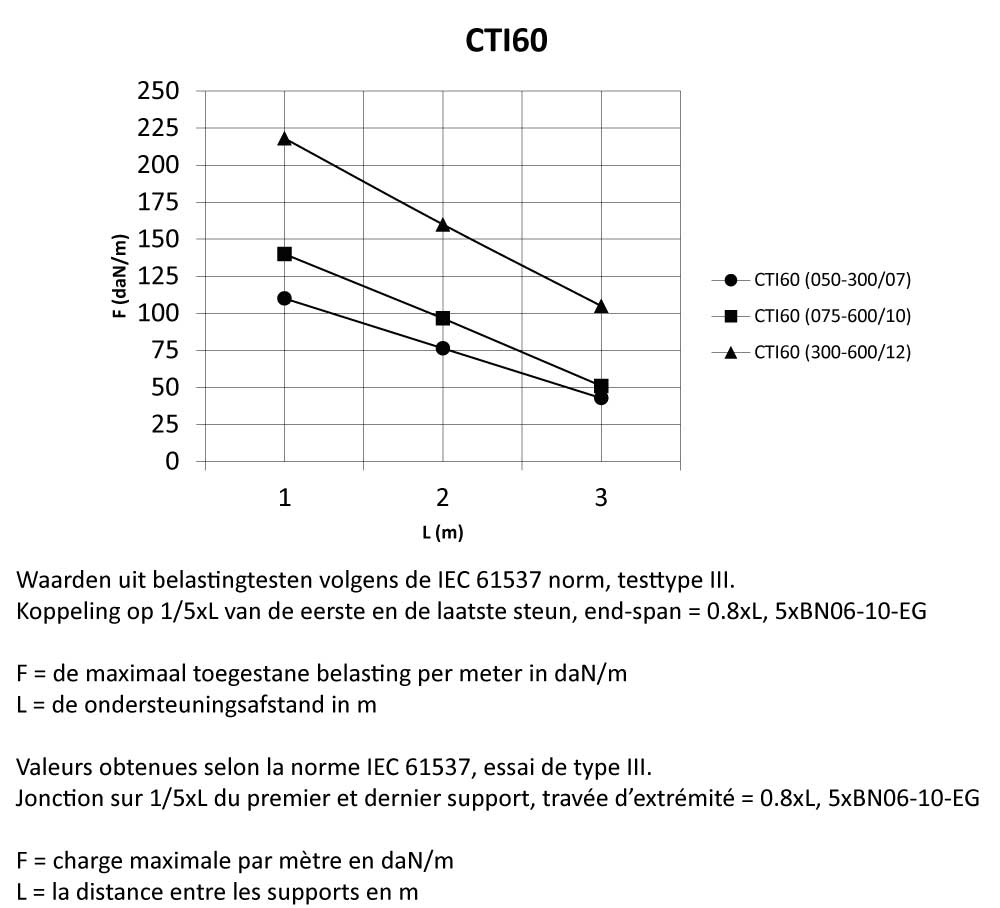
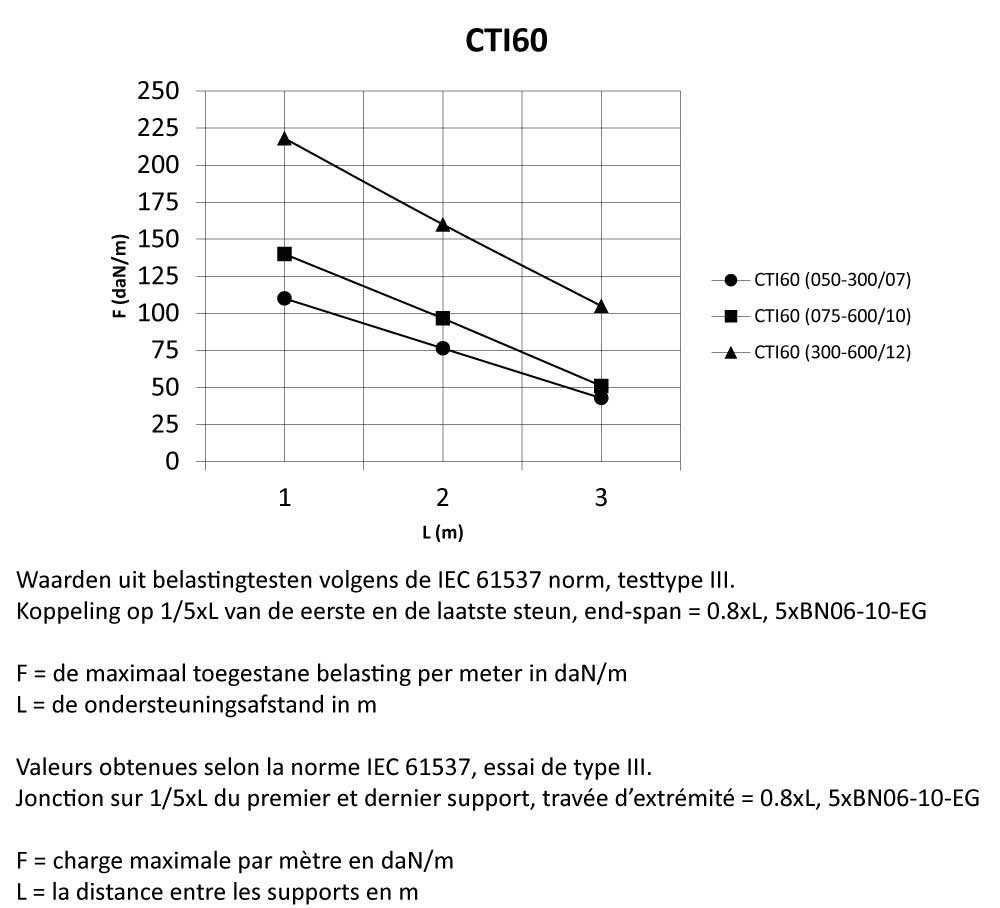
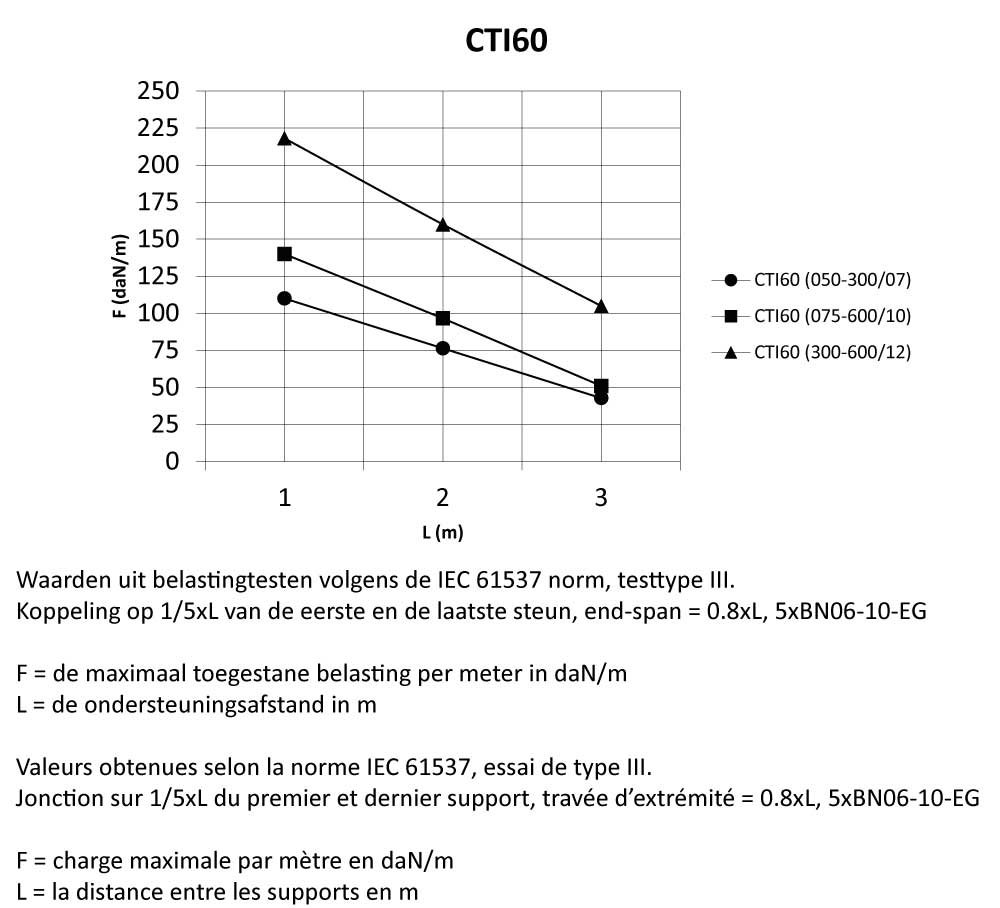
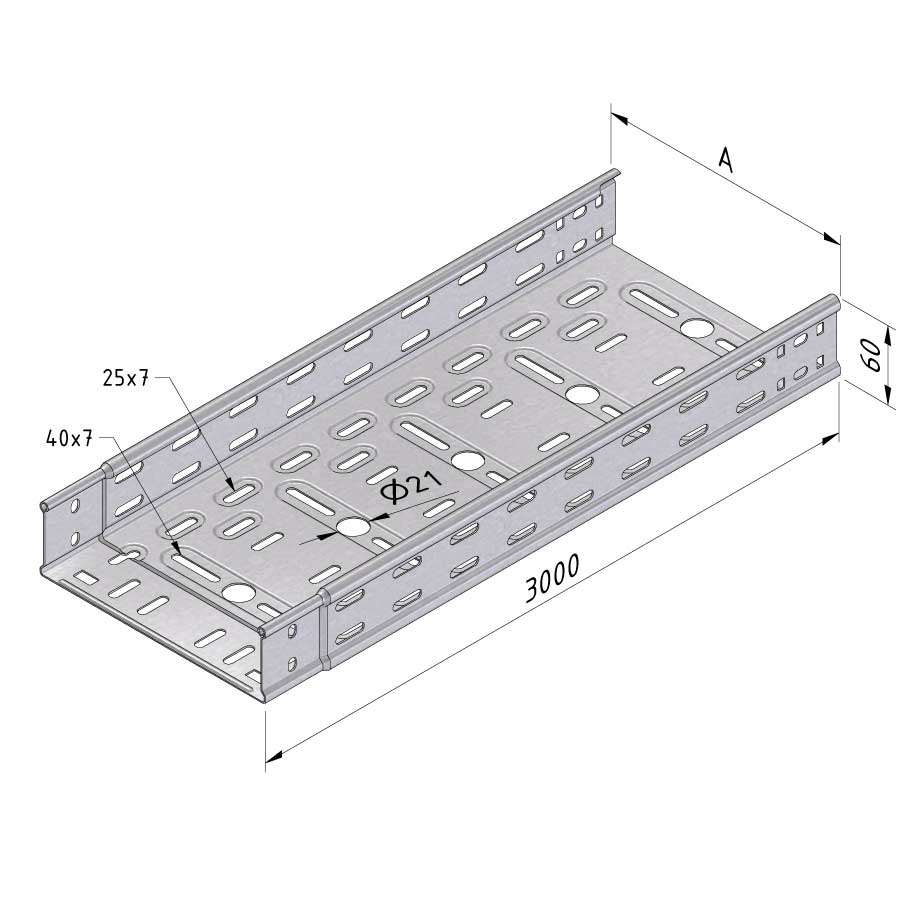
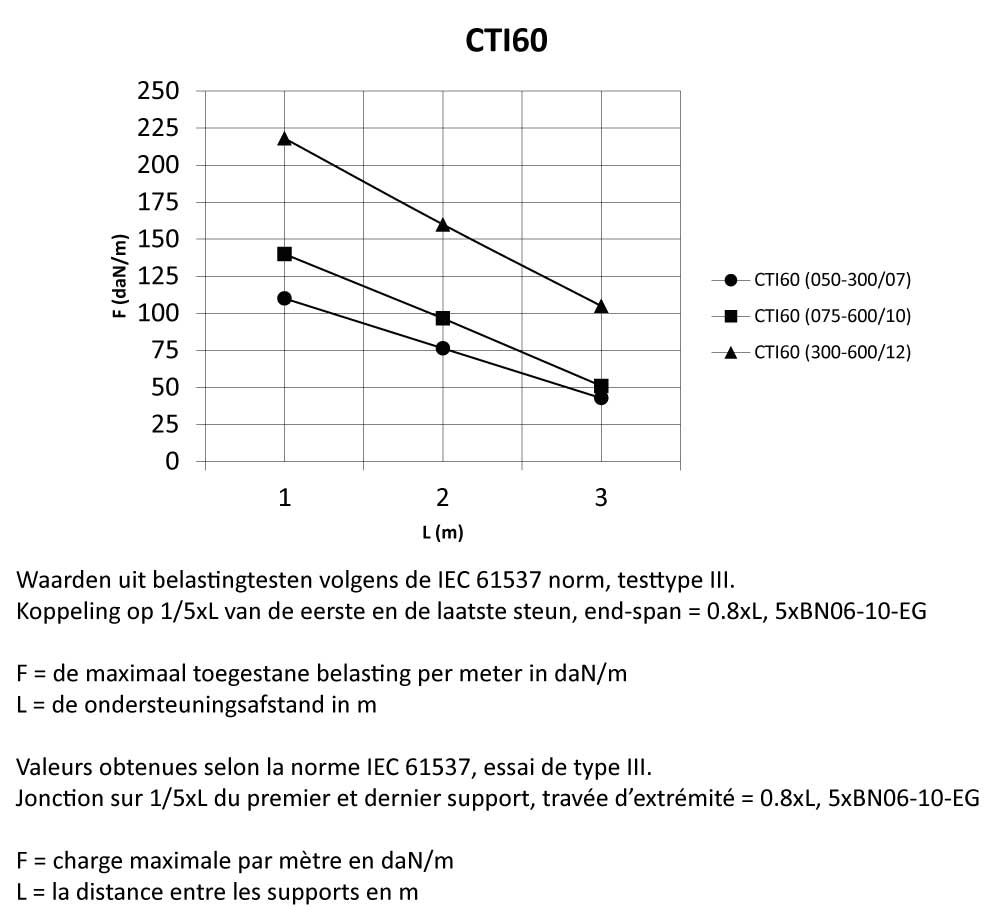
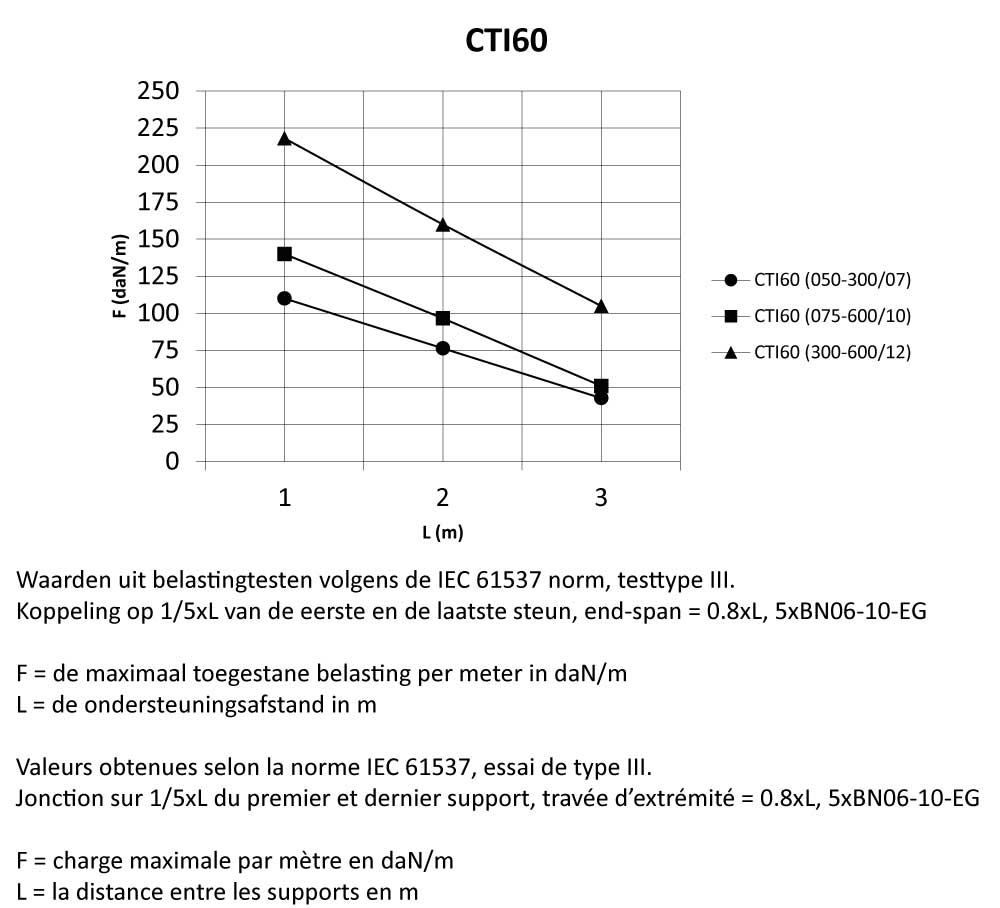
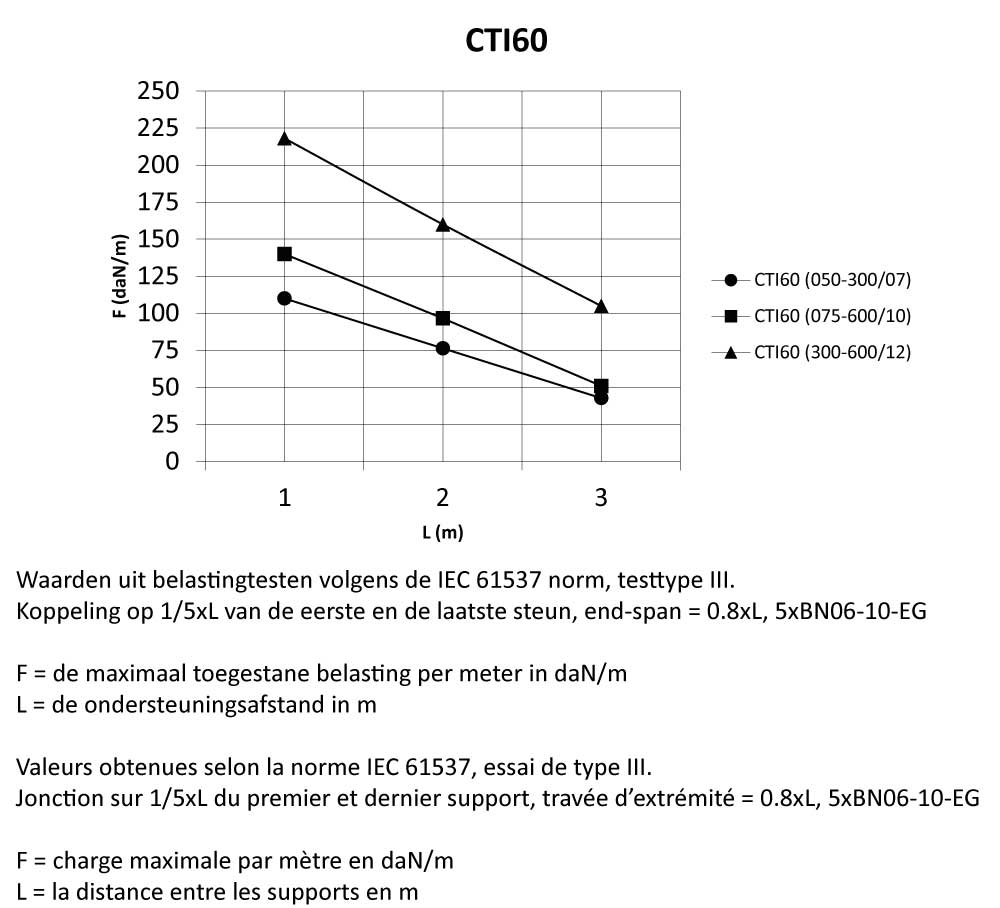
