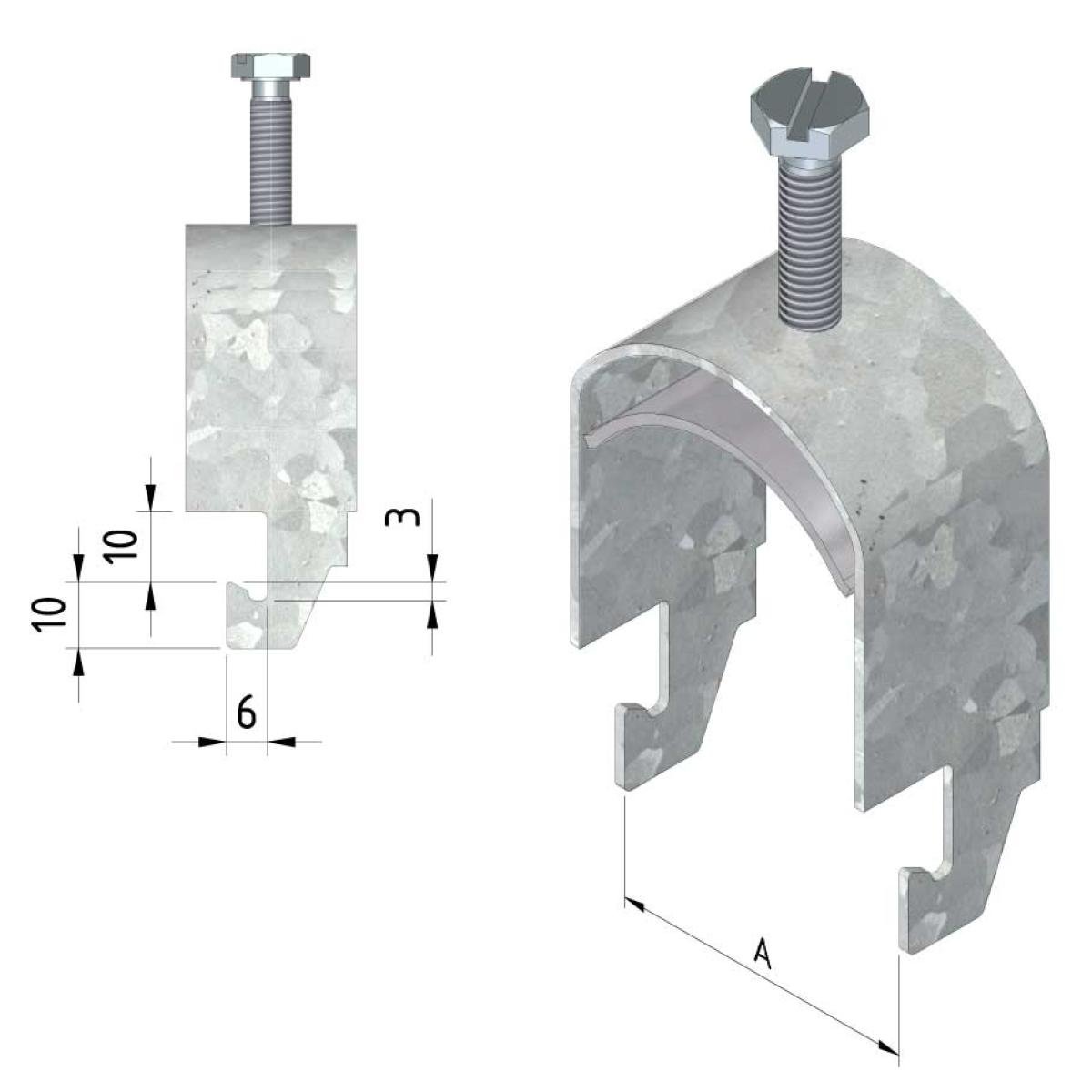
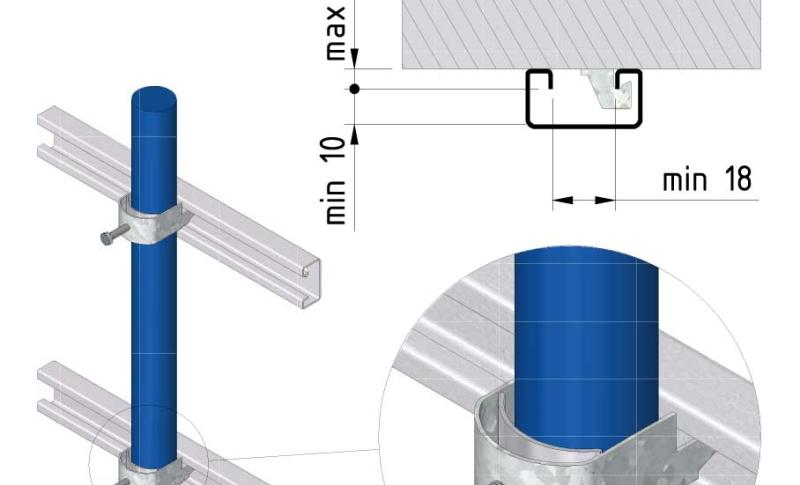
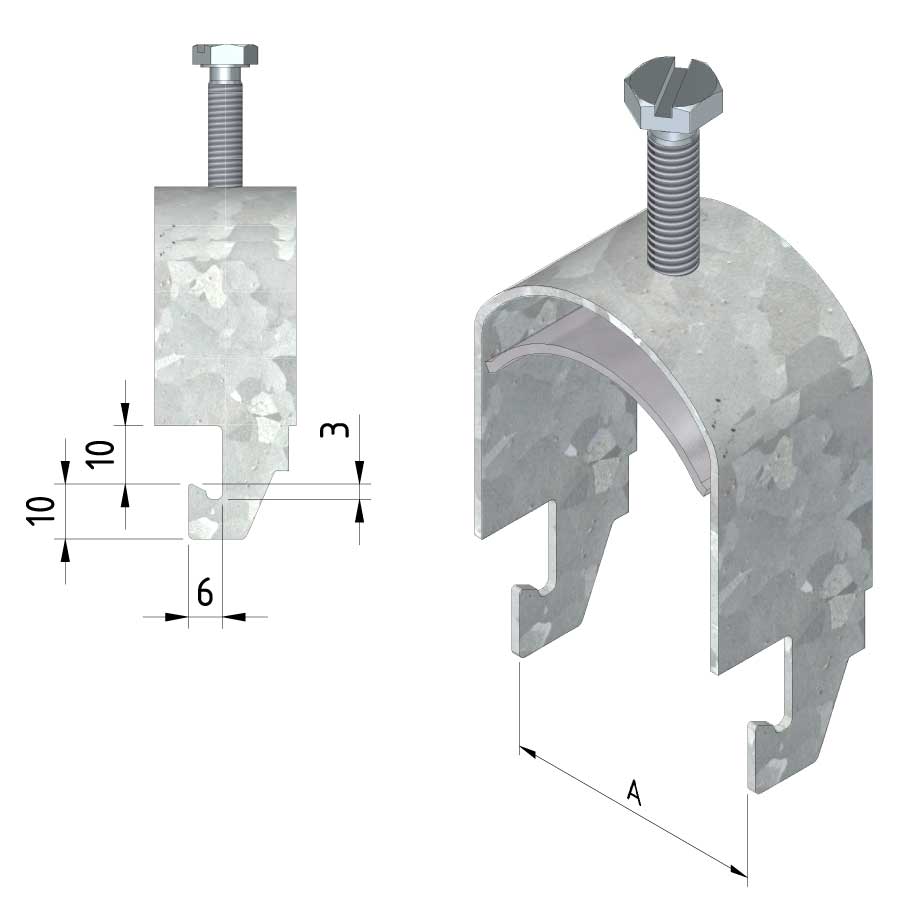
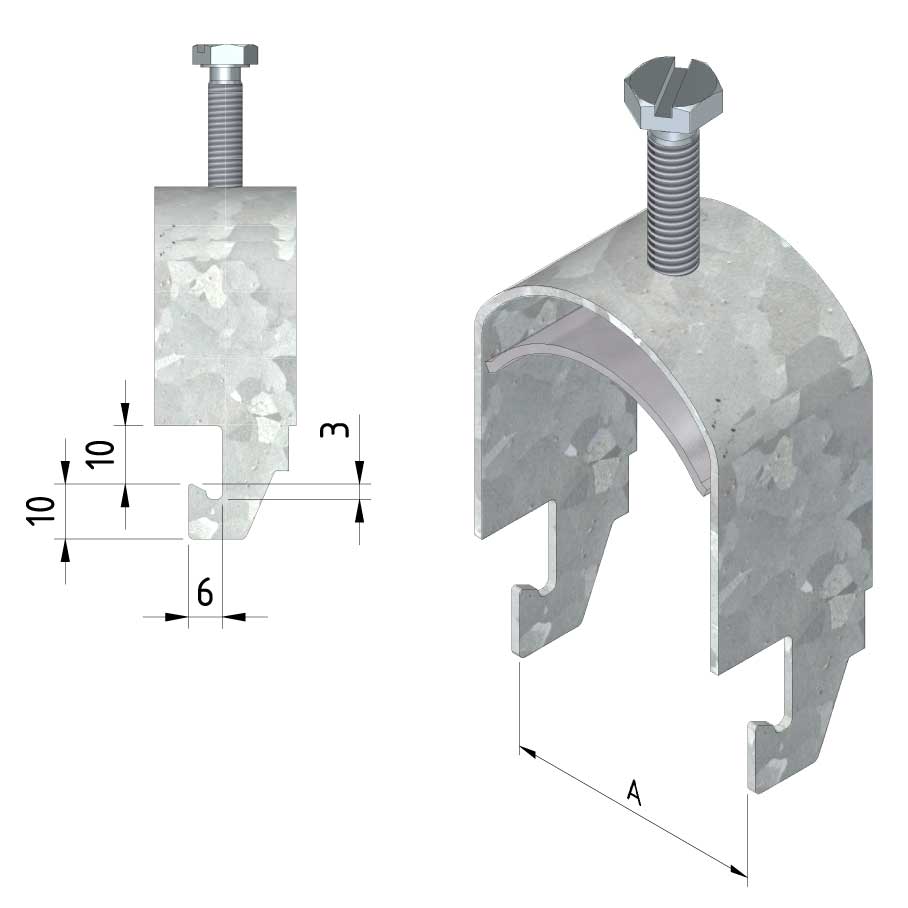
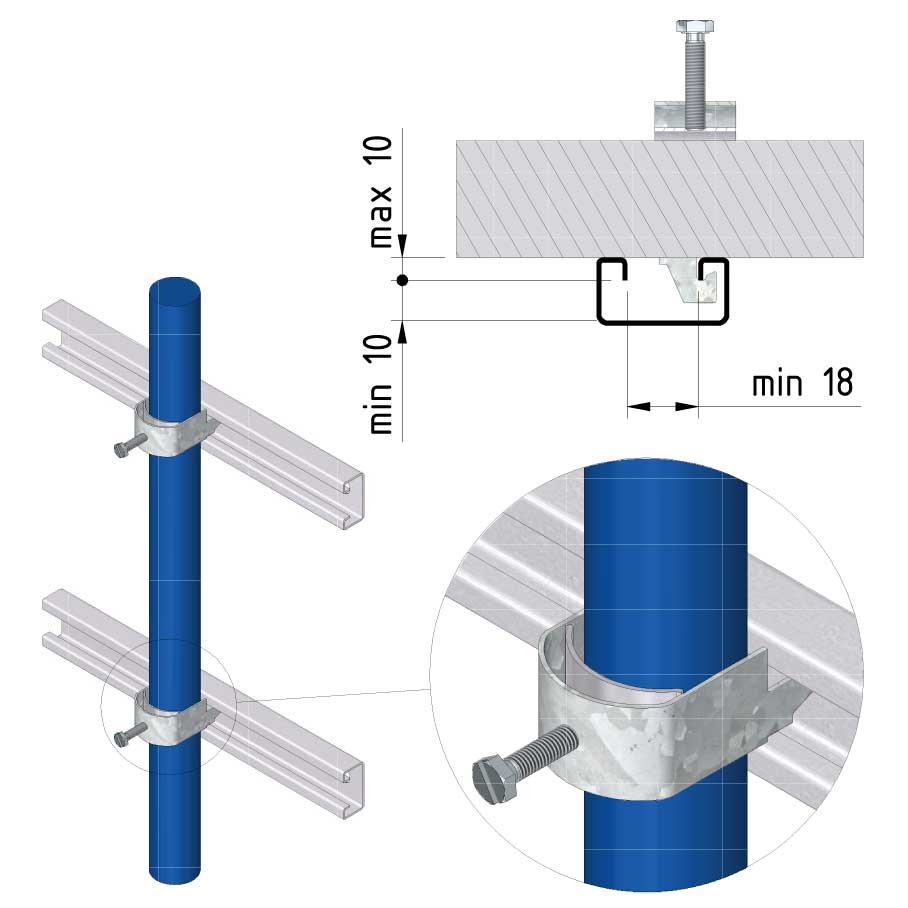
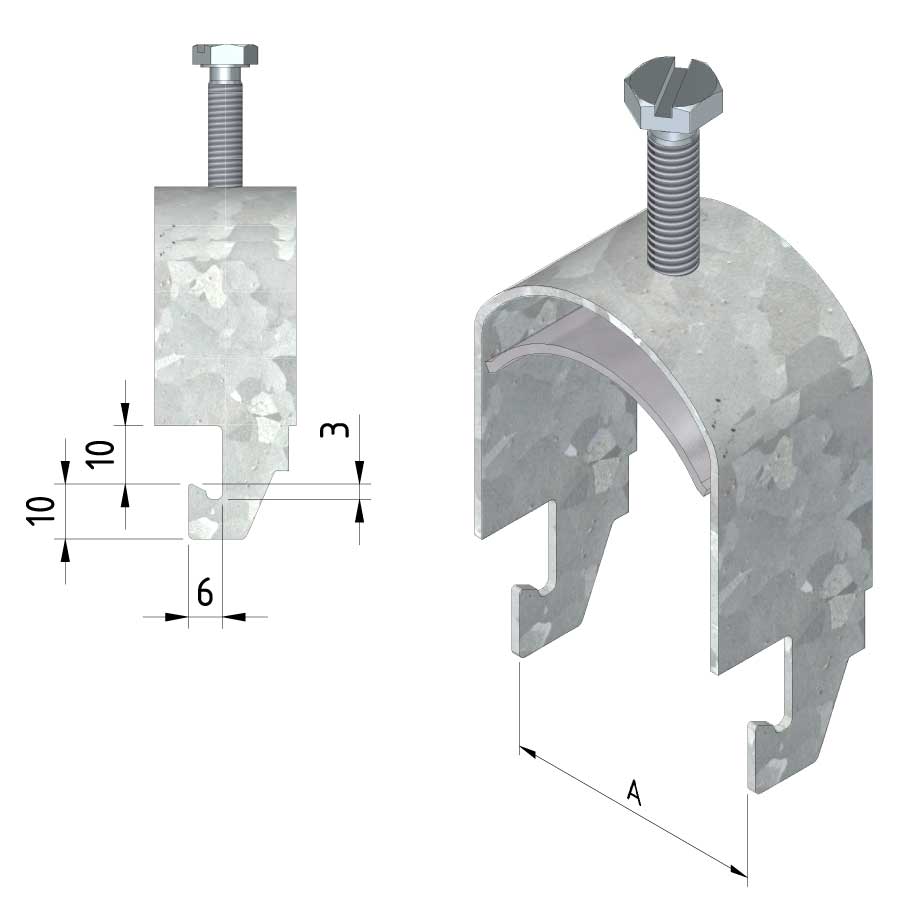
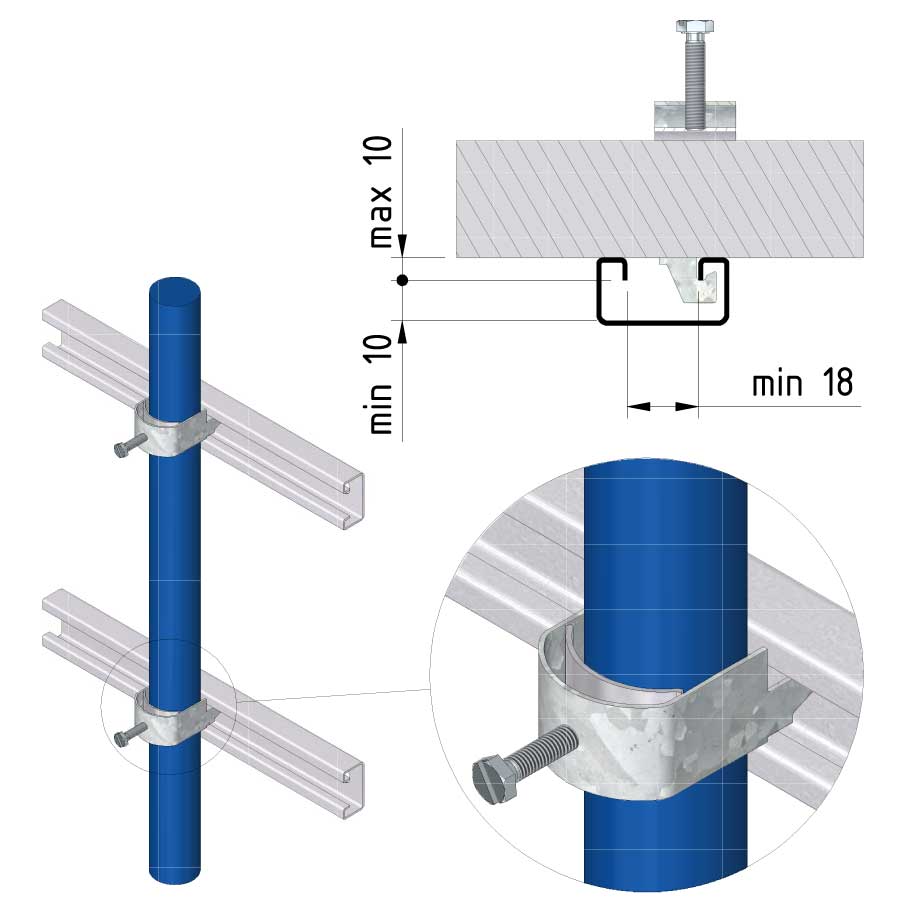
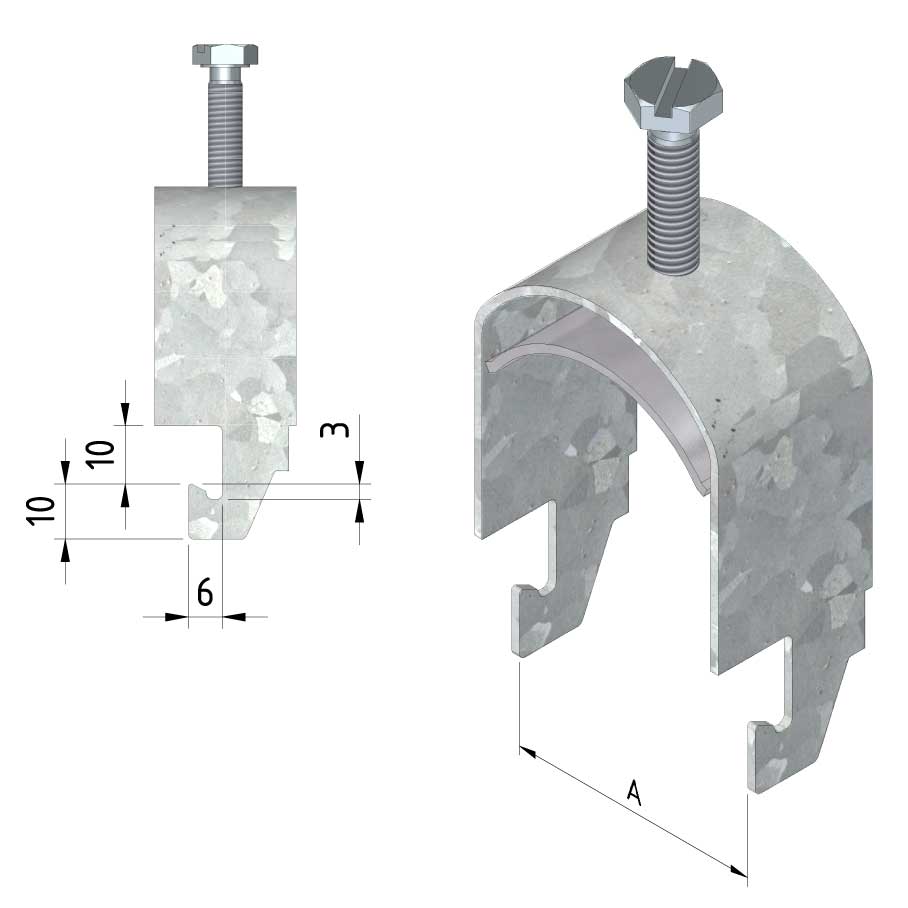
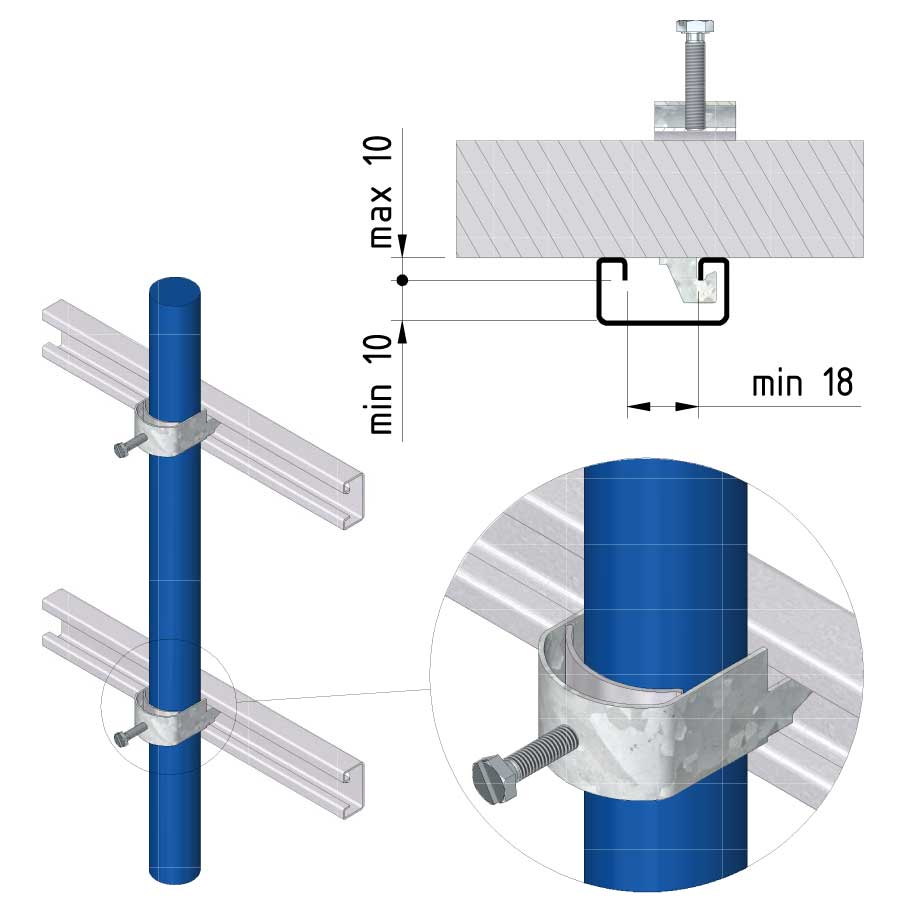
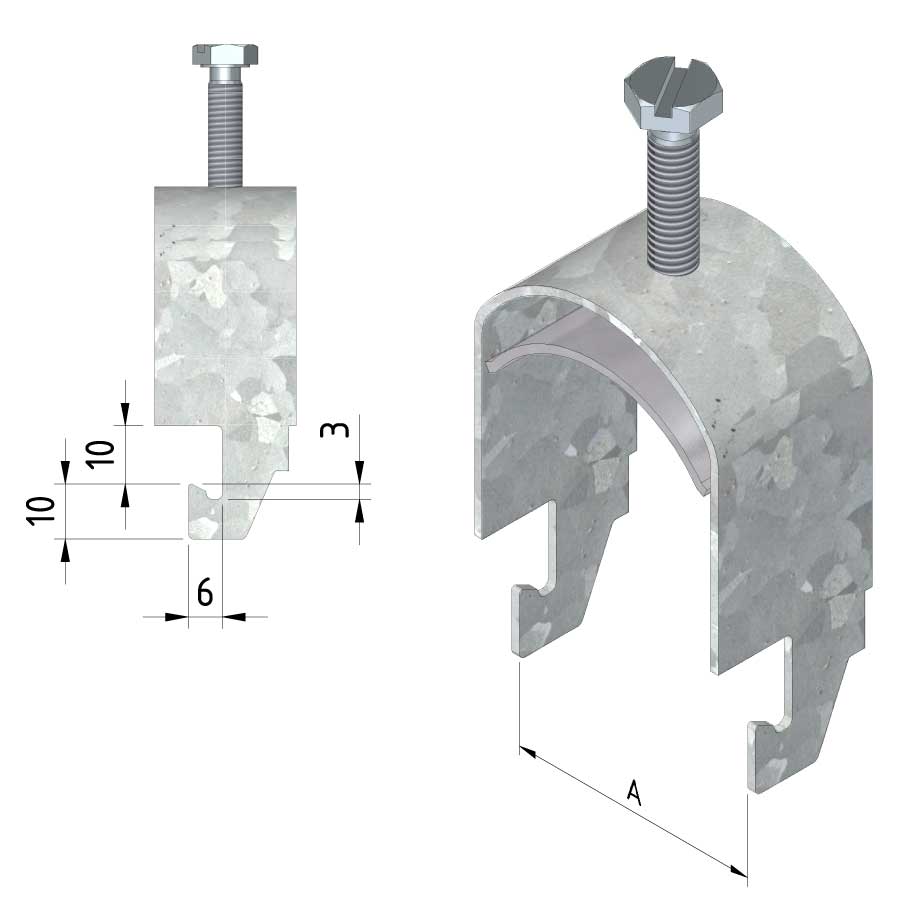
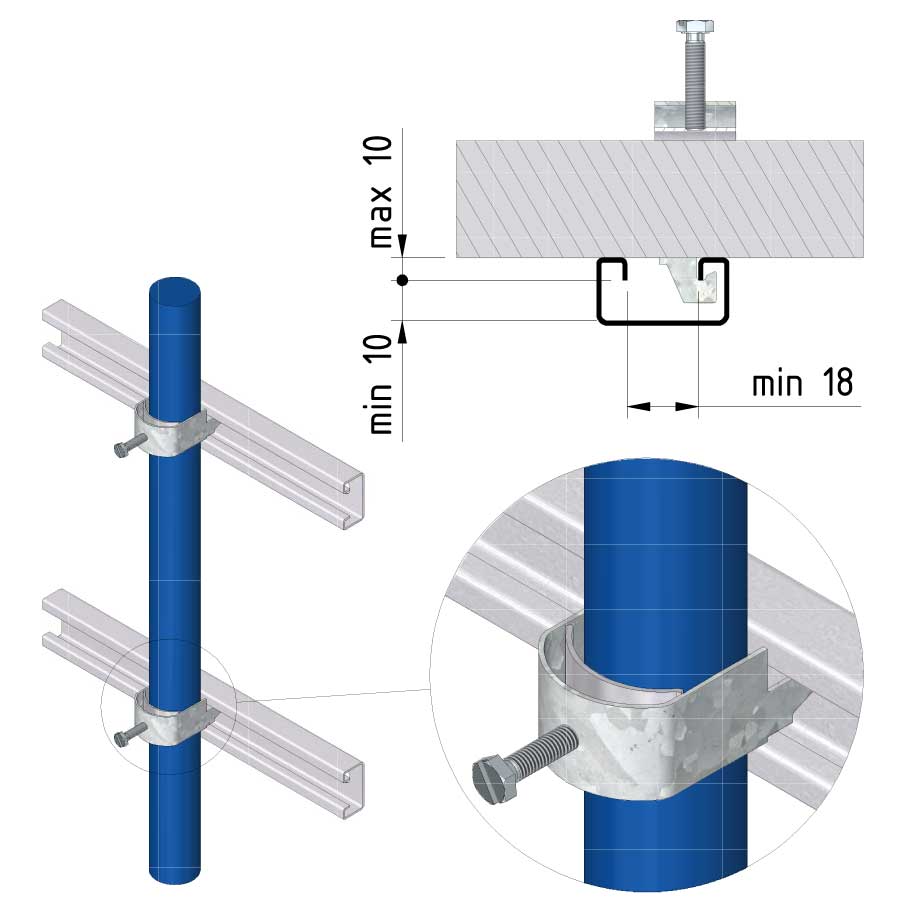
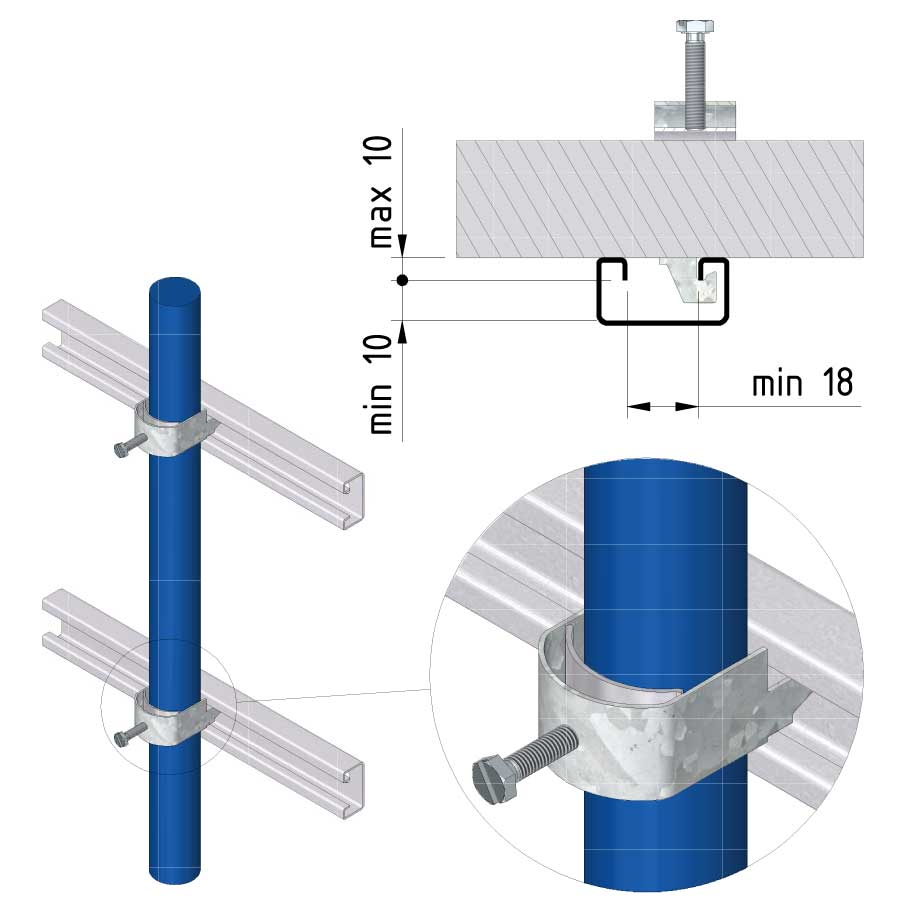
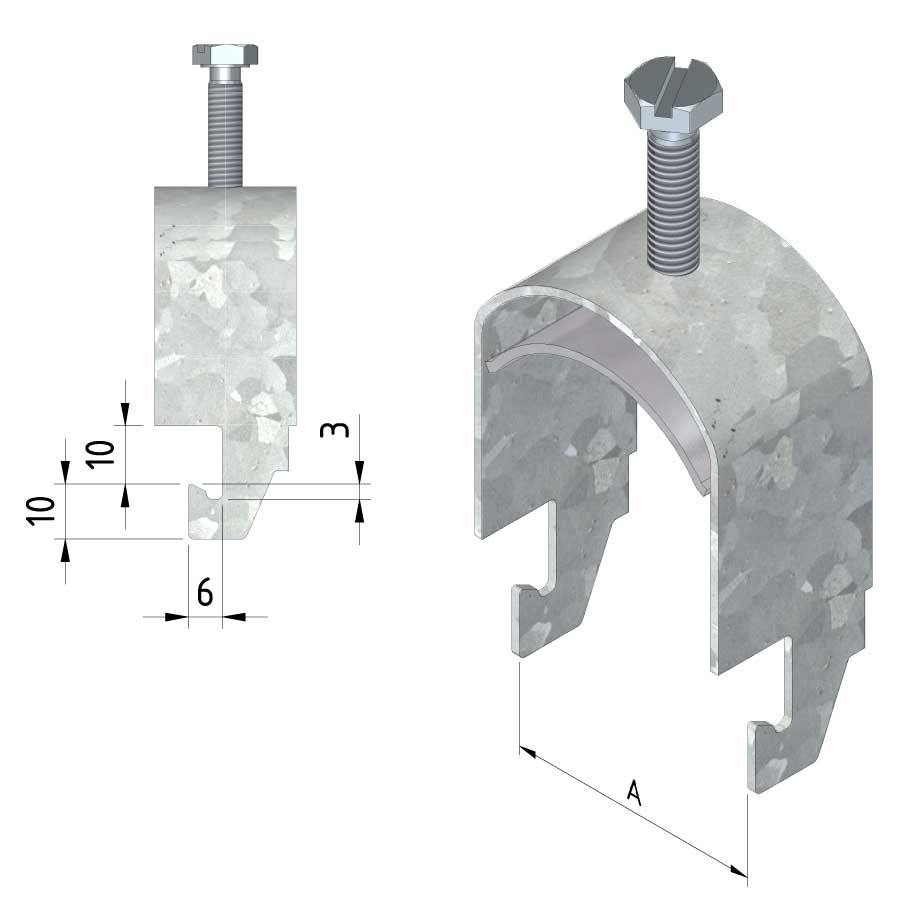
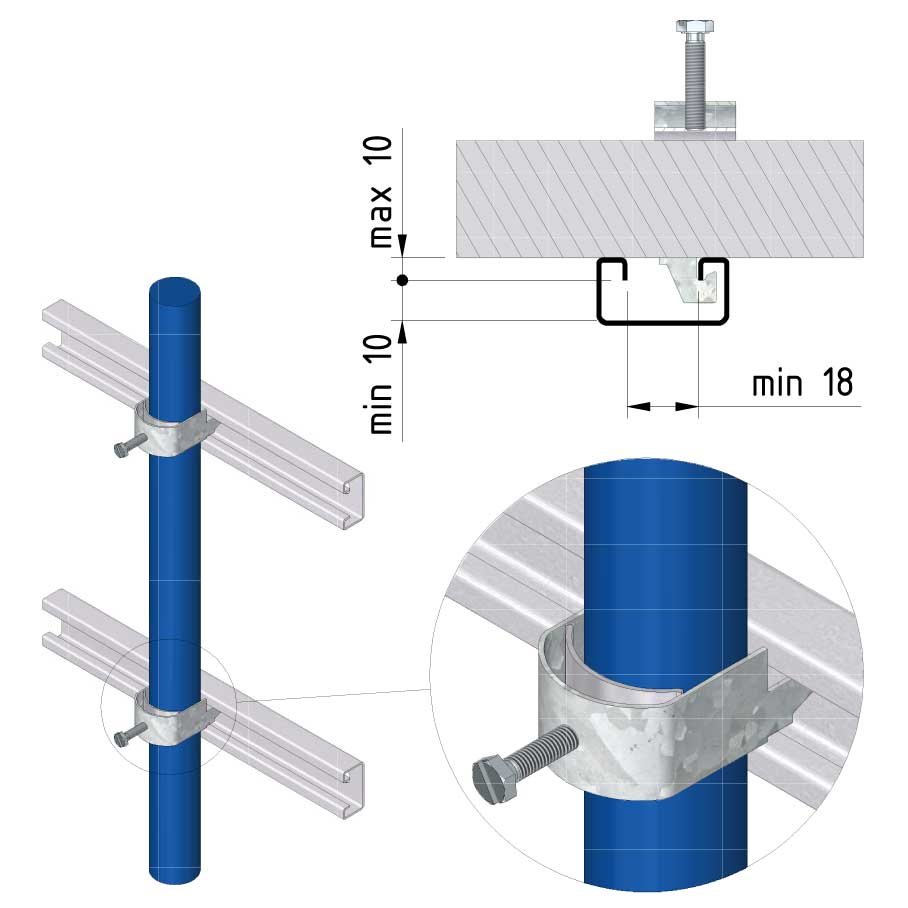
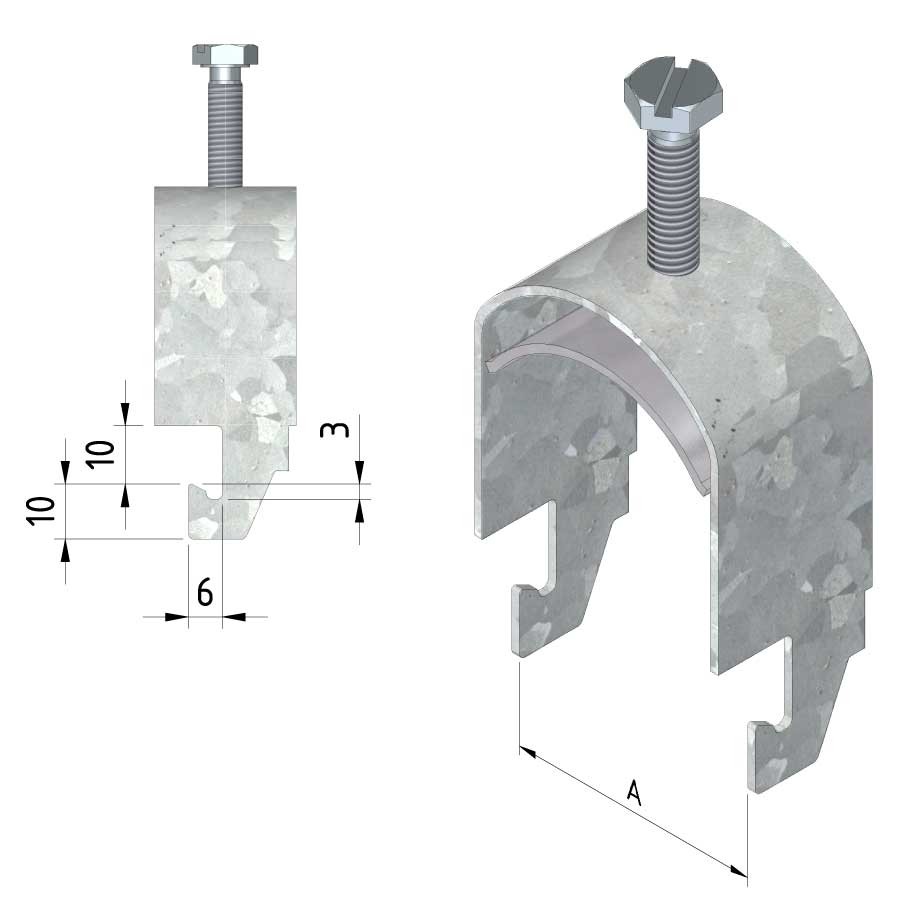
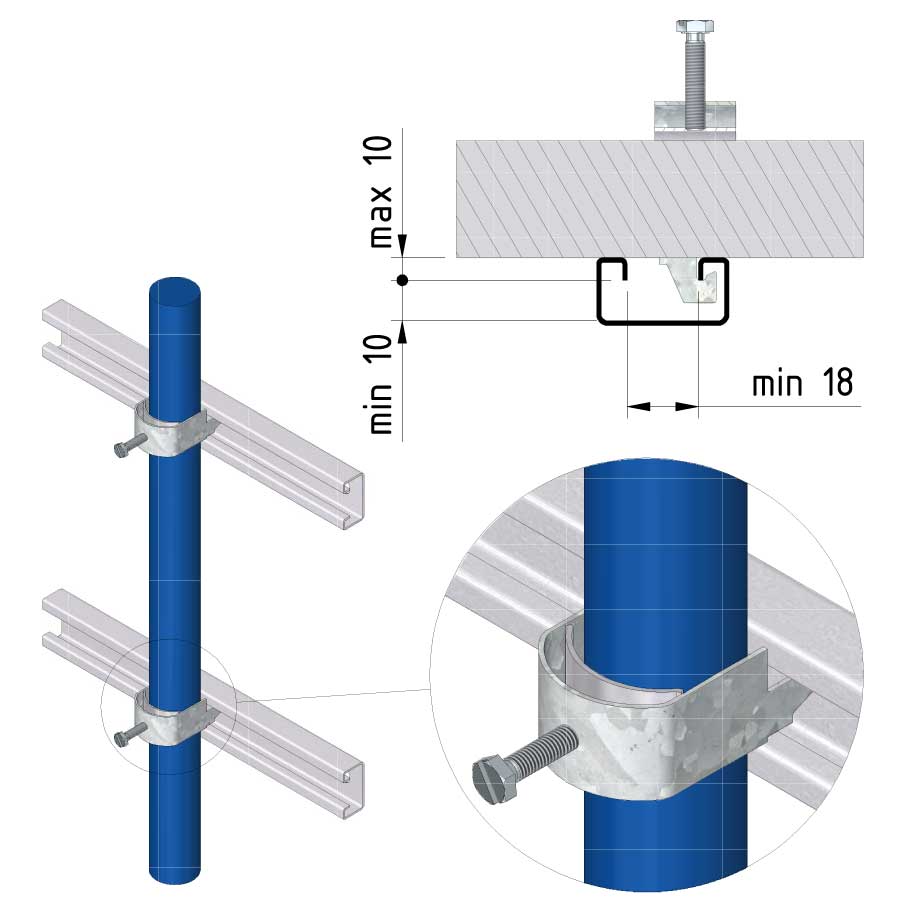
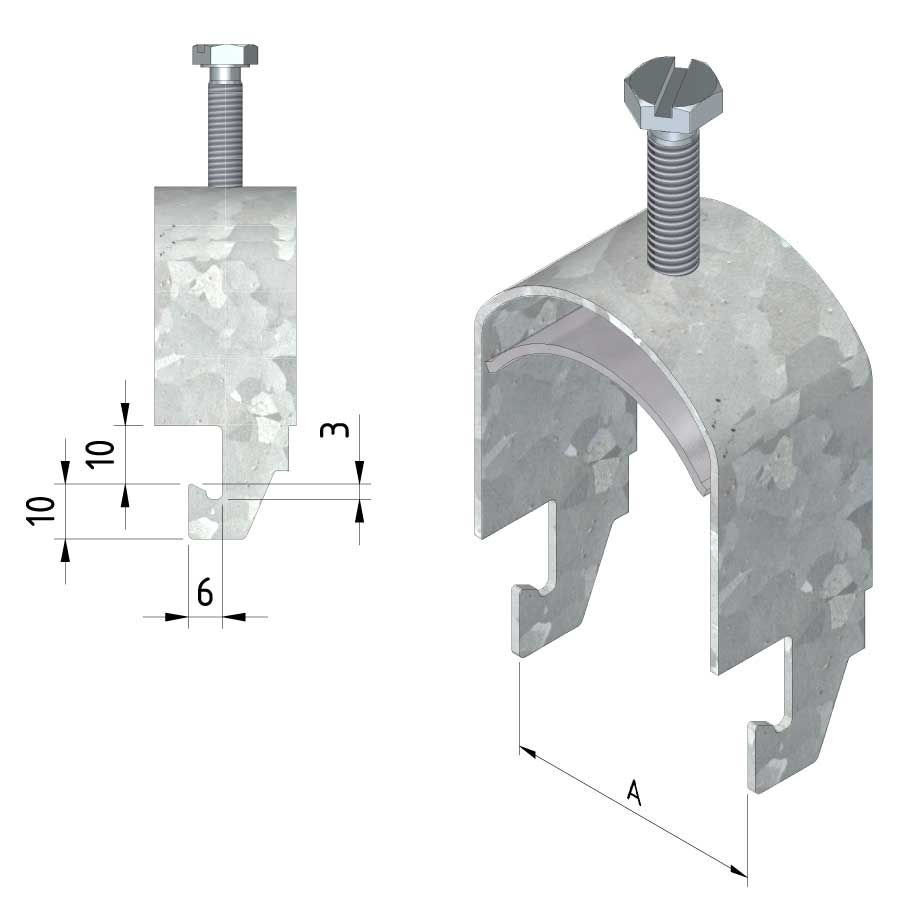
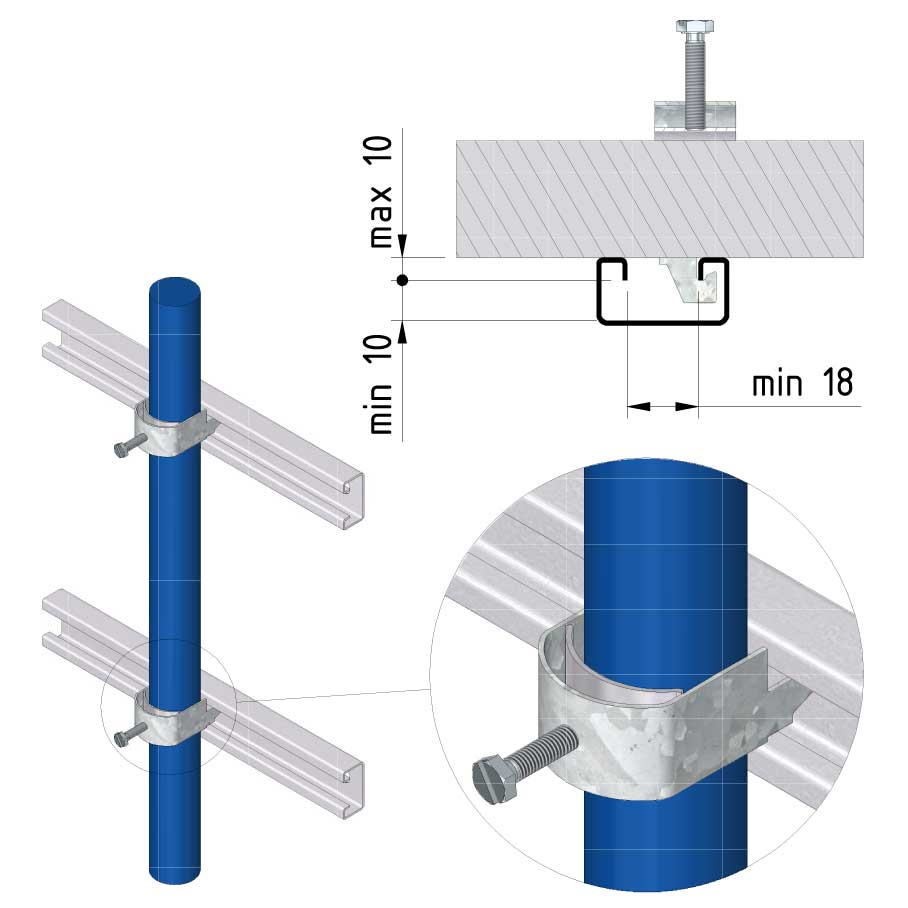
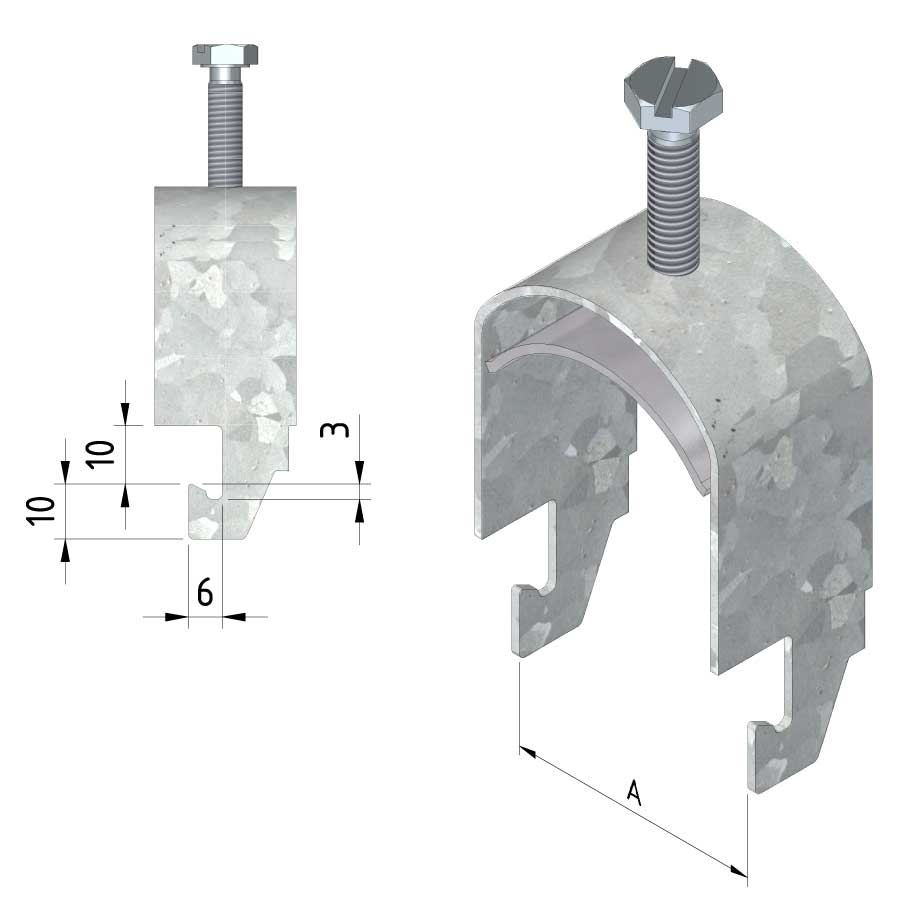
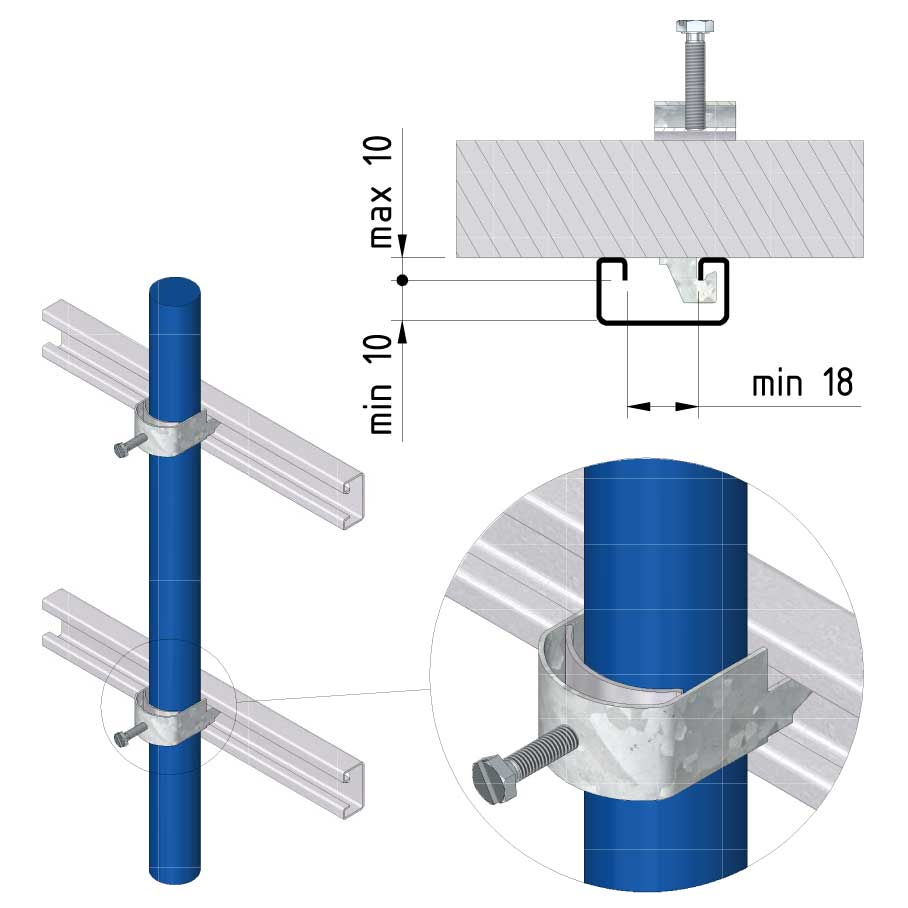
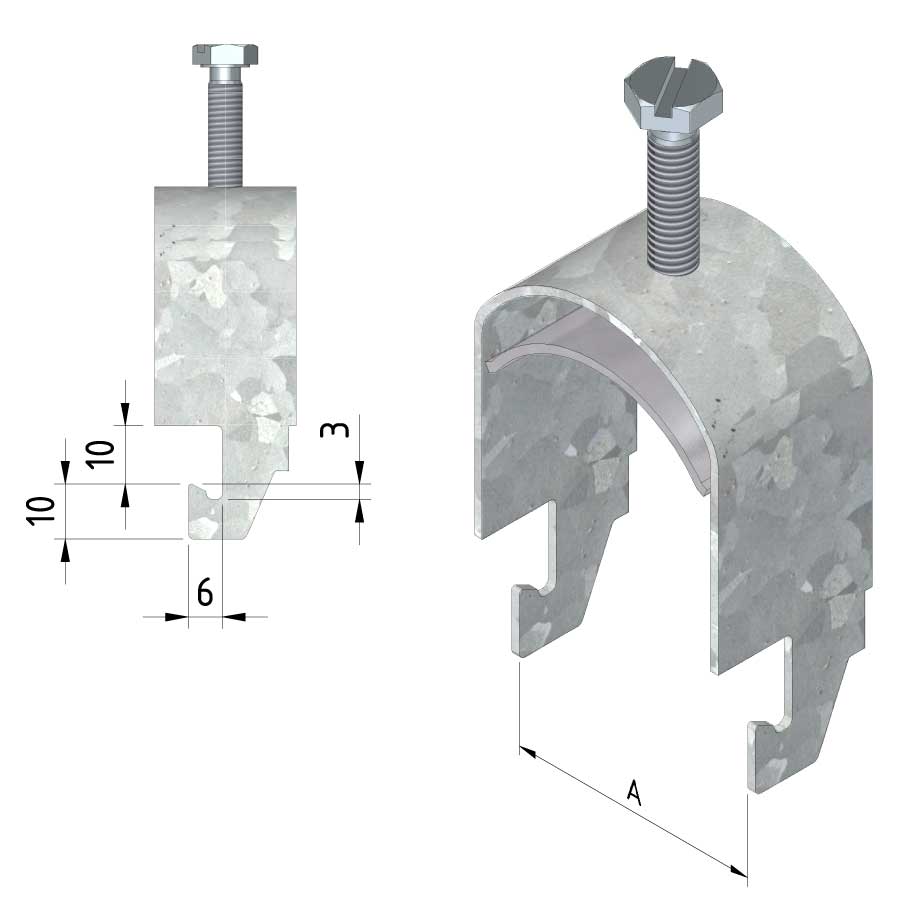
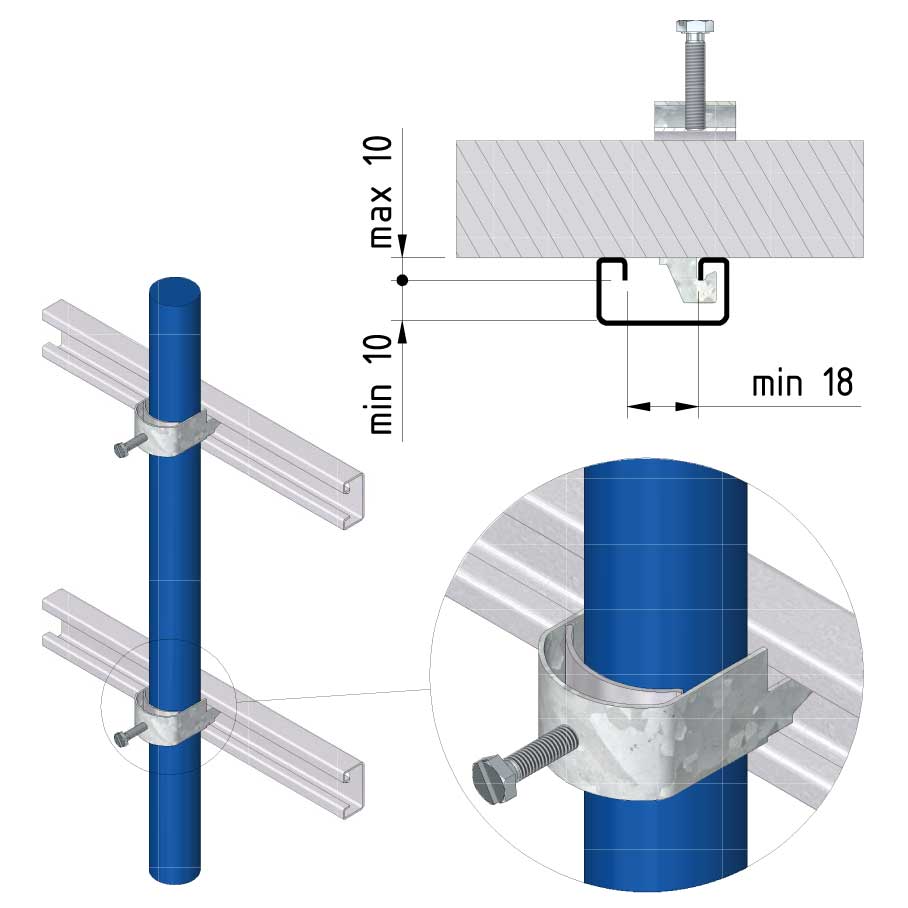
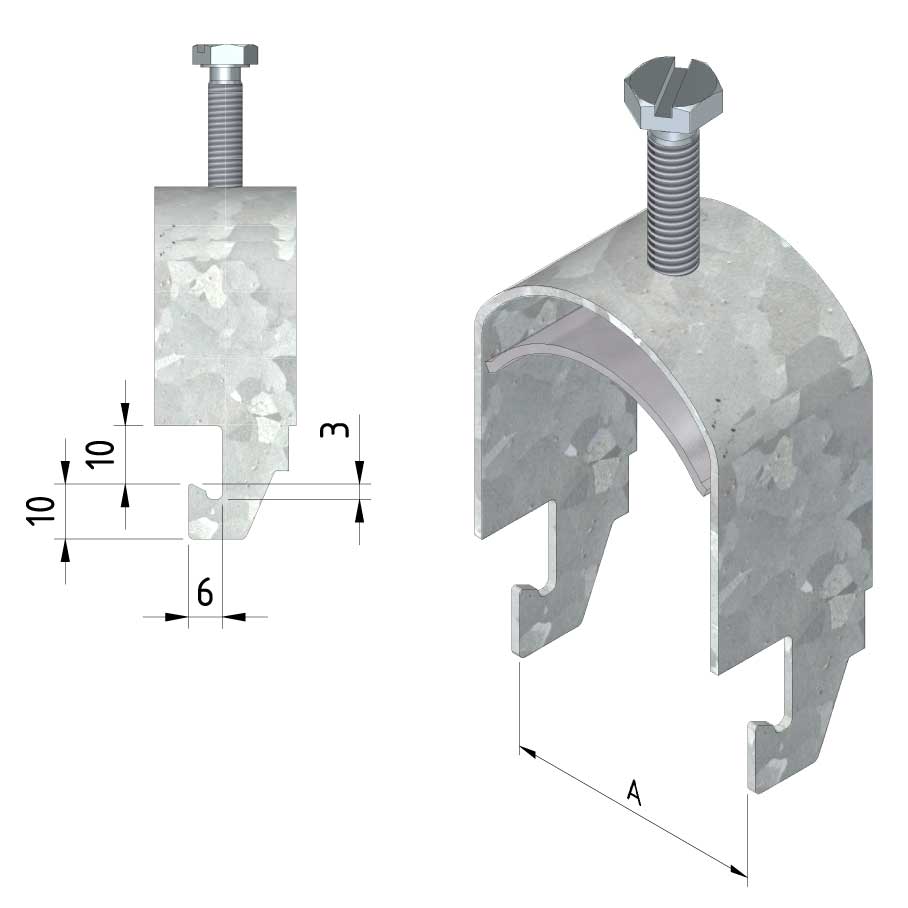
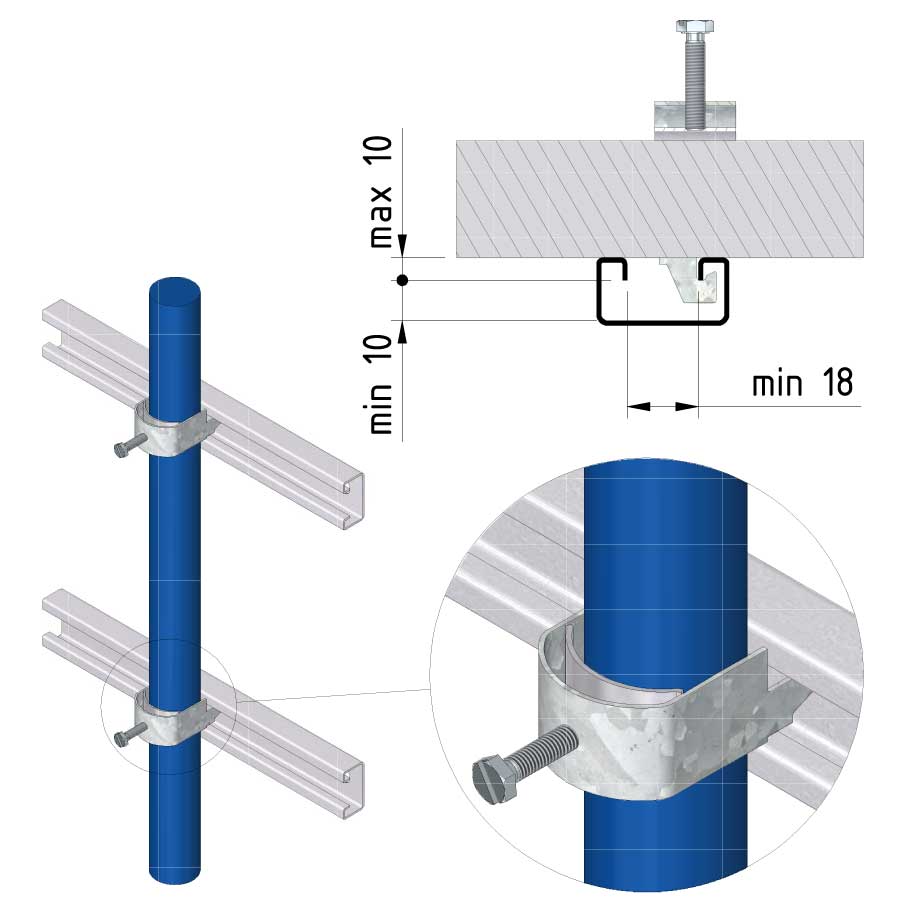
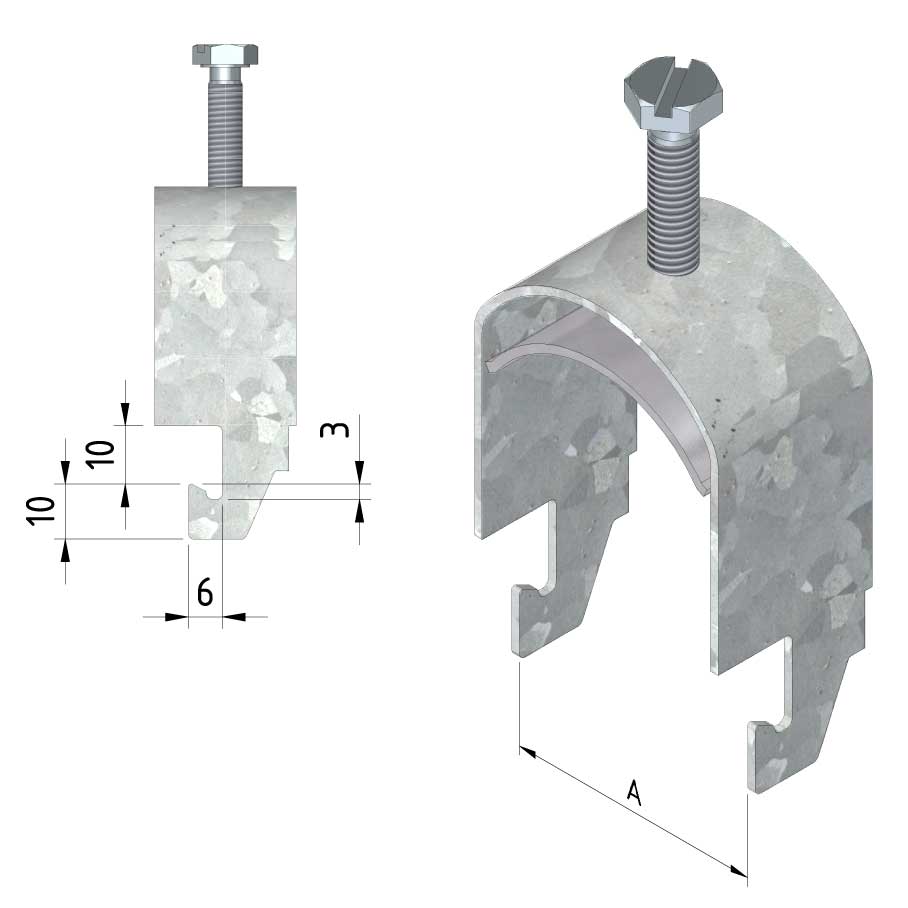
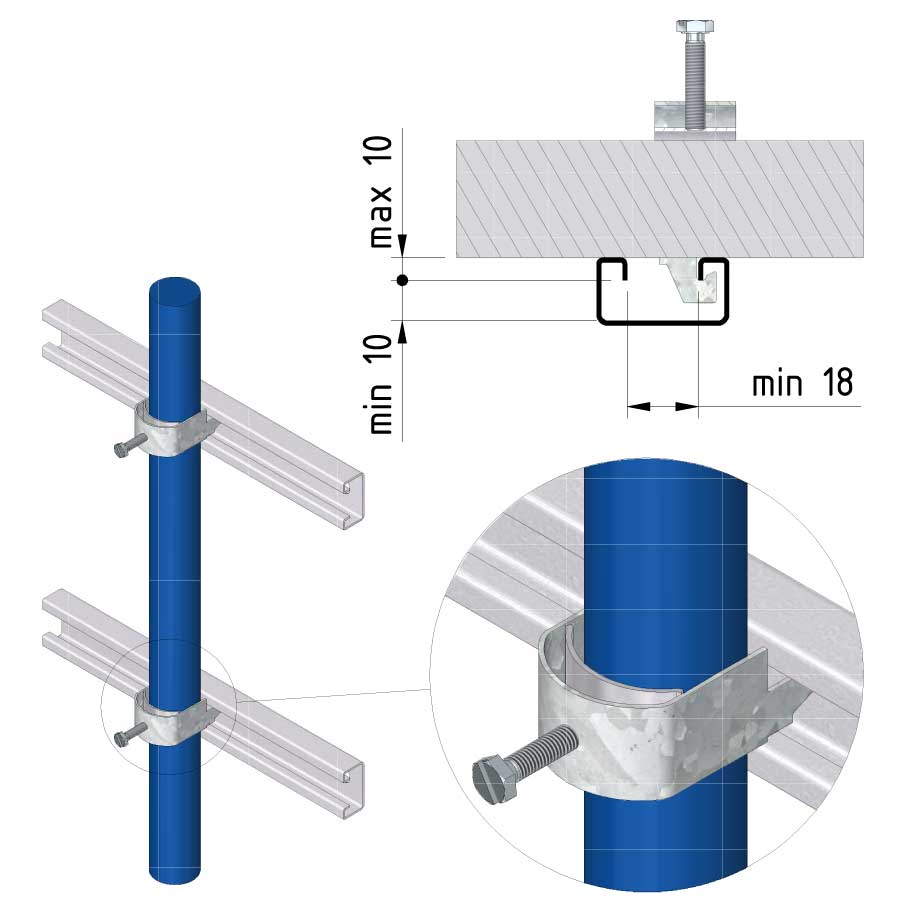
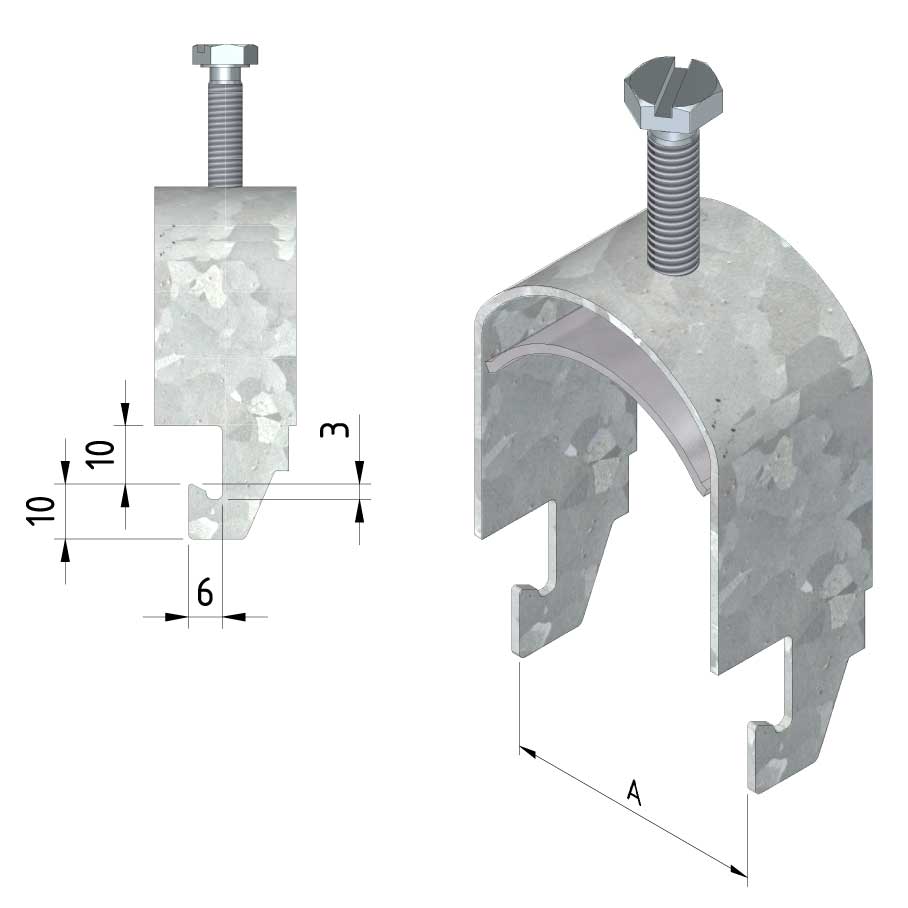
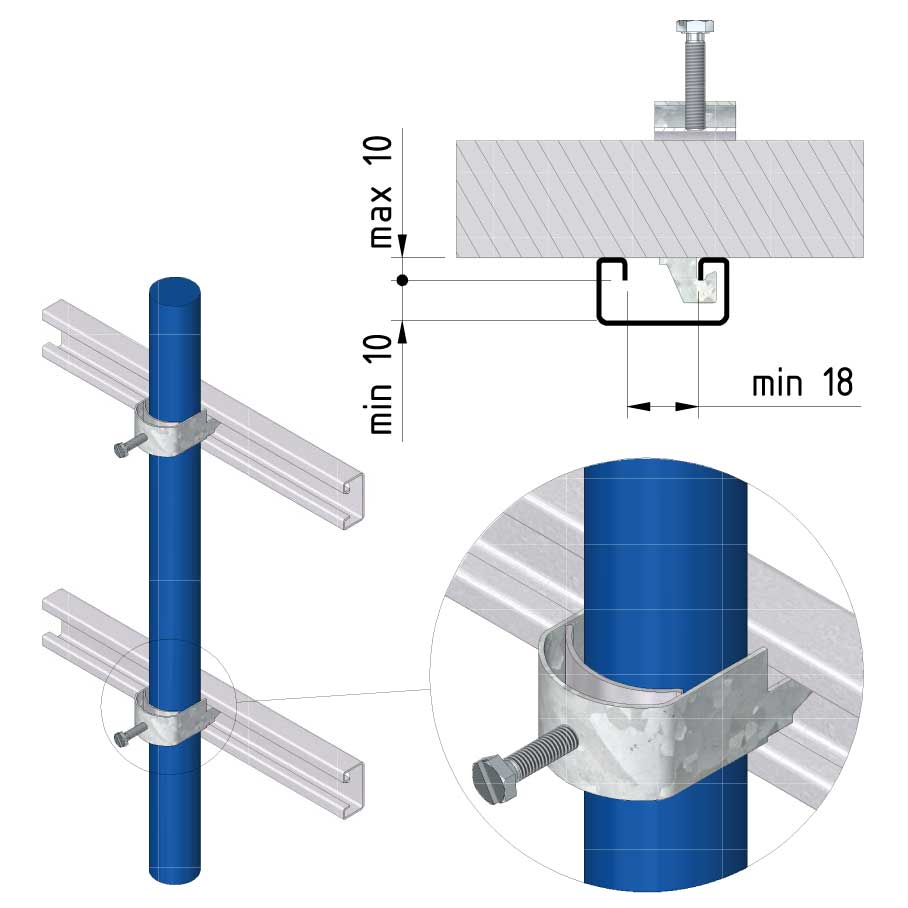
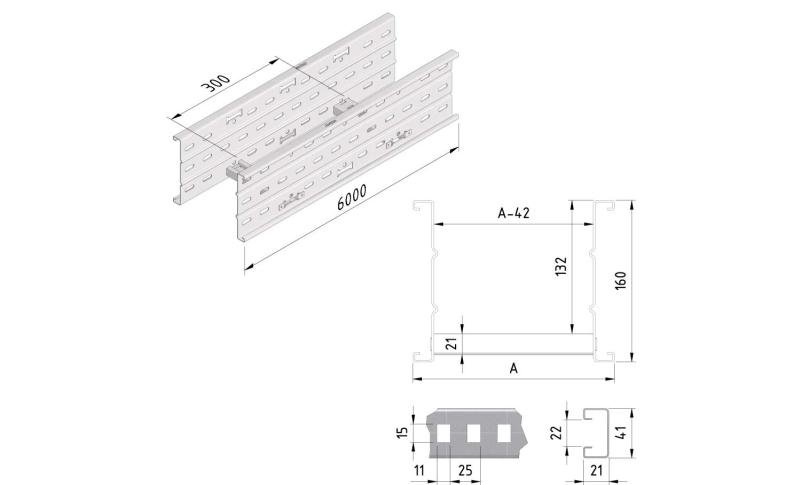
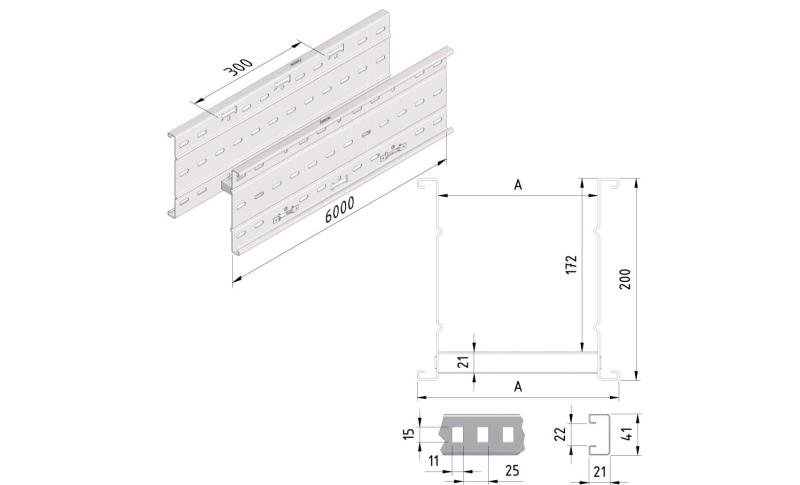
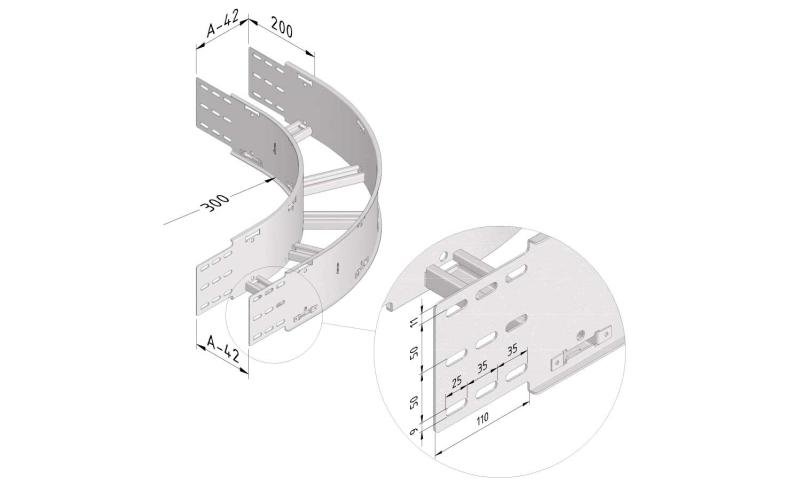
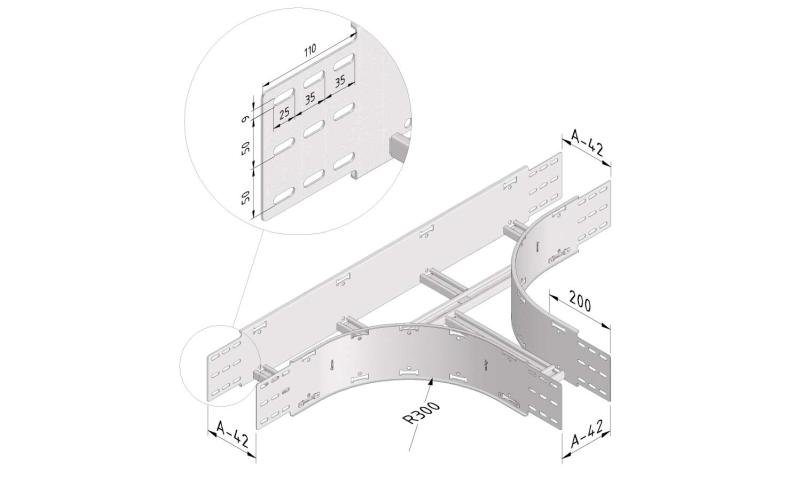
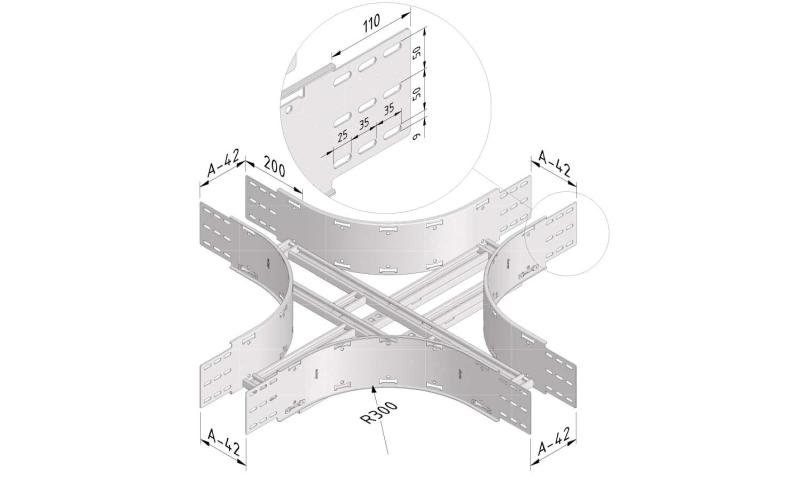
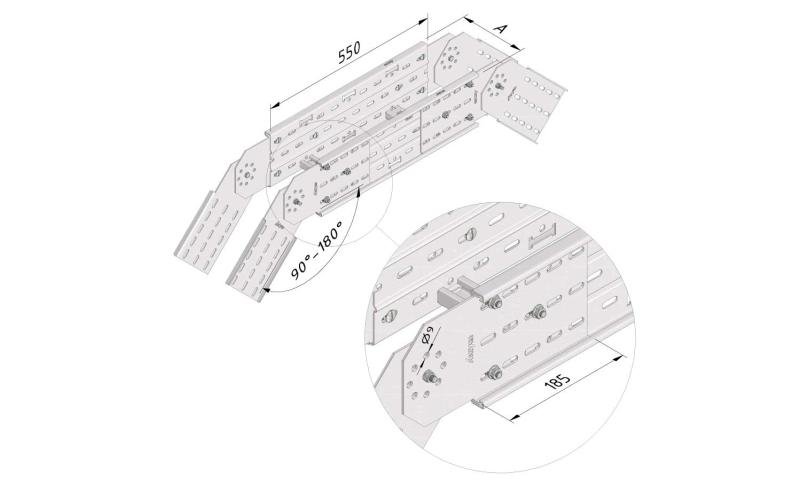
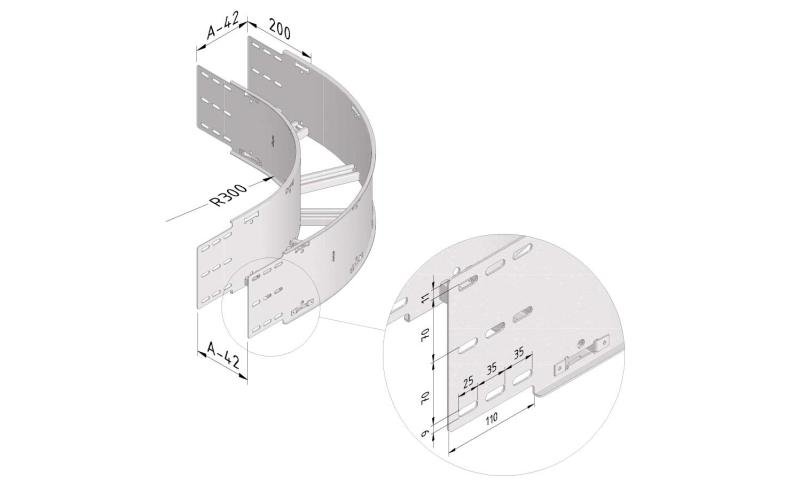
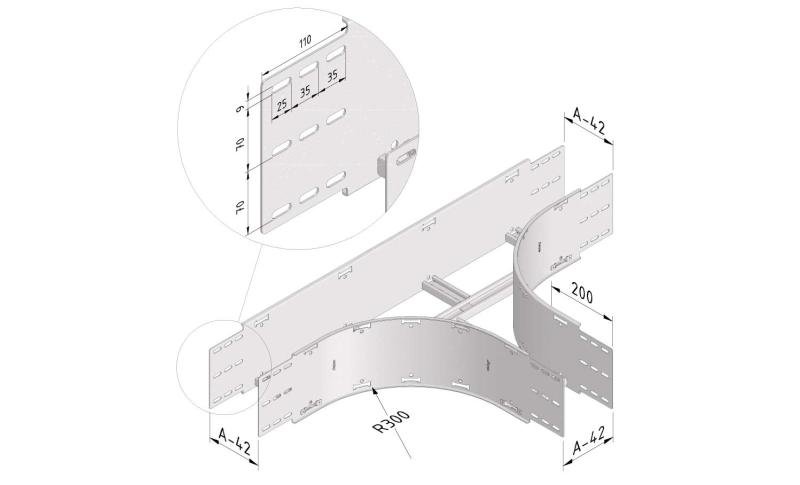
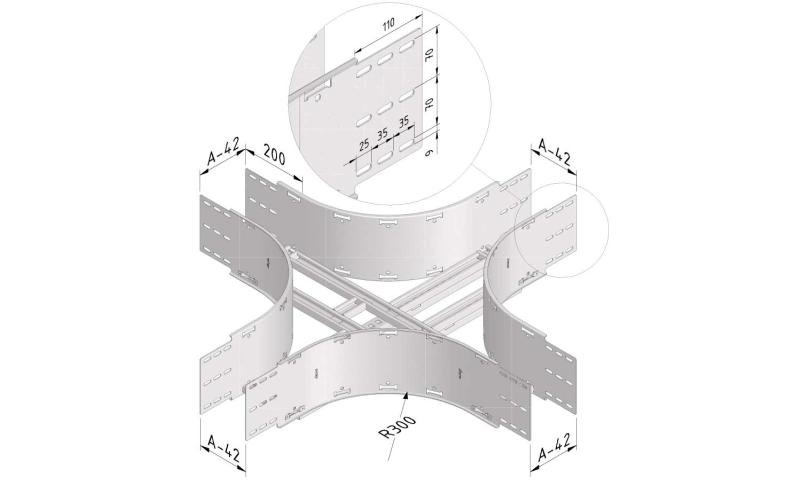
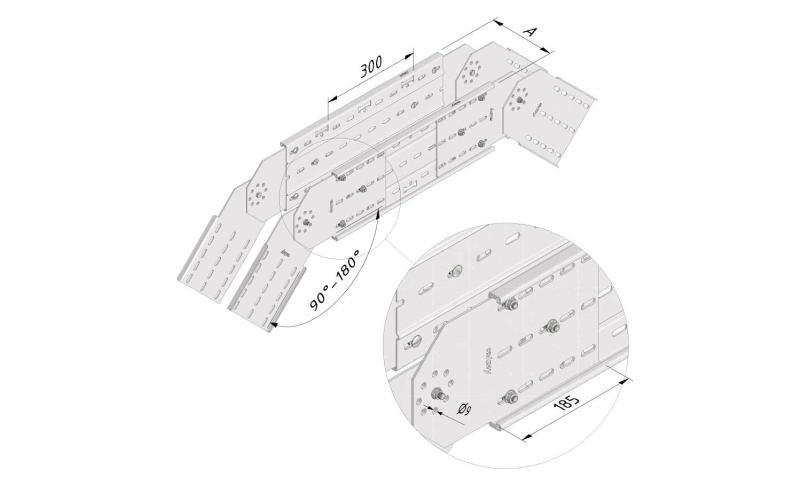
Cable ladder cable clamp
CL-CCI41
Cable ladder cable clamp