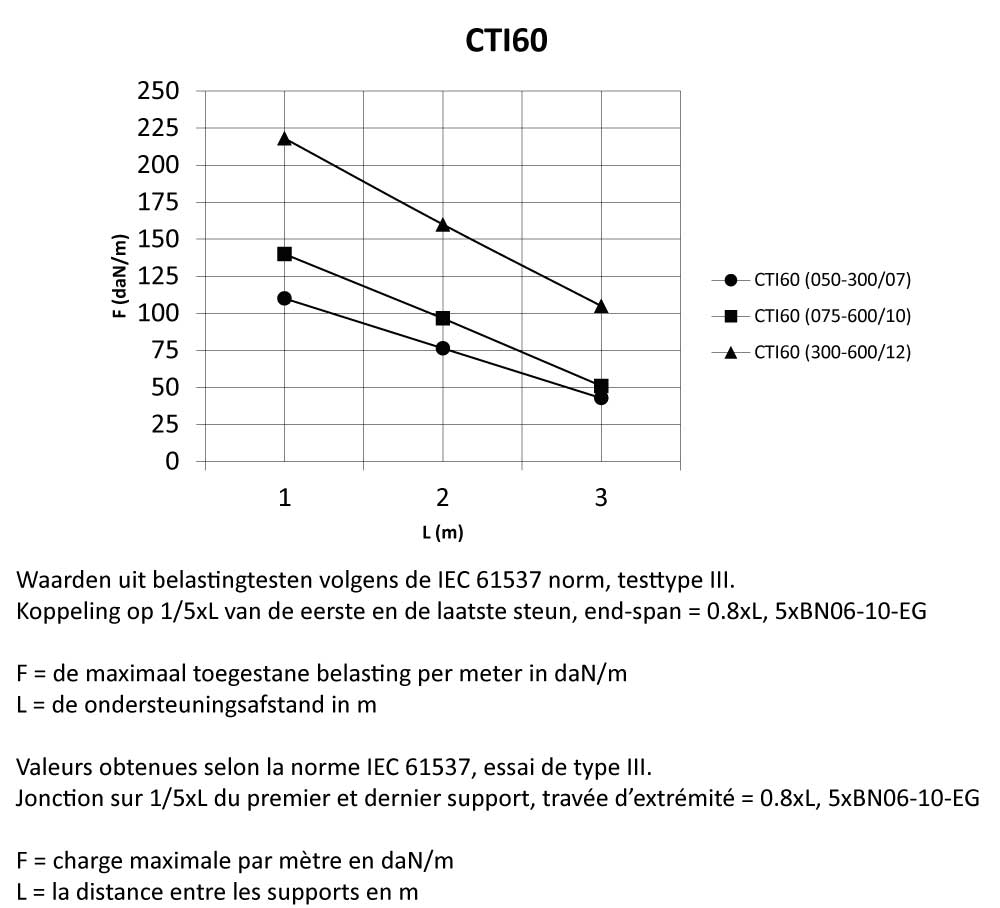
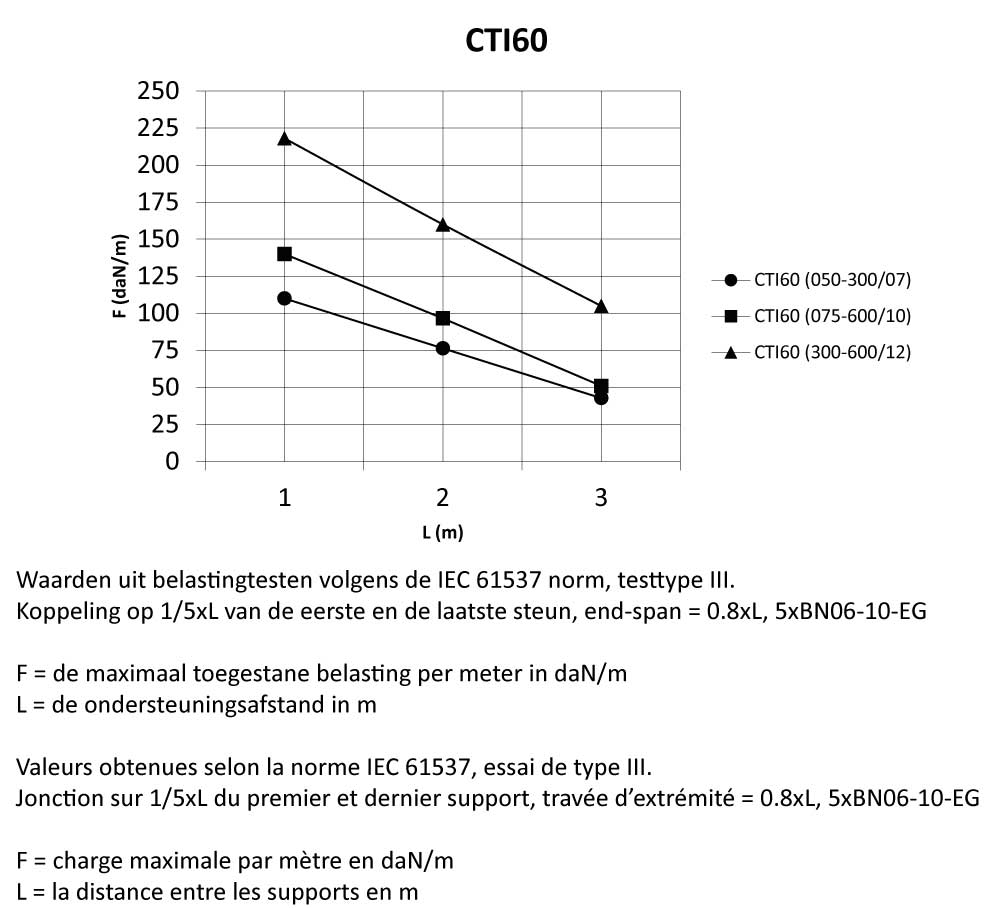
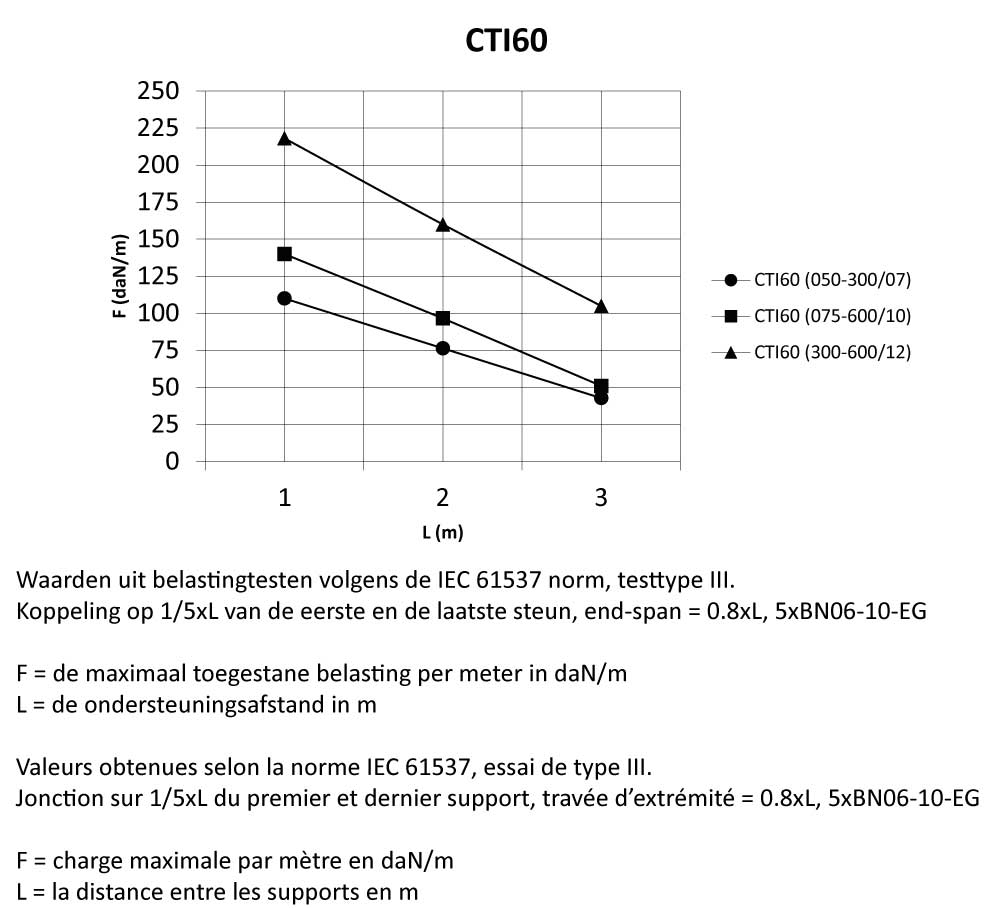
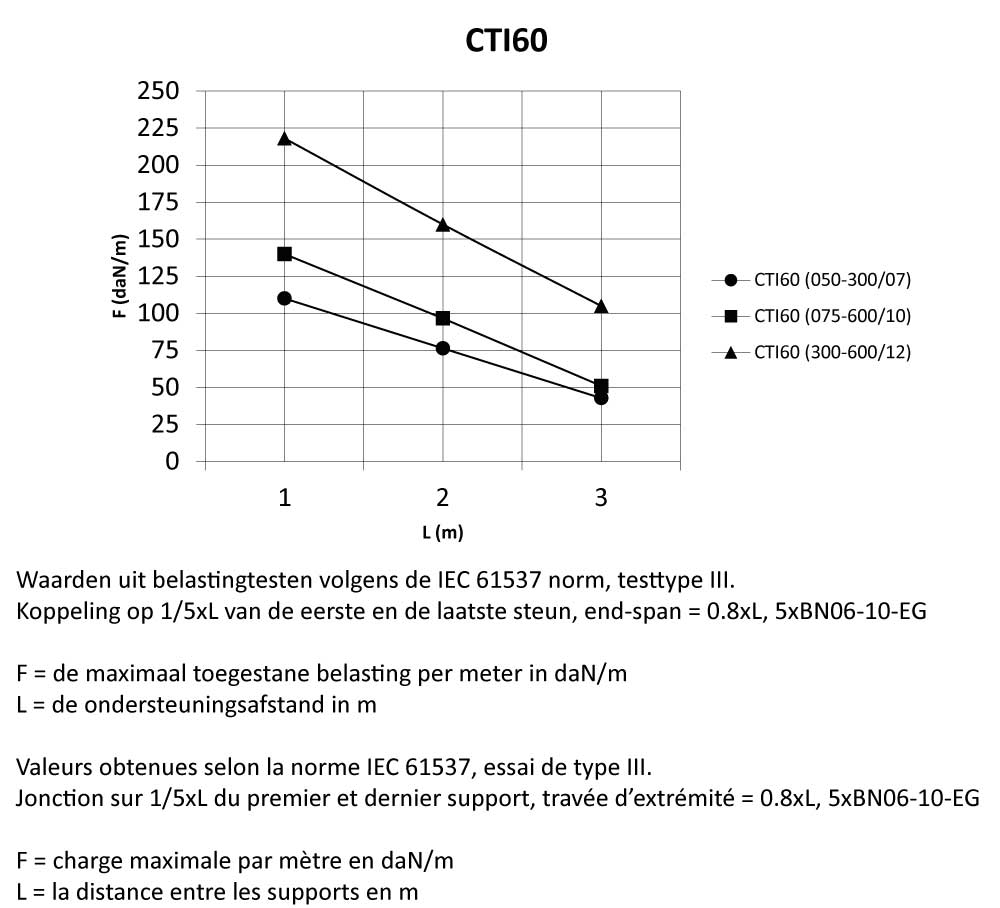
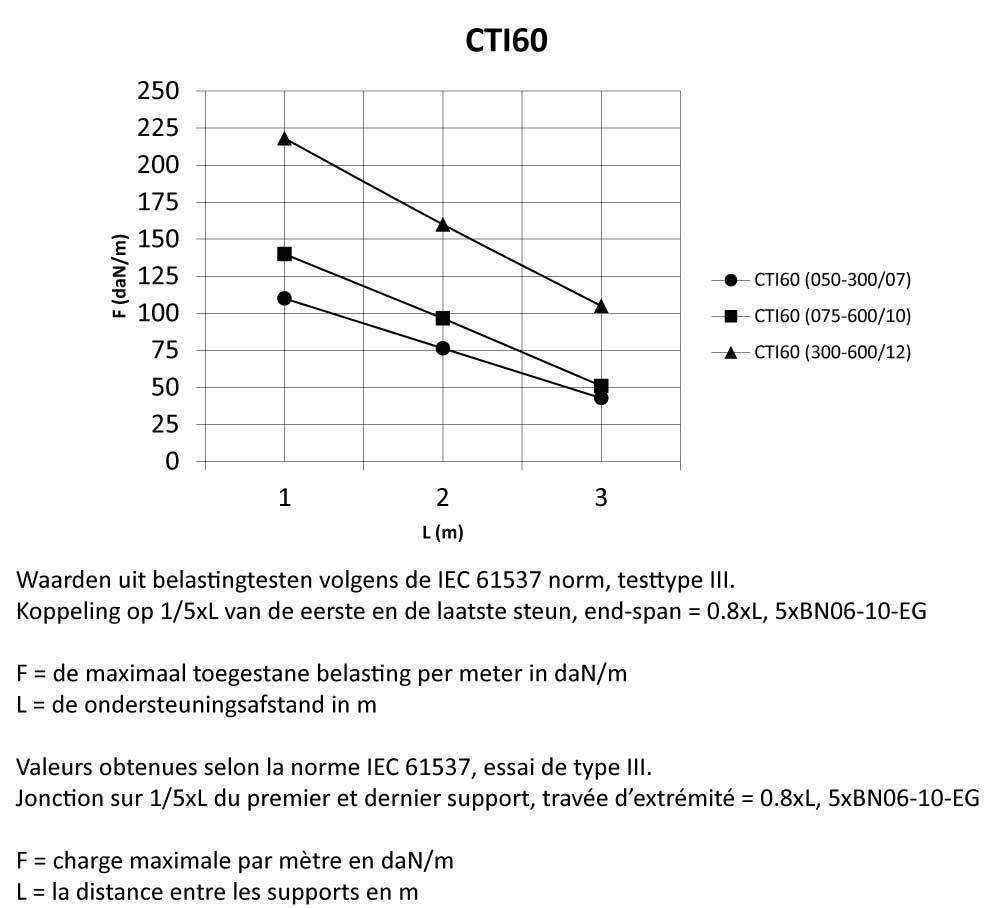
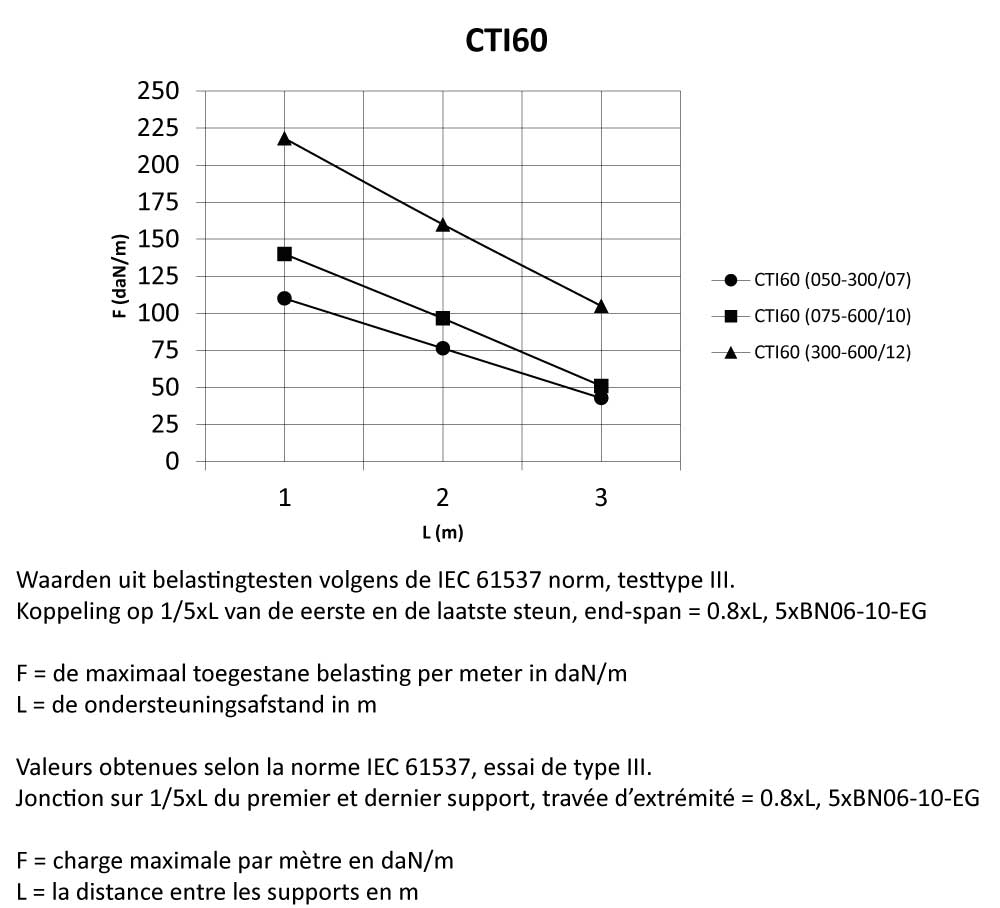
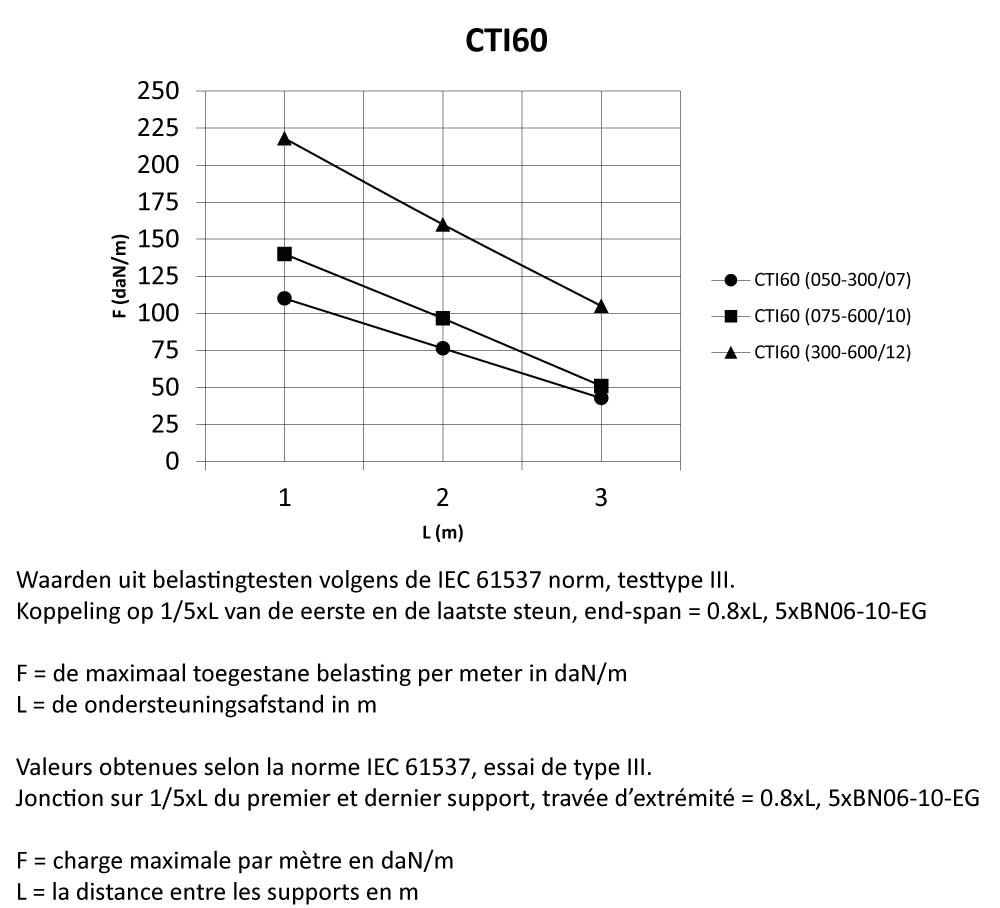