CL-CCI41
| SKU | Article code | Finishing | Dimension A | Packaging | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
16482 |
CL-CCI41-12-DG |
DG
|
8-12
|
10
|
Default
|
|
||||
Workload
Additional information
Finishing
Hot-dip galvanized (EN ISO 1461) DG (dipped-galvanised):
Whenever cable support systems are exposed to the elements and/or caustic substances (such as petrochemical applications), they are given an additional treatment in the form of hot-dip galvanizing. Hot-dip galvanizing is a materials science process designed to render the steel non-corroding. If this coating is breached, the zinc will act as a sacrifcial anode, so that the iron is protected by the zinc (aka cathodic protection). During galvanization, three alloys are formed: an iron-zinc alloy, a zinc-iron alloy and also a zinc alloy. The pre-treatment of the steel is crucially important in order to achieve a good bond. The following process steps are involved: degreasing, rinsing, pickling, re-rinsing, fl uxing, drying and hot-dipping. The coating thickness depends on the steel composition, the material thickness and the time spent in the zinc bath. In the galvanizing standard NEN-EN-ISO 1461, the minimum coating thickness are prescribed (as shown in following overview), just as the zinc shrinkage per year which will depend on environmental factors (see table entitled `Corrosion classes’). In addition, the zinc coating forms an excellent substrate for other post-treatments, such as applying a powder coating and coats of paint (better known as the duplex system). An added advantage of hot-dip galvanizing is that along