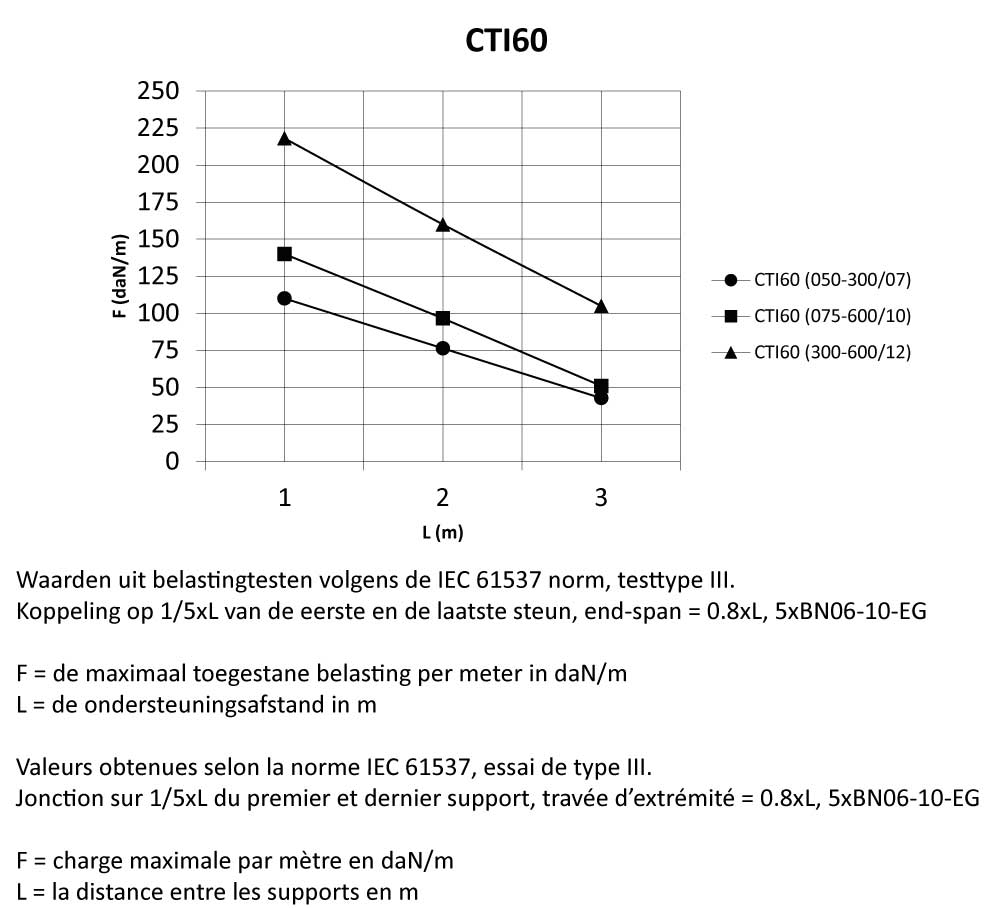
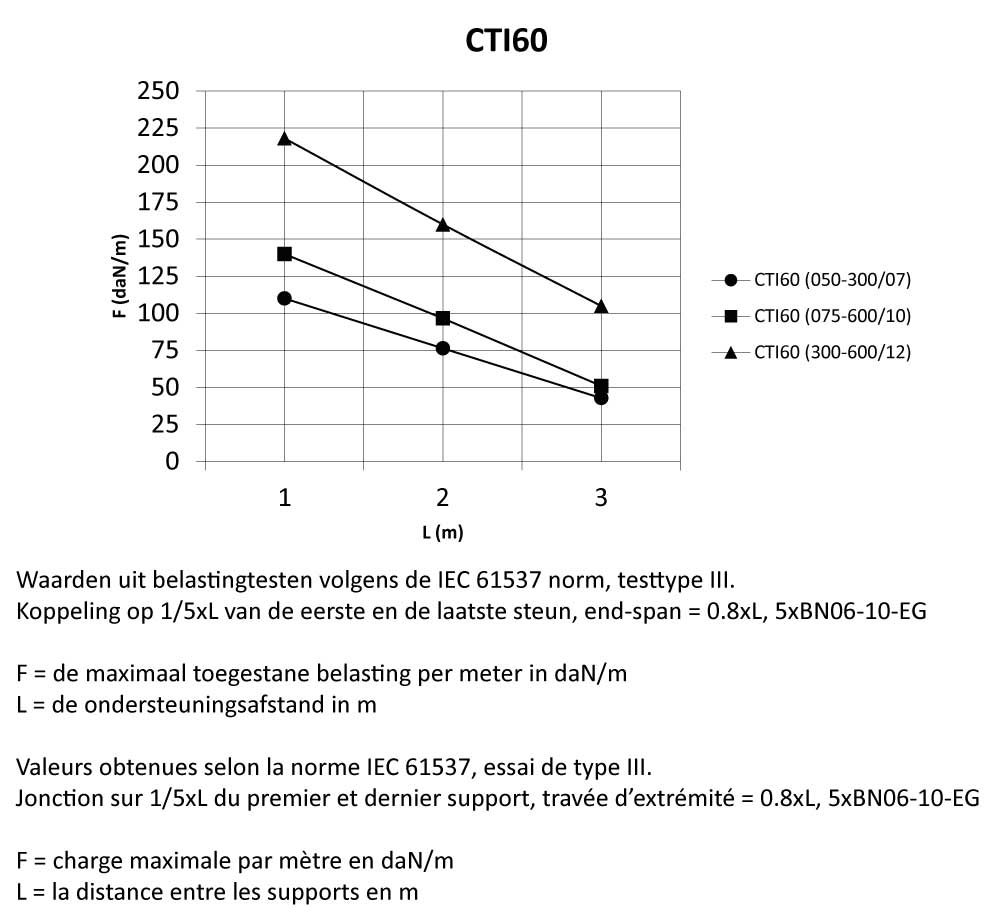
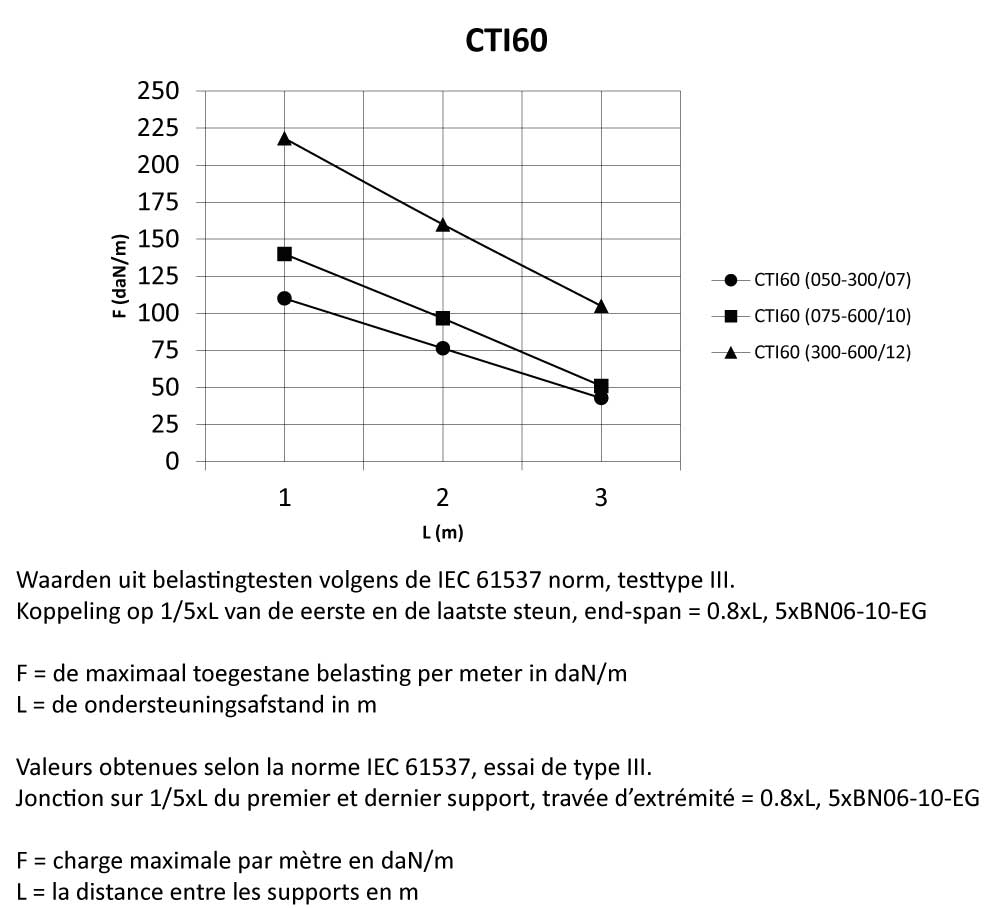
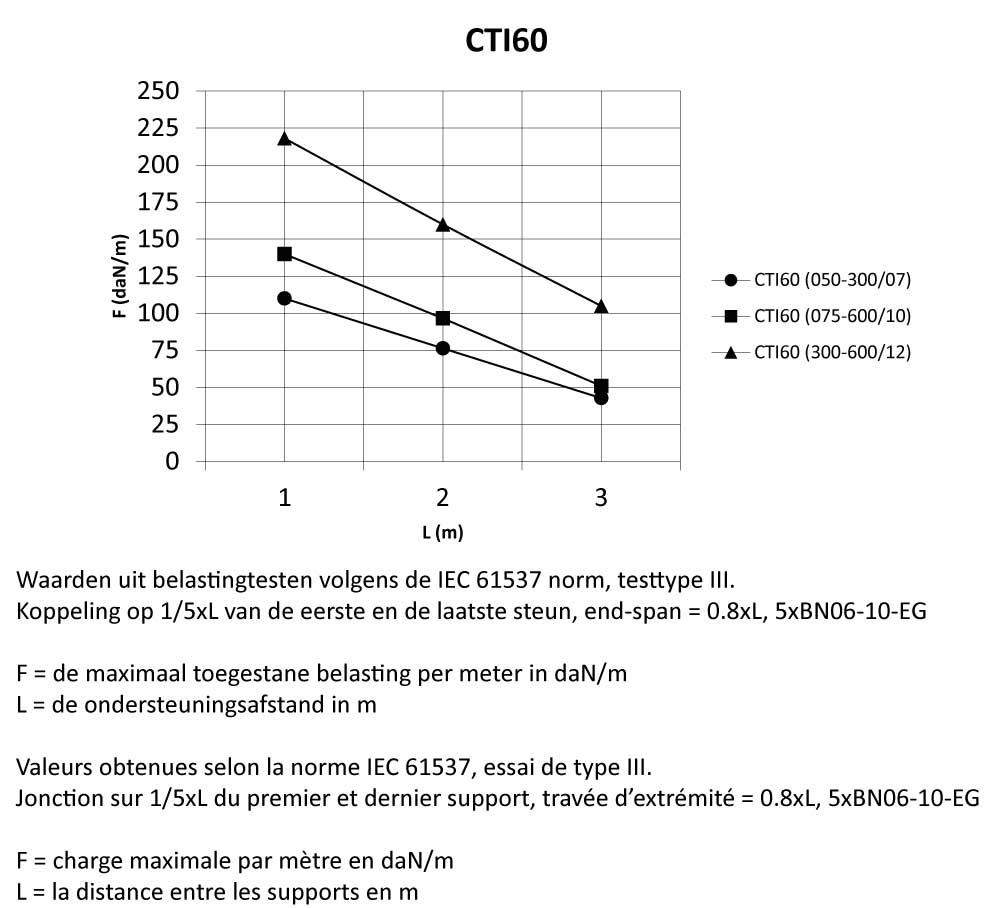
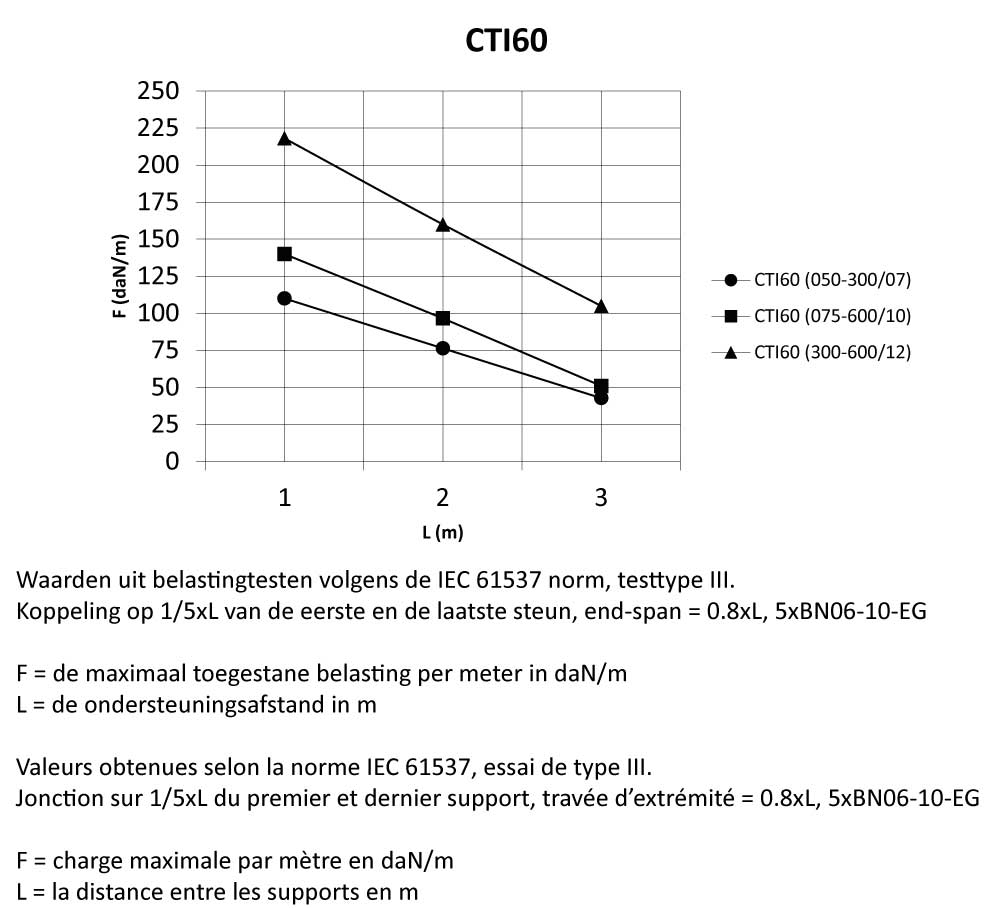
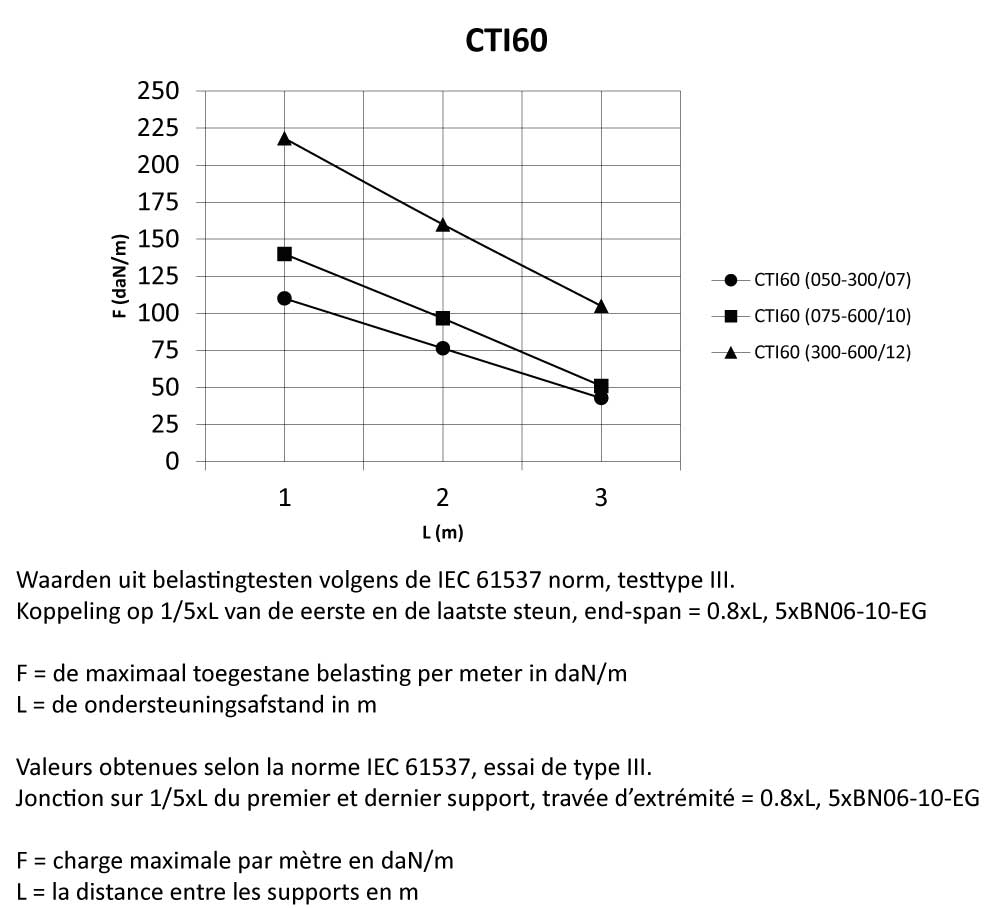
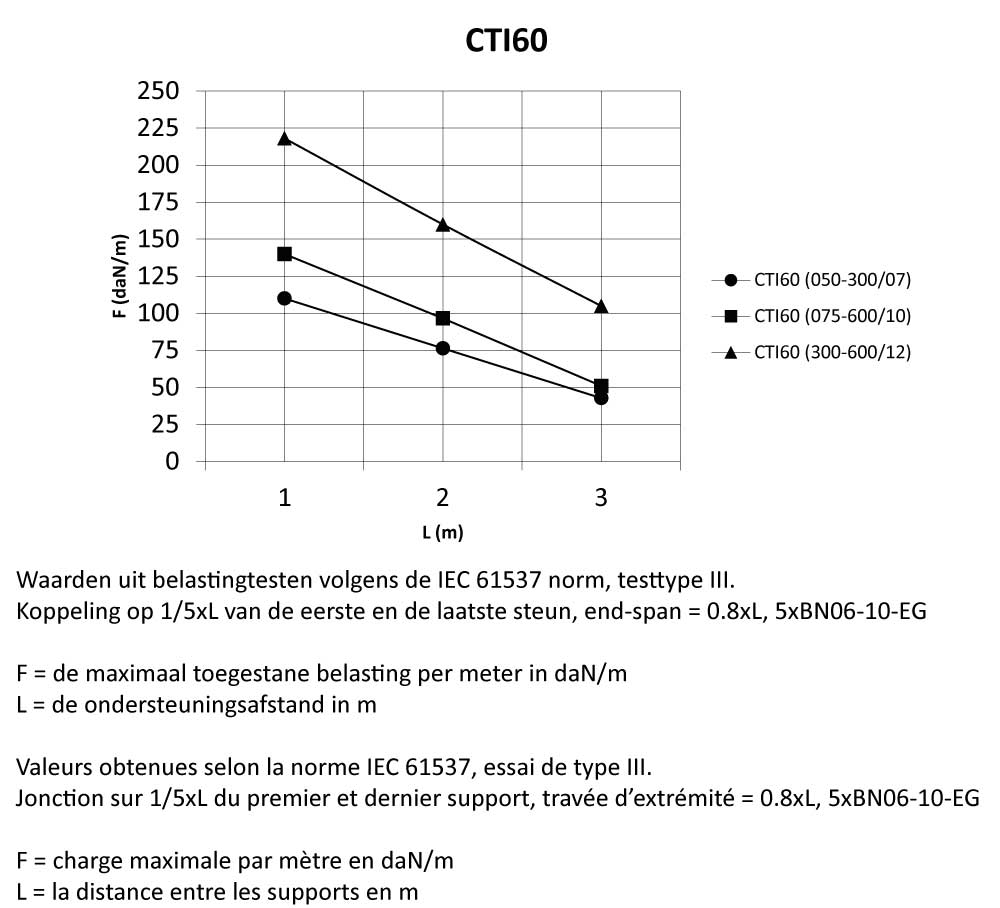
CTI60


Cable Tray Interlocking ends
CTI60


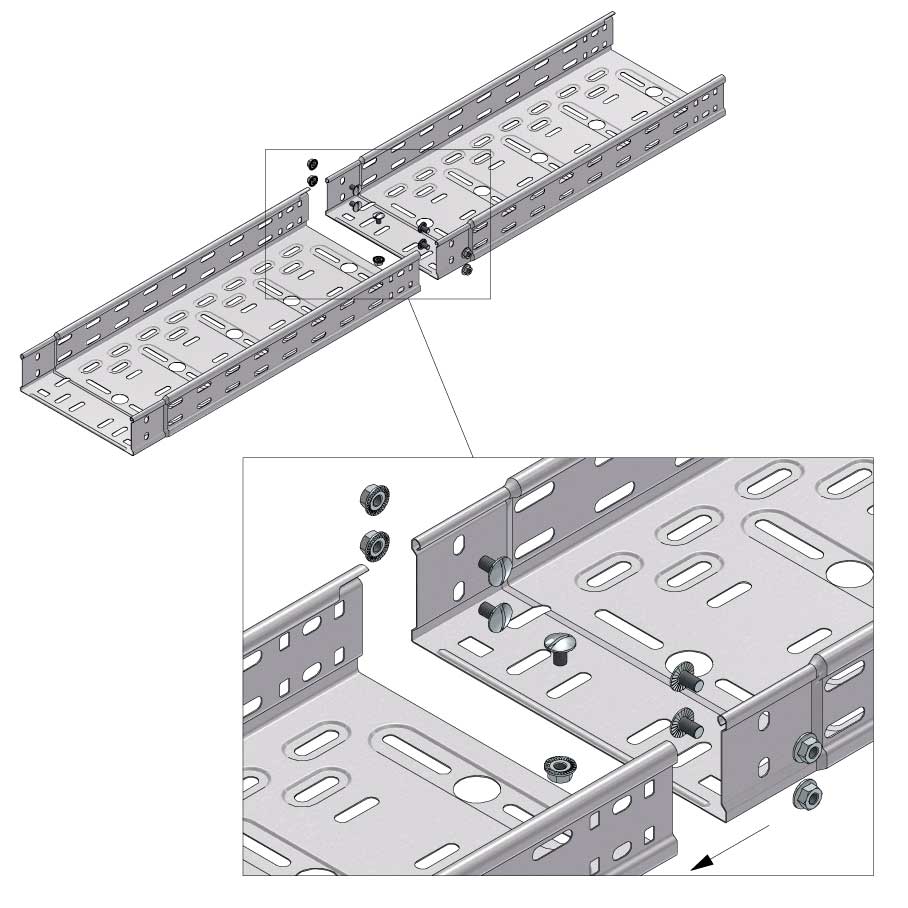
Connect with BN06-10
Coated finishing available on demand. RAL colour code to be confirmed on your order.
| SKU | Article code | Finishing | Dimension A | Usable surface (cm²) | Packaging | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
10926 |
CTI60-050-07-3PG |
PG
|
50
|
23.4
|
3
|
Default
|
|
|||