the edges and pointy bits, where objects are usually extra susceptible to corrosion, the zinc coating is thicker because of the behaviour of the liquid. Minimum thicknesses of the zinc coating according to ISO 1461 - Using the hot-dip method Material thickness ≥ 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 85µm Material thickness ≥ 3 mm to < 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 70µm Material thickness ≥ 1,5 mm to < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 1,5 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm - Using the drum method Material thickness ≥ 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm |
|||||||||||
|
|
16483 |
CL-CCI41-16-DG |
DG
|
12-16
|
10
|
Default
|
|
||||
Workload
Additional information
Finishing
Hot-dip galvanized (EN ISO 1461) DG (dipped-galvanised):
Whenever cable support systems are exposed to the elements and/or caustic substances (such as petrochemical applications), they are given an additional treatment in the form of hot-dip galvanizing. Hot-dip galvanizing is a materials science process designed to render the steel non-corroding. If this coating is breached, the zinc will act as a sacrifcial anode, so that the iron is protected by the zinc (aka cathodic protection). During galvanization, three alloys are formed: an iron-zinc alloy, a zinc-iron alloy and also a zinc alloy. The pre-treatment of the steel is crucially important in order to achieve a good bond. The following process steps are involved: degreasing, rinsing, pickling, re-rinsing, fl uxing, drying and hot-dipping. The coating thickness depends on the