Additional information
Finishing
Sendzimir galvanized (EN 10143) PG (pre-galvanized):
Products made of Sendzimir (pre-galvanized) or continuous hot-dip galvanized steel sheet and coils are mostly used wherever limited chemical contamination is likely, for example, in of ces, industrial buildings, covered parking lots, etc. Characteristic of this steel type is that – prior to mechanical deformation – it is given a zinc coating by means of a continuous dipping process. This zinc coating is easily deformed. A cathodic action occurs on cut surfaces (up to 1.5mm) that protects against oxidation. First, the steel is chemical cleaned and roughened in order to achieve a good bond. After the dipping process, the surplus zinc is blown off and one obtains an extra passivating coat (an ultra-thin protective coat) to prevent oxidation of the zinc coating (white rust). The coating thickness is usually expressed in g/m2. The most deployed type of Sendzimir steel is Z 275 = 275g/m2 (weighed on both sides), this corresponds to 18-20 µm (micron). Sendzimir galvanized steel sourced from modern galvanizing lines has, in general, a uniform, shiny appearance. The previous, common fl owery surface is scarcely seen these days. This effect is obtained under the infl uence of lead but has no eff ect on the quality of the coating. The use of lead was banned due to the ever more stringent environmental standards. |
|||||||||||
|
|
10909 |
CTI60-075-07-3PG |
PG
|
75
|
38.07
|
3
|
Default
|
|
|||


Additional information
Finishing
Sendzimir galvanized (EN 10143) PG (pre-galvanized):
Products made of Sendzimir (pre-galvanized) or continuous hot-dip galvanized steel sheet and coils are mostly used wherever limited chemical contamination is likely, for example, in of ces, industrial buildings, covered parking lots, etc. Characteristic of this steel type is that – prior to mechanical deformation – it is given a zinc coating by means of a continuous dipping process. This zinc coating is easily deformed. A cathodic action occurs on cut surfaces (up to 1.5mm) that protects against oxidation. First, the steel is chemical cleaned and roughened in order to achieve a good bond. After the dipping process, the surplus zinc is blown off and one obtains an extra passivating coat (an ultra-thin protective coat) to prevent oxidation of the zinc coating (white rust). The coating thickness is usually expressed in g/m2. The most deployed type of Sendzimir steel is Z 275 = 275g/m2 (weighed on both sides), this corresponds to 18-20 µm (micron). Sendzimir galvanized steel sourced from modern galvanizing lines has, in general, a uniform, shiny appearance. The previous, common fl owery surface is scarcely seen these days. This effect is obtained under the infl uence of lead but has no eff ect on the quality of the coating. The use of lead was banned due to the ever more stringent environmental standards. |
|||||||||||
|
|
10137 |
CTI60-075-10-3PG |
PG
|
75
|
38.07
|
3
|
Default
|
|
|||


Additional information
Finishing
Sendzimir galvanized (EN 10143) PG (pre-galvanized):
Products made of Sendzimir (pre-galvanized) or continuous hot-dip galvanized steel sheet and coils are mostly used wherever limited chemical contamination is likely, for example, in of ces, industrial buildings, covered parking lots, etc. Characteristic of this steel type is that – prior to mechanical deformation – it is given a zinc coating by means of a continuous dipping process. This zinc coating is easily deformed. A cathodic action occurs on cut surfaces (up to 1.5mm) that protects against oxidation. First, the steel is chemical cleaned and roughened in order to achieve a good bond. After the dipping process, the surplus zinc is blown off and one obtains an extra passivating coat (an ultra-thin protective coat) to prevent oxidation of the zinc coating (white rust). The coating thickness is usually expressed in g/m2. The most deployed type of Sendzimir steel is Z 275 = 275g/m2 (weighed on both sides), this corresponds to 18-20 µm (micron). Sendzimir galvanized steel sourced from modern galvanizing lines has, in general, a uniform, shiny appearance. The previous, common fl owery surface is scarcely seen these days. This effect is obtained under the infl uence of lead but has no eff ect on the quality of the coating. The use of lead was banned due to the ever more stringent environmental standards. |
|||||||||||
|
|
10910 |
CTI60-100-07-3PG |
PG
|
100
|
52.73
|
3
|
Default
|
|
|||


Additional information
Finishing
Sendzimir galvanized (EN 10143) PG (pre-galvanized):
Products made of Sendzimir (pre-galvanized) or continuous hot-dip galvanized steel sheet and coils are mostly used wherever limited chemical contamination is likely, for example, in of ces, industrial buildings, covered parking lots, etc. Characteristic of this steel type is that – prior to mechanical deformation – it is given a zinc coating by means of a continuous dipping process. This zinc coating is easily deformed. A cathodic action occurs on cut surfaces (up to 1.5mm) that protects against oxidation. First, the steel is chemical cleaned and roughened in order to achieve a good bond. After the dipping process, the surplus zinc is blown off and one obtains an extra passivating coat (an ultra-thin protective coat) to prevent oxidation of the zinc coating (white rust). The coating thickness is usually expressed in g/m2. The most deployed type of Sendzimir steel is Z 275 = 275g/m2 (weighed on both sides), this corresponds to 18-20 µm (micron). Sendzimir galvanized steel sourced from modern galvanizing lines has, in general, a uniform, shiny appearance. The previous, common fl owery surface is scarcely seen these days. This effect is obtained under the infl uence of lead but has no eff ect on the quality of the coating. The use of lead was banned due to the ever more stringent environmental standards. |
|||||||||||
|
|
10138 |
CTI60-100-10-3PG |
PG
|
100
|
52.73
|
3
|
Default
|
|
|||


Additional information
Finishing
Sendzimir galvanized (EN 10143) PG (pre-galvanized):
Products made of Sendzimir (pre-galvanized) or continuous hot-dip galvanized steel sheet and coils are mostly used wherever limited chemical contamination is likely, for example, in of ces, industrial buildings, covered parking lots, etc. Characteristic of this steel type is that – prior to mechanical deformation – it is given a zinc coating by means of a continuous dipping process. This zinc coating is easily deformed. A cathodic action occurs on cut surfaces (up to 1.5mm) that protects against oxidation. First, the steel is chemical cleaned and roughened in order to achieve a good bond. After the dipping process, the surplus zinc is blown off and one obtains an extra passivating coat (an ultra-thin protective coat) to prevent oxidation of the zinc coating (white rust). The coating thickness is usually expressed in g/m2. The most deployed type of Sendzimir steel is Z 275 = 275g/m2 (weighed on both sides), this corresponds to 18-20 µm (micron). Sendzimir galvanized steel sourced from modern galvanizing lines has, in general, a uniform, shiny appearance. The previous, common fl owery surface is scarcely seen these days. This effect is obtained under the infl uence of lead but has no eff ect on the quality of the coating. The use of lead was banned due to the ever more stringent environmental standards. |
|||||||||||
|
|
11513 |
CTI60-150-07-3PG |
PG
|
150
|
82.05
|
3
|
Default
|
|
|||


Additional information
Finishing
Sendzimir galvanized (EN 10143) PG (pre-galvanized):
Products made of Sendzimir (pre-galvanized) or continuous hot-dip galvanized steel sheet and coils are mostly used wherever limited chemical contamination is likely, for example, in of ces, industrial buildings, covered parking lots, etc. Characteristic of this steel type is that – prior to mechanical deformation – it is given a zinc coating by means of a continuous dipping process. This zinc coating is easily deformed. A cathodic action occurs on cut surfaces (up to 1.5mm) that protects against oxidation. First, the steel is chemical cleaned and roughened in order to achieve a good bond. After the dipping process, the surplus zinc is blown off and one obtains an extra passivating coat (an ultra-thin protective coat) to prevent oxidation of the zinc coating (white rust). The coating thickness is usually expressed in g/m2. The most deployed type of Sendzimir steel is Z 275 = 275g/m2 (weighed on both sides), this corresponds to 18-20 µm (micron). Sendzimir galvanized steel sourced from modern galvanizing lines has, in general, a uniform, shiny appearance. The previous, common fl owery surface is scarcely seen these days. This effect is obtained under the infl uence of lead but has no eff ect on the quality of the coating. The use of lead was banned due to the ever more stringent environmental standards. |
|||||||||||
|
|
10139 |
CTI60-150-10-3PG |
PG
|
150
|
82.05
|
3
|
Default
|
|
|||


Additional information
Finishing
Sendzimir galvanized (EN 10143) PG (pre-galvanized):
Products made of Sendzimir (pre-galvanized) or continuous hot-dip galvanized steel sheet and coils are mostly used wherever limited chemical contamination is likely, for example, in of ces, industrial buildings, covered parking lots, etc. Characteristic of this steel type is that – prior to mechanical deformation – it is given a zinc coating by means of a continuous dipping process. This zinc coating is easily deformed. A cathodic action occurs on cut surfaces (up to 1.5mm) that protects against oxidation. First, the steel is chemical cleaned and roughened in order to achieve a good bond. After the dipping process, the surplus zinc is blown off and one obtains an extra passivating coat (an ultra-thin protective coat) to prevent oxidation of the zinc coating (white rust). The coating thickness is usually expressed in g/m2. The most deployed type of Sendzimir steel is Z 275 = 275g/m2 (weighed on both sides), this corresponds to 18-20 µm (micron). Sendzimir galvanized steel sourced from modern galvanizing lines has, in general, a uniform, shiny appearance. The previous, common fl owery surface is scarcely seen these days. This effect is obtained under the infl uence of lead but has no eff ect on the quality of the coating. The use of lead was banned due to the ever more stringent environmental standards. |
|||||||||||
|
|
10911 |
CTI60-200-07-3PG |
PG
|
200
|
111.38
|
3
|
Default
|
|
|||


Additional information
Finishing
Sendzimir galvanized (EN 10143) PG (pre-galvanized):
Products made of Sendzimir (pre-galvanized) or continuous hot-dip galvanized steel sheet and coils are mostly used wherever limited chemical contamination is likely, for example, in of ces, industrial buildings, covered parking lots, etc. Characteristic of this steel type is that – prior to mechanical deformation – it is given a zinc coating by means of a continuous dipping process. This zinc coating is easily deformed. A cathodic action occurs on cut surfaces (up to 1.5mm) that protects against oxidation. First, the steel is chemical cleaned and roughened in order to achieve a good bond. After the dipping process, the surplus zinc is blown off and one obtains an extra passivating coat (an ultra-thin protective coat) to prevent oxidation of the zinc coating (white rust). The coating thickness is usually expressed in g/m2. The most deployed type of Sendzimir steel is Z 275 = 275g/m2 (weighed on both sides), this corresponds to 18-20 µm (micron). Sendzimir galvanized steel sourced from modern galvanizing lines has, in general, a uniform, shiny appearance. The previous, common fl owery surface is scarcely seen these days. This effect is obtained under the infl uence of lead but has no eff ect on the quality of the coating. The use of lead was banned due to the ever more stringent environmental standards. |
|||||||||||
|
|
10140 |
CTI60-200-10-3PG |
PG
|
200
|
111.38
|
3
|
Default
|
|
|||


Additional information
Finishing
Sendzimir galvanized (EN 10143) PG (pre-galvanized):
Products made of Sendzimir (pre-galvanized) or continuous hot-dip galvanized steel sheet and coils are mostly used wherever limited chemical contamination is likely, for example, in of ces, industrial buildings, covered parking lots, etc. Characteristic of this steel type is that – prior to mechanical deformation – it is given a zinc coating by means of a continuous dipping process. This zinc coating is easily deformed. A cathodic action occurs on cut surfaces (up to 1.5mm) that protects against oxidation. First, the steel is chemical cleaned and roughened in order to achieve a good bond. After the dipping process, the surplus zinc is blown off and one obtains an extra passivating coat (an ultra-thin protective coat) to prevent oxidation of the zinc coating (white rust). The coating thickness is usually expressed in g/m2. The most deployed type of Sendzimir steel is Z 275 = 275g/m2 (weighed on both sides), this corresponds to 18-20 µm (micron). Sendzimir galvanized steel sourced from modern galvanizing lines has, in general, a uniform, shiny appearance. The previous, common fl owery surface is scarcely seen these days. This effect is obtained under the infl uence of lead but has no eff ect on the quality of the coating. The use of lead was banned due to the ever more stringent environmental standards. |
|||||||||||
|
|
10912 |
CTI60-300-07-3PG |
PG
|
300
|
170.03
|
3
|
Default
|
|
|||


Additional information
Finishing
Sendzimir galvanized (EN 10143) PG (pre-galvanized):
Products made of Sendzimir (pre-galvanized) or continuous hot-dip galvanized steel sheet and coils are mostly used wherever limited chemical contamination is likely, for example, in of ces, industrial buildings, covered parking lots, etc. Characteristic of this steel type is that – prior to mechanical deformation – it is given a zinc coating by means of a continuous dipping process. This zinc coating is easily deformed. A cathodic action occurs on cut surfaces (up to 1.5mm) that protects against oxidation. First, the steel is chemical cleaned and roughened in order to achieve a good bond. After the dipping process, the surplus zinc is blown off and one obtains an extra passivating coat (an ultra-thin protective coat) to prevent oxidation of the zinc coating (white rust). The coating thickness is usually expressed in g/m2. The most deployed type of Sendzimir steel is Z 275 = 275g/m2 (weighed on both sides), this corresponds to 18-20 µm (micron). Sendzimir galvanized steel sourced from modern galvanizing lines has, in general, a uniform, shiny appearance. The previous, common fl owery surface is scarcely seen these days. This effect is obtained under the infl uence of lead but has no eff ect on the quality of the coating. The use of lead was banned due to the ever more stringent environmental standards. |
|||||||||||
|
|
10141 |
CTI60-300-10-3PG |
PG
|
300
|
170.03
|
3
|
Default
|
|
|||


Additional information
Finishing
Sendzimir galvanized (EN 10143) PG (pre-galvanized):
Products made of Sendzimir (pre-galvanized) or continuous hot-dip galvanized steel sheet and coils are mostly used wherever limited chemical contamination is likely, for example, in of ces, industrial buildings, covered parking lots, etc. Characteristic of this steel type is that – prior to mechanical deformation – it is given a zinc coating by means of a continuous dipping process. This zinc coating is easily deformed. A cathodic action occurs on cut surfaces (up to 1.5mm) that protects against oxidation. First, the steel is chemical cleaned and roughened in order to achieve a good bond. After the dipping process, the surplus zinc is blown off and one obtains an extra passivating coat (an ultra-thin protective coat) to prevent oxidation of the zinc coating (white rust). The coating thickness is usually expressed in g/m2. The most deployed type of Sendzimir steel is Z 275 = 275g/m2 (weighed on both sides), this corresponds to 18-20 µm (micron). Sendzimir galvanized steel sourced from modern galvanizing lines has, in general, a uniform, shiny appearance. The previous, common fl owery surface is scarcely seen these days. This effect is obtained under the infl uence of lead but has no eff ect on the quality of the coating. The use of lead was banned due to the ever more stringent environmental standards. |
|||||||||||
|
|
14513 |
CTI60-300-12-3PG |
PG
|
300
|
170.03
|
3
|
Default
|
|
|||


Additional information
Finishing
Sendzimir galvanized (EN 10143) PG (pre-galvanized):
Products made of Sendzimir (pre-galvanized) or continuous hot-dip galvanized steel sheet and coils are mostly used wherever limited chemical contamination is likely, for example, in of ces, industrial buildings, covered parking lots, etc. Characteristic of this steel type is that – prior to mechanical deformation – it is given a zinc coating by means of a continuous dipping process. This zinc coating is easily deformed. A cathodic action occurs on cut surfaces (up to 1.5mm) that protects against oxidation. First, the steel is chemical cleaned and roughened in order to achieve a good bond. After the dipping process, the surplus zinc is blown off and one obtains an extra passivating coat (an ultra-thin protective coat) to prevent oxidation of the zinc coating (white rust). The coating thickness is usually expressed in g/m2. The most deployed type of Sendzimir steel is Z 275 = 275g/m2 (weighed on both sides), this corresponds to 18-20 µm (micron). Sendzimir galvanized steel sourced from modern galvanizing lines has, in general, a uniform, shiny appearance. The previous, common fl owery surface is scarcely seen these days. This effect is obtained under the infl uence of lead but has no eff ect on the quality of the coating. The use of lead was banned due to the ever more stringent environmental standards. |
|||||||||||
|
|
10131 |
CTI60-400-10-3PG |
PG
|
400
|
228.68
|
3
|
Default
|
|
|||


Additional information
Finishing
Sendzimir galvanized (EN 10143) PG (pre-galvanized):
Products made of Sendzimir (pre-galvanized) or continuous hot-dip galvanized steel sheet and coils are mostly used wherever limited chemical contamination is likely, for example, in of ces, industrial buildings, covered parking lots, etc. Characteristic of this steel type is that – prior to mechanical deformation – it is given a zinc coating by means of a continuous dipping process. This zinc coating is easily deformed. A cathodic action occurs on cut surfaces (up to 1.5mm) that protects against oxidation. First, the steel is chemical cleaned and roughened in order to achieve a good bond. After the dipping process, the surplus zinc is blown off and one obtains an extra passivating coat (an ultra-thin protective coat) to prevent oxidation of the zinc coating (white rust). The coating thickness is usually expressed in g/m2. The most deployed type of Sendzimir steel is Z 275 = 275g/m2 (weighed on both sides), this corresponds to 18-20 µm (micron). Sendzimir galvanized steel sourced from modern galvanizing lines has, in general, a uniform, shiny appearance. The previous, common fl owery surface is scarcely seen these days. This effect is obtained under the infl uence of lead but has no eff ect on the quality of the coating. The use of lead was banned due to the ever more stringent environmental standards. |
|||||||||||
|
|
14903 |
CTI60-400-12-3PG |
PG
|
400
|
228.68
|
3
|
Default
|
|
|||


Additional information
Finishing
Sendzimir galvanized (EN 10143) PG (pre-galvanized):
Products made of Sendzimir (pre-galvanized) or continuous hot-dip galvanized steel sheet and coils are mostly used wherever limited chemical contamination is likely, for example, in of ces, industrial buildings, covered parking lots, etc. Characteristic of this steel type is that – prior to mechanical deformation – it is given a zinc coating by means of a continuous dipping process. This zinc coating is easily deformed. A cathodic action occurs on cut surfaces (up to 1.5mm) that protects against oxidation. First, the steel is chemical cleaned and roughened in order to achieve a good bond. After the dipping process, the surplus zinc is blown off and one obtains an extra passivating coat (an ultra-thin protective coat) to prevent oxidation of the zinc coating (white rust). The coating thickness is usually expressed in g/m2. The most deployed type of Sendzimir steel is Z 275 = 275g/m2 (weighed on both sides), this corresponds to 18-20 µm (micron). Sendzimir galvanized steel sourced from modern galvanizing lines has, in general, a uniform, shiny appearance. The previous, common fl owery surface is scarcely seen these days. This effect is obtained under the infl uence of lead but has no eff ect on the quality of the coating. The use of lead was banned due to the ever more stringent environmental standards. |
|||||||||||
|
|
13331 |
CTI60-500-10-3PG |
PG
|
500
|
287.33
|
3
|
Default
|
|
|||


Additional information
Finishing
Sendzimir galvanized (EN 10143) PG (pre-galvanized):
Products made of Sendzimir (pre-galvanized) or continuous hot-dip galvanized steel sheet and coils are mostly used wherever limited chemical contamination is likely, for example, in of ces, industrial buildings, covered parking lots, etc. Characteristic of this steel type is that – prior to mechanical deformation – it is given a zinc coating by means of a continuous dipping process. This zinc coating is easily deformed. A cathodic action occurs on cut surfaces (up to 1.5mm) that protects against oxidation. First, the steel is chemical cleaned and roughened in order to achieve a good bond. After the dipping process, the surplus zinc is blown off and one obtains an extra passivating coat (an ultra-thin protective coat) to prevent oxidation of the zinc coating (white rust). The coating thickness is usually expressed in g/m2. The most deployed type of Sendzimir steel is Z 275 = 275g/m2 (weighed on both sides), this corresponds to 18-20 µm (micron). Sendzimir galvanized steel sourced from modern galvanizing lines has, in general, a uniform, shiny appearance. The previous, common fl owery surface is scarcely seen these days. This effect is obtained under the infl uence of lead but has no eff ect on the quality of the coating. The use of lead was banned due to the ever more stringent environmental standards. |
|||||||||||
|
|
14904 |
CTI60-500-12-3PG |
PG
|
500
|
287.33
|
3
|
Default
|
|
|||


Additional information
Finishing
Sendzimir galvanized (EN 10143) PG (pre-galvanized):
Products made of Sendzimir (pre-galvanized) or continuous hot-dip galvanized steel sheet and coils are mostly used wherever limited chemical contamination is likely, for example, in of ces, industrial buildings, covered parking lots, etc. Characteristic of this steel type is that – prior to mechanical deformation – it is given a zinc coating by means of a continuous dipping process. This zinc coating is easily deformed. A cathodic action occurs on cut surfaces (up to 1.5mm) that protects against oxidation. First, the steel is chemical cleaned and roughened in order to achieve a good bond. After the dipping process, the surplus zinc is blown off and one obtains an extra passivating coat (an ultra-thin protective coat) to prevent oxidation of the zinc coating (white rust). The coating thickness is usually expressed in g/m2. The most deployed type of Sendzimir steel is Z 275 = 275g/m2 (weighed on both sides), this corresponds to 18-20 µm (micron). Sendzimir galvanized steel sourced from modern galvanizing lines has, in general, a uniform, shiny appearance. The previous, common fl owery surface is scarcely seen these days. This effect is obtained under the infl uence of lead but has no eff ect on the quality of the coating. The use of lead was banned due to the ever more stringent environmental standards. |
|||||||||||
|
|
13268 |
CTI60-600-10-3PG |
PG
|
600
|
345.98
|
3
|
Default
|
|
|||


Additional information
Finishing
Sendzimir galvanized (EN 10143) PG (pre-galvanized):
Products made of Sendzimir (pre-galvanized) or continuous hot-dip galvanized steel sheet and coils are mostly used wherever limited chemical contamination is likely, for example, in of ces, industrial buildings, covered parking lots, etc. Characteristic of this steel type is that – prior to mechanical deformation – it is given a zinc coating by means of a continuous dipping process. This zinc coating is easily deformed. A cathodic action occurs on cut surfaces (up to 1.5mm) that protects against oxidation. First, the steel is chemical cleaned and roughened in order to achieve a good bond. After the dipping process, the surplus zinc is blown off and one obtains an extra passivating coat (an ultra-thin protective coat) to prevent oxidation of the zinc coating (white rust). The coating thickness is usually expressed in g/m2. The most deployed type of Sendzimir steel is Z 275 = 275g/m2 (weighed on both sides), this corresponds to 18-20 µm (micron). Sendzimir galvanized steel sourced from modern galvanizing lines has, in general, a uniform, shiny appearance. The previous, common fl owery surface is scarcely seen these days. This effect is obtained under the infl uence of lead but has no eff ect on the quality of the coating. The use of lead was banned due to the ever more stringent environmental standards. |
|||||||||||
|
|
14623 |
CTI60-600-12-3PG |
PG
|
600
|
345.98
|
3
|
Default
|
|
|||


Additional information
Finishing
Sendzimir galvanized (EN 10143) PG (pre-galvanized):
Products made of Sendzimir (pre-galvanized) or continuous hot-dip galvanized steel sheet and coils are mostly used wherever limited chemical contamination is likely, for example, in of ces, industrial buildings, covered parking lots, etc. Characteristic of this steel type is that – prior to mechanical deformation – it is given a zinc coating by means of a continuous dipping process. This zinc coating is easily deformed. A cathodic action occurs on cut surfaces (up to 1.5mm) that protects against oxidation. First, the steel is chemical cleaned and roughened in order to achieve a good bond. After the dipping process, the surplus zinc is blown off and one obtains an extra passivating coat (an ultra-thin protective coat) to prevent oxidation of the zinc coating (white rust). The coating thickness is usually expressed in g/m2. The most deployed type of Sendzimir steel is Z 275 = 275g/m2 (weighed on both sides), this corresponds to 18-20 µm (micron). Sendzimir galvanized steel sourced from modern galvanizing lines has, in general, a uniform, shiny appearance. The previous, common fl owery surface is scarcely seen these days. This effect is obtained under the infl uence of lead but has no eff ect on the quality of the coating. The use of lead was banned due to the ever more stringent environmental standards. |
|||||||||||
|
|
10932 |
CTI60-050-07-3DG |
DG
|
50
|
23.4
|
3
|
|
|
|||


Additional information
Finishing
Hot-dip galvanized (EN ISO 1461) DG (dipped-galvanised):
Whenever cable support systems are exposed to the elements and/or caustic substances (such as petrochemical applications), they are given an additional treatment in the form of hot-dip galvanizing. Hot-dip galvanizing is a materials science process designed to render the steel non-corroding. If this coating is breached, the zinc will act as a sacrifcial anode, so that the iron is protected by the zinc (aka cathodic protection). During galvanization, three alloys are formed: an iron-zinc alloy, a zinc-iron alloy and also a zinc alloy. The pre-treatment of the steel is crucially important in order to achieve a good bond. The following process steps are involved: degreasing, rinsing, pickling, re-rinsing, fl uxing, drying and hot-dipping. The coating thickness depends on the steel composition, the material thickness and the time spent in the zinc bath. In the galvanizing standard NEN-EN-ISO 1461, the minimum coating thickness are prescribed (as shown in following overview), just as the zinc shrinkage per year which will depend on environmental factors (see table entitled `Corrosion classes’). In addition, the zinc coating forms an excellent substrate for other post-treatments, such as applying a powder coating and coats of paint (better known as the duplex system). An added advantage of hot-dip galvanizing is that along the edges and pointy bits, where objects are usually extra susceptible to corrosion, the zinc coating is thicker because of the behaviour of the liquid. Minimum thicknesses of the zinc coating according to ISO 1461 - Using the hot-dip method Material thickness ≥ 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 85µm Material thickness ≥ 3 mm to < 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 70µm Material thickness ≥ 1,5 mm to < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 1,5 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm - Using the drum method Material thickness ≥ 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm |
|||||||||||
|
|
10943 |
CTI60-075-07-3DG |
DG
|
75
|
38.07
|
3
|
|
|
|||


Additional information
Finishing
Hot-dip galvanized (EN ISO 1461) DG (dipped-galvanised):
Whenever cable support systems are exposed to the elements and/or caustic substances (such as petrochemical applications), they are given an additional treatment in the form of hot-dip galvanizing. Hot-dip galvanizing is a materials science process designed to render the steel non-corroding. If this coating is breached, the zinc will act as a sacrifcial anode, so that the iron is protected by the zinc (aka cathodic protection). During galvanization, three alloys are formed: an iron-zinc alloy, a zinc-iron alloy and also a zinc alloy. The pre-treatment of the steel is crucially important in order to achieve a good bond. The following process steps are involved: degreasing, rinsing, pickling, re-rinsing, fl uxing, drying and hot-dipping. The coating thickness depends on the steel composition, the material thickness and the time spent in the zinc bath. In the galvanizing standard NEN-EN-ISO 1461, the minimum coating thickness are prescribed (as shown in following overview), just as the zinc shrinkage per year which will depend on environmental factors (see table entitled `Corrosion classes’). In addition, the zinc coating forms an excellent substrate for other post-treatments, such as applying a powder coating and coats of paint (better known as the duplex system). An added advantage of hot-dip galvanizing is that along the edges and pointy bits, where objects are usually extra susceptible to corrosion, the zinc coating is thicker because of the behaviour of the liquid. Minimum thicknesses of the zinc coating according to ISO 1461 - Using the hot-dip method Material thickness ≥ 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 85µm Material thickness ≥ 3 mm to < 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 70µm Material thickness ≥ 1,5 mm to < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 1,5 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm - Using the drum method Material thickness ≥ 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm |
|||||||||||
|
|
10459 |
CTI60-075-10-3DG |
DG
|
75
|
38.07
|
3
|
|
|
|||


Additional information
Finishing
Hot-dip galvanized (EN ISO 1461) DG (dipped-galvanised):
Whenever cable support systems are exposed to the elements and/or caustic substances (such as petrochemical applications), they are given an additional treatment in the form of hot-dip galvanizing. Hot-dip galvanizing is a materials science process designed to render the steel non-corroding. If this coating is breached, the zinc will act as a sacrifcial anode, so that the iron is protected by the zinc (aka cathodic protection). During galvanization, three alloys are formed: an iron-zinc alloy, a zinc-iron alloy and also a zinc alloy. The pre-treatment of the steel is crucially important in order to achieve a good bond. The following process steps are involved: degreasing, rinsing, pickling, re-rinsing, fl uxing, drying and hot-dipping. The coating thickness depends on the steel composition, the material thickness and the time spent in the zinc bath. In the galvanizing standard NEN-EN-ISO 1461, the minimum coating thickness are prescribed (as shown in following overview), just as the zinc shrinkage per year which will depend on environmental factors (see table entitled `Corrosion classes’). In addition, the zinc coating forms an excellent substrate for other post-treatments, such as applying a powder coating and coats of paint (better known as the duplex system). An added advantage of hot-dip galvanizing is that along the edges and pointy bits, where objects are usually extra susceptible to corrosion, the zinc coating is thicker because of the behaviour of the liquid. Minimum thicknesses of the zinc coating according to ISO 1461 - Using the hot-dip method Material thickness ≥ 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 85µm Material thickness ≥ 3 mm to < 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 70µm Material thickness ≥ 1,5 mm to < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 1,5 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm - Using the drum method Material thickness ≥ 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm |
|||||||||||
|
|
10944 |
CTI60-100-07-3DG |
DG
|
100
|
52.73
|
3
|
|
|
|||


Additional information
Finishing
Hot-dip galvanized (EN ISO 1461) DG (dipped-galvanised):
Whenever cable support systems are exposed to the elements and/or caustic substances (such as petrochemical applications), they are given an additional treatment in the form of hot-dip galvanizing. Hot-dip galvanizing is a materials science process designed to render the steel non-corroding. If this coating is breached, the zinc will act as a sacrifcial anode, so that the iron is protected by the zinc (aka cathodic protection). During galvanization, three alloys are formed: an iron-zinc alloy, a zinc-iron alloy and also a zinc alloy. The pre-treatment of the steel is crucially important in order to achieve a good bond. The following process steps are involved: degreasing, rinsing, pickling, re-rinsing, fl uxing, drying and hot-dipping. The coating thickness depends on the steel composition, the material thickness and the time spent in the zinc bath. In the galvanizing standard NEN-EN-ISO 1461, the minimum coating thickness are prescribed (as shown in following overview), just as the zinc shrinkage per year which will depend on environmental factors (see table entitled `Corrosion classes’). In addition, the zinc coating forms an excellent substrate for other post-treatments, such as applying a powder coating and coats of paint (better known as the duplex system). An added advantage of hot-dip galvanizing is that along the edges and pointy bits, where objects are usually extra susceptible to corrosion, the zinc coating is thicker because of the behaviour of the liquid. Minimum thicknesses of the zinc coating according to ISO 1461 - Using the hot-dip method Material thickness ≥ 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 85µm Material thickness ≥ 3 mm to < 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 70µm Material thickness ≥ 1,5 mm to < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 1,5 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm - Using the drum method Material thickness ≥ 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm |
|||||||||||
|
|
10460 |
CTI60-100-10-3DG |
DG
|
100
|
52.73
|
3
|
|
|
|||


Additional information
Finishing
Hot-dip galvanized (EN ISO 1461) DG (dipped-galvanised):
Whenever cable support systems are exposed to the elements and/or caustic substances (such as petrochemical applications), they are given an additional treatment in the form of hot-dip galvanizing. Hot-dip galvanizing is a materials science process designed to render the steel non-corroding. If this coating is breached, the zinc will act as a sacrifcial anode, so that the iron is protected by the zinc (aka cathodic protection). During galvanization, three alloys are formed: an iron-zinc alloy, a zinc-iron alloy and also a zinc alloy. The pre-treatment of the steel is crucially important in order to achieve a good bond. The following process steps are involved: degreasing, rinsing, pickling, re-rinsing, fl uxing, drying and hot-dipping. The coating thickness depends on the steel composition, the material thickness and the time spent in the zinc bath. In the galvanizing standard NEN-EN-ISO 1461, the minimum coating thickness are prescribed (as shown in following overview), just as the zinc shrinkage per year which will depend on environmental factors (see table entitled `Corrosion classes’). In addition, the zinc coating forms an excellent substrate for other post-treatments, such as applying a powder coating and coats of paint (better known as the duplex system). An added advantage of hot-dip galvanizing is that along the edges and pointy bits, where objects are usually extra susceptible to corrosion, the zinc coating is thicker because of the behaviour of the liquid. Minimum thicknesses of the zinc coating according to ISO 1461 - Using the hot-dip method Material thickness ≥ 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 85µm Material thickness ≥ 3 mm to < 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 70µm Material thickness ≥ 1,5 mm to < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 1,5 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm - Using the drum method Material thickness ≥ 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm |
|||||||||||
|
|
11514 |
CTI60-150-07-3DG |
DG
|
150
|
82.05
|
3
|
|
|
|||