steel composition, the material thickness and the time spent in the zinc bath. In the galvanizing standard NEN-EN-ISO 1461, the minimum coating thickness are prescribed (as shown in following overview), just as the zinc shrinkage per year which will depend on environmental factors (see table entitled `Corrosion classes’). In addition, the zinc coating forms an excellent substrate for other post-treatments, such as applying a powder coating and coats of paint (better known as the duplex system). An added advantage of hot-dip galvanizing is that along the edges and pointy bits, where objects are usually extra susceptible to corrosion, the zinc coating is thicker because of the behaviour of the liquid. Minimum thicknesses of the zinc coating according to ISO 1461 - Using the hot-dip method Material thickness ≥ 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 85µm Material thickness ≥ 3 mm to < 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 70µm Material thickness ≥ 1,5 mm to < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 1,5 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm - Using the drum method Material thickness ≥ 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm |
|||||||||||
|
|
16484 |
CL-CCI41-20-DG |
DG
|
16-20
|
10
|
Default
|
|
||||
Workload
Additional information
Finishing
Hot-dip galvanized (EN ISO 1461) DG (dipped-galvanised):
Whenever cable support systems are exposed to the elements and/or caustic substances (such as petrochemical applications), they are given an additional treatment in the form of hot-dip galvanizing. Hot-dip galvanizing is a materials science process designed to render the steel non-corroding. If this coating is breached, the zinc will act as a sacrifcial anode, so that the iron is protected by the zinc (aka cathodic protection). During galvanization, three alloys are formed: an iron-zinc alloy, a zinc-iron alloy and also a zinc alloy. The pre-treatment of the steel is crucially important in order to achieve a good bond. The following process steps are involved: degreasing, rinsing, pickling, re-rinsing, fl uxing, drying and hot-dipping. The coating thickness depends on the steel composition, the material thickness and the time spent in the zinc bath. In the galvanizing standard NEN-EN-ISO 1461, the minimum coating thickness are prescribed (as shown in following overview), just as the zinc shrinkage per year which will depend on environmental factors (see table entitled `Corrosion classes’). In addition, the zinc coating forms an excellent substrate for other post-treatments, such as applying a powder coating and coats of paint (better known as the duplex system). An added advantage of hot-dip galvanizing is that along the edges and pointy bits, where objects are usually extra susceptible to corrosion, the zinc coating is thicker because of the behaviour of the liquid. Minimum thicknesses of the zinc coating according to ISO 1461 - Using the hot-dip method Material thickness ≥ 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 85µm Material thickness ≥ 3 mm to < 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 70µm Material thickness ≥ 1,5 mm to < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 1,5 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm - Using the drum method Material thickness ≥ 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm |
|||||||||||
|
|
16485 |
CL-CCI41-24-DG |
DG
|
20-24
|
10
|
Default
|
|
||||
Workload
Additional information
Finishing
Hot-dip galvanized (EN ISO 1461) DG (dipped-galvanised):
Whenever cable support systems are exposed to the elements and/or caustic substances (such as petrochemical applications), they are given an additional treatment in the form of hot-dip galvanizing. Hot-dip galvanizing is a materials science process designed to render the steel non-corroding. If this coating is breached, the zinc will act as a sacrifcial anode, so that the iron is protected by the zinc (aka cathodic protection). During galvanization, three alloys are formed: an iron-zinc alloy, a zinc-iron alloy and also a zinc alloy. The pre-treatment of the steel is crucially important in order to achieve a good bond. The following process steps are involved: degreasing, rinsing, pickling, re-rinsing, fl uxing, drying and hot-dipping. The coating thickness depends on the steel composition, the material thickness and the time spent in the zinc bath. In the galvanizing standard NEN-EN-ISO 1461, the minimum coating thickness are prescribed (as shown in following overview), just as the zinc shrinkage per year which will depend on environmental factors (see table entitled `Corrosion classes’). In addition, the zinc coating forms an excellent substrate for other post-treatments, such as applying a powder coating and coats of paint (better known as the duplex system). An