Additional information
Finishing
Hot-dip galvanized (EN ISO 1461) DG (dipped-galvanised):
Whenever cable support systems are exposed to the elements and/or caustic substances (such as petrochemical applications), they are given an additional treatment in the form of hot-dip galvanizing. Hot-dip galvanizing is a materials science process designed to render the steel non-corroding. If this coating is breached, the zinc will act as a sacrifcial anode, so that the iron is protected by the zinc (aka cathodic protection). During galvanization, three alloys are formed: an iron-zinc alloy, a zinc-iron alloy and also a zinc alloy. The pre-treatment of the steel is crucially important in order to achieve a good bond. The following process steps are involved: degreasing, rinsing, pickling, re-rinsing, fl uxing, drying and hot-dipping. The coating thickness depends on the steel composition, the material thickness and the time spent in the zinc bath. In the galvanizing standard NEN-EN-ISO 1461, the minimum coating thickness are prescribed (as shown in following overview), just as the zinc shrinkage per year which will depend on environmental factors (see table entitled `Corrosion classes’). In addition, the zinc coating forms an excellent substrate for other post-treatments, such as applying a powder coating and coats of paint (better known as the duplex system). An added advantage of hot-dip galvanizing is that along the edges and pointy bits, where objects are usually extra susceptible to corrosion, the zinc coating is thicker because of the behaviour of the liquid. Minimum thicknesses of the zinc coating according to ISO 1461 - Using the hot-dip method Material thickness ≥ 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 85µm Material thickness ≥ 3 mm to < 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 70µm Material thickness ≥ 1,5 mm to < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 1,5 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm - Using the drum method Material thickness ≥ 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm |
|||||||||||
|
|
10461 |
CTI60-150-10-3DG |
DG
|
150
|
82.05
|
3
|
|
|
|||


Additional information
Finishing
Hot-dip galvanized (EN ISO 1461) DG (dipped-galvanised):
Whenever cable support systems are exposed to the elements and/or caustic substances (such as petrochemical applications), they are given an additional treatment in the form of hot-dip galvanizing. Hot-dip galvanizing is a materials science process designed to render the steel non-corroding. If this coating is breached, the zinc will act as a sacrifcial anode, so that the iron is protected by the zinc (aka cathodic protection). During galvanization, three alloys are formed: an iron-zinc alloy, a zinc-iron alloy and also a zinc alloy. The pre-treatment of the steel is crucially important in order to achieve a good bond. The following process steps are involved: degreasing, rinsing, pickling, re-rinsing, fl uxing, drying and hot-dipping. The coating thickness depends on the steel composition, the material thickness and the time spent in the zinc bath. In the galvanizing standard NEN-EN-ISO 1461, the minimum coating thickness are prescribed (as shown in following overview), just as the zinc shrinkage per year which will depend on environmental factors (see table entitled `Corrosion classes’). In addition, the zinc coating forms an excellent substrate for other post-treatments, such as applying a powder coating and coats of paint (better known as the duplex system). An added advantage of hot-dip galvanizing is that along the edges and pointy bits, where objects are usually extra susceptible to corrosion, the zinc coating is thicker because of the behaviour of the liquid. Minimum thicknesses of the zinc coating according to ISO 1461 - Using the hot-dip method Material thickness ≥ 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 85µm Material thickness ≥ 3 mm to < 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 70µm Material thickness ≥ 1,5 mm to < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 1,5 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm - Using the drum method Material thickness ≥ 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm |
|||||||||||
|
|
10945 |
CTI60-200-07-3DG |
DG
|
200
|
111.38
|
3
|
|
|
|||


Additional information
Finishing
Hot-dip galvanized (EN ISO 1461) DG (dipped-galvanised):
Whenever cable support systems are exposed to the elements and/or caustic substances (such as petrochemical applications), they are given an additional treatment in the form of hot-dip galvanizing. Hot-dip galvanizing is a materials science process designed to render the steel non-corroding. If this coating is breached, the zinc will act as a sacrifcial anode, so that the iron is protected by the zinc (aka cathodic protection). During galvanization, three alloys are formed: an iron-zinc alloy, a zinc-iron alloy and also a zinc alloy. The pre-treatment of the steel is crucially important in order to achieve a good bond. The following process steps are involved: degreasing, rinsing, pickling, re-rinsing, fl uxing, drying and hot-dipping. The coating thickness depends on the steel composition, the material thickness and the time spent in the zinc bath. In the galvanizing standard NEN-EN-ISO 1461, the minimum coating thickness are prescribed (as shown in following overview), just as the zinc shrinkage per year which will depend on environmental factors (see table entitled `Corrosion classes’). In addition, the zinc coating forms an excellent substrate for other post-treatments, such as applying a powder coating and coats of paint (better known as the duplex system). An added advantage of hot-dip galvanizing is that along the edges and pointy bits, where objects are usually extra susceptible to corrosion, the zinc coating is thicker because of the behaviour of the liquid. Minimum thicknesses of the zinc coating according to ISO 1461 - Using the hot-dip method Material thickness ≥ 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 85µm Material thickness ≥ 3 mm to < 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 70µm Material thickness ≥ 1,5 mm to < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 1,5 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm - Using the drum method Material thickness ≥ 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm |
|||||||||||
|
|
10462 |
CTI60-200-10-3DG |
DG
|
200
|
111.38
|
3
|
|
|
|||


Additional information
Finishing
Hot-dip galvanized (EN ISO 1461) DG (dipped-galvanised):
Whenever cable support systems are exposed to the elements and/or caustic substances (such as petrochemical applications), they are given an additional treatment in the form of hot-dip galvanizing. Hot-dip galvanizing is a materials science process designed to render the steel non-corroding. If this coating is breached, the zinc will act as a sacrifcial anode, so that the iron is protected by the zinc (aka cathodic protection). During galvanization, three alloys are formed: an iron-zinc alloy, a zinc-iron alloy and also a zinc alloy. The pre-treatment of the steel is crucially important in order to achieve a good bond. The following process steps are involved: degreasing, rinsing, pickling, re-rinsing, fl uxing, drying and hot-dipping. The coating thickness depends on the steel composition, the material thickness and the time spent in the zinc bath. In the galvanizing standard NEN-EN-ISO 1461, the minimum coating thickness are prescribed (as shown in following overview), just as the zinc shrinkage per year which will depend on environmental factors (see table entitled `Corrosion classes’). In addition, the zinc coating forms an excellent substrate for other post-treatments, such as applying a powder coating and coats of paint (better known as the duplex system). An added advantage of hot-dip galvanizing is that along the edges and pointy bits, where objects are usually extra susceptible to corrosion, the zinc coating is thicker because of the behaviour of the liquid. Minimum thicknesses of the zinc coating according to ISO 1461 - Using the hot-dip method Material thickness ≥ 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 85µm Material thickness ≥ 3 mm to < 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 70µm Material thickness ≥ 1,5 mm to < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 1,5 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm - Using the drum method Material thickness ≥ 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm |
|||||||||||
|
|
10946 |
CTI60-300-07-3DG |
DG
|
300
|
170.03
|
3
|
|
|
|||


Additional information
Finishing
Hot-dip galvanized (EN ISO 1461) DG (dipped-galvanised):
Whenever cable support systems are exposed to the elements and/or caustic substances (such as petrochemical applications), they are given an additional treatment in the form of hot-dip galvanizing. Hot-dip galvanizing is a materials science process designed to render the steel non-corroding. If this coating is breached, the zinc will act as a sacrifcial anode, so that the iron is protected by the zinc (aka cathodic protection). During galvanization, three alloys are formed: an iron-zinc alloy, a zinc-iron alloy and also a zinc alloy. The pre-treatment of the steel is crucially important in order to achieve a good bond. The following process steps are involved: degreasing, rinsing, pickling, re-rinsing, fl uxing, drying and hot-dipping. The coating thickness depends on the steel composition, the material thickness and the time spent in the zinc bath. In the galvanizing standard NEN-EN-ISO 1461, the minimum coating thickness are prescribed (as shown in following overview), just as the zinc shrinkage per year which will depend on environmental factors (see table entitled `Corrosion classes’). In addition, the zinc coating forms an excellent substrate for other post-treatments, such as applying a powder coating and coats of paint (better known as the duplex system). An added advantage of hot-dip galvanizing is that along the edges and pointy bits, where objects are usually extra susceptible to corrosion, the zinc coating is thicker because of the behaviour of the liquid. Minimum thicknesses of the zinc coating according to ISO 1461 - Using the hot-dip method Material thickness ≥ 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 85µm Material thickness ≥ 3 mm to < 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 70µm Material thickness ≥ 1,5 mm to < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 1,5 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm - Using the drum method Material thickness ≥ 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm |
|||||||||||
|
|
10463 |
CTI60-300-10-3DG |
DG
|
300
|
170.03
|
3
|
|
|
|||


Additional information
Finishing
Hot-dip galvanized (EN ISO 1461) DG (dipped-galvanised):
Whenever cable support systems are exposed to the elements and/or caustic substances (such as petrochemical applications), they are given an additional treatment in the form of hot-dip galvanizing. Hot-dip galvanizing is a materials science process designed to render the steel non-corroding. If this coating is breached, the zinc will act as a sacrifcial anode, so that the iron is protected by the zinc (aka cathodic protection). During galvanization, three alloys are formed: an iron-zinc alloy, a zinc-iron alloy and also a zinc alloy. The pre-treatment of the steel is crucially important in order to achieve a good bond. The following process steps are involved: degreasing, rinsing, pickling, re-rinsing, fl uxing, drying and hot-dipping. The coating thickness depends on the steel composition, the material thickness and the time spent in the zinc bath. In the galvanizing standard NEN-EN-ISO 1461, the minimum coating thickness are prescribed (as shown in following overview), just as the zinc shrinkage per year which will depend on environmental factors (see table entitled `Corrosion classes’). In addition, the zinc coating forms an excellent substrate for other post-treatments, such as applying a powder coating and coats of paint (better known as the duplex system). An added advantage of hot-dip galvanizing is that along the edges and pointy bits, where objects are usually extra susceptible to corrosion, the zinc coating is thicker because of the behaviour of the liquid. Minimum thicknesses of the zinc coating according to ISO 1461 - Using the hot-dip method Material thickness ≥ 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 85µm Material thickness ≥ 3 mm to < 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 70µm Material thickness ≥ 1,5 mm to < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 1,5 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm - Using the drum method Material thickness ≥ 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm |
|||||||||||
|
|
14905 |
CTI60-300-12-3DG |
DG
|
300
|
170.03
|
3
|
|
|
|||


Additional information
Finishing
Hot-dip galvanized (EN ISO 1461) DG (dipped-galvanised):
Whenever cable support systems are exposed to the elements and/or caustic substances (such as petrochemical applications), they are given an additional treatment in the form of hot-dip galvanizing. Hot-dip galvanizing is a materials science process designed to render the steel non-corroding. If this coating is breached, the zinc will act as a sacrifcial anode, so that the iron is protected by the zinc (aka cathodic protection). During galvanization, three alloys are formed: an iron-zinc alloy, a zinc-iron alloy and also a zinc alloy. The pre-treatment of the steel is crucially important in order to achieve a good bond. The following process steps are involved: degreasing, rinsing, pickling, re-rinsing, fl uxing, drying and hot-dipping. The coating thickness depends on the steel composition, the material thickness and the time spent in the zinc bath. In the galvanizing standard NEN-EN-ISO 1461, the minimum coating thickness are prescribed (as shown in following overview), just as the zinc shrinkage per year which will depend on environmental factors (see table entitled `Corrosion classes’). In addition, the zinc coating forms an excellent substrate for other post-treatments, such as applying a powder coating and coats of paint (better known as the duplex system). An added advantage of hot-dip galvanizing is that along the edges and pointy bits, where objects are usually extra susceptible to corrosion, the zinc coating is thicker because of the behaviour of the liquid. Minimum thicknesses of the zinc coating according to ISO 1461 - Using the hot-dip method Material thickness ≥ 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 85µm Material thickness ≥ 3 mm to < 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 70µm Material thickness ≥ 1,5 mm to < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 1,5 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm - Using the drum method Material thickness ≥ 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm |
|||||||||||
|
|
10453 |
CTI60-400-10-3DG |
DG
|
400
|
228.68
|
3
|
|
|
|||


Additional information
Finishing
Hot-dip galvanized (EN ISO 1461) DG (dipped-galvanised):
Whenever cable support systems are exposed to the elements and/or caustic substances (such as petrochemical applications), they are given an additional treatment in the form of hot-dip galvanizing. Hot-dip galvanizing is a materials science process designed to render the steel non-corroding. If this coating is breached, the zinc will act as a sacrifcial anode, so that the iron is protected by the zinc (aka cathodic protection). During galvanization, three alloys are formed: an iron-zinc alloy, a zinc-iron alloy and also a zinc alloy. The pre-treatment of the steel is crucially important in order to achieve a good bond. The following process steps are involved: degreasing, rinsing, pickling, re-rinsing, fl uxing, drying and hot-dipping. The coating thickness depends on the steel composition, the material thickness and the time spent in the zinc bath. In the galvanizing standard NEN-EN-ISO 1461, the minimum coating thickness are prescribed (as shown in following overview), just as the zinc shrinkage per year which will depend on environmental factors (see table entitled `Corrosion classes’). In addition, the zinc coating forms an excellent substrate for other post-treatments, such as applying a powder coating and coats of paint (better known as the duplex system). An added advantage of hot-dip galvanizing is that along the edges and pointy bits, where objects are usually extra susceptible to corrosion, the zinc coating is thicker because of the behaviour of the liquid. Minimum thicknesses of the zinc coating according to ISO 1461 - Using the hot-dip method Material thickness ≥ 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 85µm Material thickness ≥ 3 mm to < 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 70µm Material thickness ≥ 1,5 mm to < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 1,5 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm - Using the drum method Material thickness ≥ 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm |
|||||||||||
|
|
14906 |
CTI60-400-12-3DG |
DG
|
400
|
228.68
|
3
|
|
|
|||


Additional information
Finishing
Hot-dip galvanized (EN ISO 1461) DG (dipped-galvanised):
Whenever cable support systems are exposed to the elements and/or caustic substances (such as petrochemical applications), they are given an additional treatment in the form of hot-dip galvanizing. Hot-dip galvanizing is a materials science process designed to render the steel non-corroding. If this coating is breached, the zinc will act as a sacrifcial anode, so that the iron is protected by the zinc (aka cathodic protection). During galvanization, three alloys are formed: an iron-zinc alloy, a zinc-iron alloy and also a zinc alloy. The pre-treatment of the steel is crucially important in order to achieve a good bond. The following process steps are involved: degreasing, rinsing, pickling, re-rinsing, fl uxing, drying and hot-dipping. The coating thickness depends on the steel composition, the material thickness and the time spent in the zinc bath. In the galvanizing standard NEN-EN-ISO 1461, the minimum coating thickness are prescribed (as shown in following overview), just as the zinc shrinkage per year which will depend on environmental factors (see table entitled `Corrosion classes’). In addition, the zinc coating forms an excellent substrate for other post-treatments, such as applying a powder coating and coats of paint (better known as the duplex system). An added advantage of hot-dip galvanizing is that along the edges and pointy bits, where objects are usually extra susceptible to corrosion, the zinc coating is thicker because of the behaviour of the liquid. Minimum thicknesses of the zinc coating according to ISO 1461 - Using the hot-dip method Material thickness ≥ 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 85µm Material thickness ≥ 3 mm to < 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 70µm Material thickness ≥ 1,5 mm to < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 1,5 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm - Using the drum method Material thickness ≥ 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm |
|||||||||||
|
|
13460 |
CTI60-500-10-3DG |
DG
|
500
|
287.33
|
3
|
|
|
|||