added advantage of hot-dip galvanizing is that along the edges and pointy bits, where objects are usually extra susceptible to corrosion, the zinc coating is thicker because of the behaviour of the liquid. Minimum thicknesses of the zinc coating according to ISO 1461 - Using the hot-dip method Material thickness ≥ 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 85µm Material thickness ≥ 3 mm to < 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 70µm Material thickness ≥ 1,5 mm to < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 1,5 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm - Using the drum method Material thickness ≥ 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm |
|||||||||||
|
|
16486 |
CL-CCI41-28-DG |
DG
|
24-28
|
10
|
Default
|
|
||||
Workload
Additional information
Finishing
Hot-dip galvanized (EN ISO 1461) DG (dipped-galvanised):
Whenever cable support systems are exposed to the elements and/or caustic substances (such as petrochemical applications), they are given an additional treatment in the form of hot-dip galvanizing. Hot-dip galvanizing is a materials science process designed to render the steel non-corroding. If this coating is breached, the zinc will act as a sacrifcial anode, so that the iron is protected by the zinc (aka cathodic protection). During galvanization, three alloys are formed: an iron-zinc alloy, a zinc-iron alloy and also a zinc alloy. The pre-treatment of the steel is crucially important in order to achieve a good bond. The following process steps are involved: degreasing, rinsing, pickling, re-rinsing, fl uxing, drying and