Additional information
Finishing
Hot-dip galvanized (EN ISO 1461) DG (dipped-galvanised):
Whenever cable support systems are exposed to the elements and/or caustic substances (such as petrochemical applications), they are given an additional treatment in the form of hot-dip galvanizing. Hot-dip galvanizing is a materials science process designed to render the steel non-corroding. If this coating is breached, the zinc will act as a sacrifcial anode, so that the iron is protected by the zinc (aka cathodic protection). During galvanization, three alloys are formed: an iron-zinc alloy, a zinc-iron alloy and also a zinc alloy. The pre-treatment of the steel is crucially important in order to achieve a good bond. The following process steps are involved: degreasing, rinsing, pickling, re-rinsing, fl uxing, drying and hot-dipping. The coating thickness depends on the steel composition, the material thickness and the time spent in the zinc bath. In the galvanizing standard NEN-EN-ISO 1461, the minimum coating thickness are prescribed (as shown in following overview), just as the zinc shrinkage per year which will depend on environmental factors (see table entitled `Corrosion classes’). In addition, the zinc coating forms an excellent substrate for other post-treatments, such as applying a powder coating and coats of paint (better known as the duplex system). An added advantage of hot-dip galvanizing is that along the edges and pointy bits, where objects are usually extra susceptible to corrosion, the zinc coating is thicker because of the behaviour of the liquid. Minimum thicknesses of the zinc coating according to ISO 1461 - Using the hot-dip method Material thickness ≥ 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 85µm Material thickness ≥ 3 mm to < 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 70µm Material thickness ≥ 1,5 mm to < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 1,5 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm - Using the drum method Material thickness ≥ 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm |
|||||||||||
|
|
14907 |
CTI60-500-12-3DG |
DG
|
500
|
287.33
|
3
|
|
|
|||


Additional information
Finishing
Hot-dip galvanized (EN ISO 1461) DG (dipped-galvanised):
Whenever cable support systems are exposed to the elements and/or caustic substances (such as petrochemical applications), they are given an additional treatment in the form of hot-dip galvanizing. Hot-dip galvanizing is a materials science process designed to render the steel non-corroding. If this coating is breached, the zinc will act as a sacrifcial anode, so that the iron is protected by the zinc (aka cathodic protection). During galvanization, three alloys are formed: an iron-zinc alloy, a zinc-iron alloy and also a zinc alloy. The pre-treatment of the steel is crucially important in order to achieve a good bond. The following process steps are involved: degreasing, rinsing, pickling, re-rinsing, fl uxing, drying and hot-dipping. The coating thickness depends on the steel composition, the material thickness and the time spent in the zinc bath. In the galvanizing standard NEN-EN-ISO 1461, the minimum coating thickness are prescribed (as shown in following overview), just as the zinc shrinkage per year which will depend on environmental factors (see table entitled `Corrosion classes’). In addition, the zinc coating forms an excellent substrate for other post-treatments, such as applying a powder coating and coats of paint (better known as the duplex system). An added advantage of hot-dip galvanizing is that along the edges and pointy bits, where objects are usually extra susceptible to corrosion, the zinc coating is thicker because of the behaviour of the liquid. Minimum thicknesses of the zinc coating according to ISO 1461 - Using the hot-dip method Material thickness ≥ 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 85µm Material thickness ≥ 3 mm to < 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 70µm Material thickness ≥ 1,5 mm to < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 1,5 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm - Using the drum method Material thickness ≥ 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm |
|||||||||||
|
|
13474 |
CTI60-600-10-3DG |
DG
|
600
|
345.98
|
3
|
|
|
|||


Additional information
Finishing
Hot-dip galvanized (EN ISO 1461) DG (dipped-galvanised):
Whenever cable support systems are exposed to the elements and/or caustic substances (such as petrochemical applications), they are given an additional treatment in the form of hot-dip galvanizing. Hot-dip galvanizing is a materials science process designed to render the steel non-corroding. If this coating is breached, the zinc will act as a sacrifcial anode, so that the iron is protected by the zinc (aka cathodic protection). During galvanization, three alloys are formed: an iron-zinc alloy, a zinc-iron alloy and also a zinc alloy. The pre-treatment of the steel is crucially important in order to achieve a good bond. The following process steps are involved: degreasing, rinsing, pickling, re-rinsing, fl uxing, drying and hot-dipping. The coating thickness depends on the steel composition, the material thickness and the time spent in the zinc bath. In the galvanizing standard NEN-EN-ISO 1461, the minimum coating thickness are prescribed (as shown in following overview), just as the zinc shrinkage per year which will depend on environmental factors (see table entitled `Corrosion classes’). In addition, the zinc coating forms an excellent substrate for other post-treatments, such as applying a powder coating and coats of paint (better known as the duplex system). An added advantage of hot-dip galvanizing is that along the edges and pointy bits, where objects are usually extra susceptible to corrosion, the zinc coating is thicker because of the behaviour of the liquid. Minimum thicknesses of the zinc coating according to ISO 1461 - Using the hot-dip method Material thickness ≥ 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 85µm Material thickness ≥ 3 mm to < 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 70µm Material thickness ≥ 1,5 mm to < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 1,5 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm - Using the drum method Material thickness ≥ 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm |
|||||||||||
|
|
14908 |
CTI60-600-12-3DG |
DG
|
600
|
345.98
|
3
|
|
|
|||


Additional information
Finishing
Hot-dip galvanized (EN ISO 1461) DG (dipped-galvanised):
Whenever cable support systems are exposed to the elements and/or caustic substances (such as petrochemical applications), they are given an additional treatment in the form of hot-dip galvanizing. Hot-dip galvanizing is a materials science process designed to render the steel non-corroding. If this coating is breached, the zinc will act as a sacrifcial anode, so that the iron is protected by the zinc (aka cathodic protection). During galvanization, three alloys are formed: an iron-zinc alloy, a zinc-iron alloy and also a zinc alloy. The pre-treatment of the steel is crucially important in order to achieve a good bond. The following process steps are involved: degreasing, rinsing, pickling, re-rinsing, fl uxing, drying and hot-dipping. The coating thickness depends on the steel composition, the material thickness and the time spent in the zinc bath. In the galvanizing standard NEN-EN-ISO 1461, the minimum coating thickness are prescribed (as shown in following overview), just as the zinc shrinkage per year which will depend on environmental factors (see table entitled `Corrosion classes’). In addition, the zinc coating forms an excellent substrate for other post-treatments, such as applying a powder coating and coats of paint (better known as the duplex system). An added advantage of hot-dip galvanizing is that along the edges and pointy bits, where objects are usually extra susceptible to corrosion, the zinc coating is thicker because of the behaviour of the liquid. Minimum thicknesses of the zinc coating according to ISO 1461 - Using the hot-dip method Material thickness ≥ 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 85µm Material thickness ≥ 3 mm to < 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 70µm Material thickness ≥ 1,5 mm to < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 1,5 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm - Using the drum method Material thickness ≥ 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm |
|||||||||||
|
|
19399 |
CTI60-500-10-3UG |
UG
|
500
|
287.33
|
3
|
|
|
|||


Additional information
Finishing
ULTRA GALVA (UG)
This a high-performant metallic coating which offers an optimum surface protection in a wide variety of agressive and demanding environments, indoor as well as outdoor. The unique alloy of small amounts of magnesium and/or aluminium in the zinc bath provides ULTRA protection with a self-healing effect. Whilst zinc is essential for cathodic protection, magnesium prevents red rust. The passivation layer that comes on top, creates a seal that slows down the first traces of white rust. ULTRA GALVA offers a number of advantages compared to the traditional hot dip finishing. - the passivation layer offers a superior protection level. Hence, ULTRA GALVA, being cathodical, is self-healing in case of scratches, edges or perforations. Compared to hot dip, the articles remain very straight, no deflections appear nor flux or dull spots/ashes - ULTRA GALVA can conveniently be cold-processed without any risk on flakes because of the perfect adhesion of the coating to the metal - no zinc pins appear which enables one to install cables in a fast way avoiding any risk on damages to cables nor injuries of workers - thanks to the longer life span, ULTRA GALVA does not require ongoing maintenance nor post painting actions - three times less zinc is being applied compared to hot dip finishing - there is hence a lower impact on natural ressources as well as less pollution -on top, its production process generates less CO2 emission and ULTRA GALVA is 100% recyclable. ULTRA GALVA is hence a vary valuable environmentally friendly alternative for the traditional stainless steel and hot-dip finishing! |
|||||||||||
|
|
19400 |
CTI60-600-10-3UG |
UG
|
600
|
345.98
|
3
|
|
|
|||


Additional information
Finishing
ULTRA GALVA (UG)
This a high-performant metallic coating which offers an optimum surface protection in a wide variety of agressive and demanding environments, indoor as well as outdoor. The unique alloy of small amounts of magnesium and/or aluminium in the zinc bath provides ULTRA protection with a self-healing effect. Whilst zinc is essential for cathodic protection, magnesium prevents red rust. The passivation layer that comes on top, creates a seal that slows down the first traces of white rust. ULTRA GALVA offers a number of advantages compared to the traditional hot dip finishing. - the passivation layer offers a superior protection level. Hence, ULTRA GALVA, being cathodical, is self-healing in case of scratches, edges or perforations. Compared to hot dip, the articles remain very straight, no deflections appear nor flux or dull spots/ashes - ULTRA GALVA can conveniently be cold-processed without any risk on flakes because of the perfect adhesion of the coating to the metal - no zinc pins appear which enables one to install cables in a fast way avoiding any risk on damages to cables nor injuries of workers - thanks to the longer life span, ULTRA GALVA does not require ongoing maintenance nor post painting actions - three times less zinc is being applied compared to hot dip finishing - there is hence a lower impact on natural ressources as well as less pollution -on top, its production process generates less CO2 emission and ULTRA GALVA is 100% recyclable. ULTRA GALVA is hence a vary valuable environmentally friendly alternative for the traditional stainless steel and hot-dip finishing! |
|||||||||||
|
|
20472 |
CTI60-100-10-3UG |
UG
|
100
|
52.73
|
3
|
Default
|
|
|||


Additional information
Finishing
ULTRA GALVA (UG)
This a high-performant metallic coating which offers an optimum surface protection in a wide variety of agressive and demanding environments, indoor as well as outdoor. The unique alloy of small amounts of magnesium and/or aluminium in the zinc bath provides ULTRA protection with a self-healing effect. Whilst zinc is essential for cathodic protection, magnesium prevents red rust. The passivation layer that comes on top, creates a seal that slows down the first traces of white rust. ULTRA GALVA offers a number of advantages compared to the traditional hot dip finishing. - the passivation layer offers a superior protection level. Hence, ULTRA GALVA, being cathodical, is self-healing in case of scratches, edges or perforations. Compared to hot dip, the articles remain very straight, no deflections appear nor flux or dull spots/ashes - ULTRA GALVA can conveniently be cold-processed without any risk on flakes because of the perfect adhesion of the coating to the metal - no zinc pins appear which enables one to install cables in a fast way avoiding any risk on damages to cables nor injuries of workers - thanks to the longer life span, ULTRA GALVA does not require ongoing maintenance nor post painting actions - three times less zinc is being applied compared to hot dip finishing - there is hence a lower impact on natural ressources as well as less pollution -on top, its production process generates less CO2 emission and ULTRA GALVA is 100% recyclable. ULTRA GALVA is hence a vary valuable environmentally friendly alternative for the traditional stainless steel and hot-dip finishing! |
|||||||||||
|
|
20561 |
CTI60-200-10-3UG |
UG
|
200
|
111.38
|
3
|
Default
|
|
|||


Additional information
Finishing
ULTRA GALVA (UG)
This a high-performant metallic coating which offers an optimum surface protection in a wide variety of agressive and demanding environments, indoor as well as outdoor. The unique alloy of small amounts of magnesium and/or aluminium in the zinc bath provides ULTRA protection with a self-healing effect. Whilst zinc is essential for cathodic protection, magnesium prevents red rust. The passivation layer that comes on top, creates a seal that slows down the first traces of white rust. ULTRA GALVA offers a number of advantages compared to the traditional hot dip finishing. - the passivation layer offers a superior protection level. Hence, ULTRA GALVA, being cathodical, is self-healing in case of scratches, edges or perforations. Compared to hot dip, the articles remain very straight, no deflections appear nor flux or dull spots/ashes - ULTRA GALVA can conveniently be cold-processed without any risk on flakes because of the perfect adhesion of the coating to the metal - no zinc pins appear which enables one to install cables in a fast way avoiding any risk on damages to cables nor injuries of workers - thanks to the longer life span, ULTRA GALVA does not require ongoing maintenance nor post painting actions - three times less zinc is being applied compared to hot dip finishing - there is hence a lower impact on natural ressources as well as less pollution -on top, its production process generates less CO2 emission and ULTRA GALVA is 100% recyclable. ULTRA GALVA is hence a vary valuable environmentally friendly alternative for the traditional stainless steel and hot-dip finishing! |
|||||||||||
|
|
20880 |
CTI60-300-10-3UG |
UG
|
300
|
170.03
|
3
|
Default
|
|
|||


Additional information
Finishing
ULTRA GALVA (UG)
This a high-performant metallic coating which offers an optimum surface protection in a wide variety of agressive and demanding environments, indoor as well as outdoor. The unique alloy of small amounts of magnesium and/or aluminium in the zinc bath provides ULTRA protection with a self-healing effect. Whilst zinc is essential for cathodic protection, magnesium prevents red rust. The passivation layer that comes on top, creates a seal that slows down the first traces of white rust. ULTRA GALVA offers a number of advantages compared to the traditional hot dip finishing. - the passivation layer offers a superior protection level. Hence, ULTRA GALVA, being cathodical, is self-healing in case of scratches, edges or perforations. Compared to hot dip, the articles remain very straight, no deflections appear nor flux or dull spots/ashes - ULTRA GALVA can conveniently be cold-processed without any risk on flakes because of the perfect adhesion of the coating to the metal - no zinc pins appear which enables one to install cables in a fast way avoiding any risk on damages to cables nor injuries of workers - thanks to the longer life span, ULTRA GALVA does not require ongoing maintenance nor post painting actions - three times less zinc is being applied compared to hot dip finishing - there is hence a lower impact on natural ressources as well as less pollution -on top, its production process generates less CO2 emission and ULTRA GALVA is 100% recyclable. ULTRA GALVA is hence a vary valuable environmentally friendly alternative for the traditional stainless steel and hot-dip finishing! |
|||||||||||
|
|
20685 |
CTI60-400-10-3UG |
UG
|
400
|
228.68
|
3
|
Default
|
|
|||


Additional information
Finishing
ULTRA GALVA (UG)
This a high-performant metallic coating which offers an optimum surface protection in a wide variety of agressive and demanding environments, indoor as well as outdoor. The unique alloy of small amounts of magnesium and/or aluminium in the zinc bath provides ULTRA protection with a self-healing effect. Whilst zinc is essential for cathodic protection, magnesium prevents red rust. The passivation layer that comes on top, creates a seal that slows down the first traces of white rust. ULTRA GALVA offers a number of advantages compared to the traditional hot dip finishing. - the passivation layer offers a superior protection level. Hence, ULTRA GALVA, being cathodical, is self-healing in case of scratches, edges or perforations. Compared to hot dip, the articles remain very straight, no deflections appear nor flux or dull spots/ashes - ULTRA GALVA can conveniently be cold-processed without any risk on flakes because of the perfect adhesion of the coating to the metal - no zinc pins appear which enables one to install cables in a fast way avoiding any risk on damages to cables nor injuries of workers - thanks to the longer life span, ULTRA GALVA does not require ongoing maintenance nor post painting actions - three times less zinc is being applied compared to hot dip finishing - there is hence a lower impact on natural ressources as well as less pollution -on top, its production process generates less CO2 emission and ULTRA GALVA is 100% recyclable. ULTRA GALVA is hence a vary valuable environmentally friendly alternative for the traditional stainless steel and hot-dip finishing! |
|||||||||||
No results
No results were found for your current search