hot-dipping. The coating thickness depends on the steel composition, the material thickness and the time spent in the zinc bath. In the galvanizing standard NEN-EN-ISO 1461, the minimum coating thickness are prescribed (as shown in following overview), just as the zinc shrinkage per year which will depend on environmental factors (see table entitled `Corrosion classes’). In addition, the zinc coating forms an excellent substrate for other post-treatments, such as applying a powder coating and coats of paint (better known as the duplex system). An added advantage of hot-dip galvanizing is that along the edges and pointy bits, where objects are usually extra susceptible to corrosion, the zinc coating is thicker because of the behaviour of the liquid. Minimum thicknesses of the zinc coating according to ISO 1461 - Using the hot-dip method Material thickness ≥ 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 85µm Material thickness ≥ 3 mm to < 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 70µm Material thickness ≥ 1,5 mm to < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 1,5 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm - Using the drum method Material thickness ≥ 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm |
|||||||||||
|
|
16487 |
CL-CCI41-32-DG |
DG
|
28-32
|
10
|
Default
|
|
||||
Workload
Additional information
Finishing
Hot-dip galvanized (EN ISO 1461) DG (dipped-galvanised):
Whenever cable support systems are exposed to the elements and/or caustic substances (such as petrochemical applications), they are given an additional treatment in the form of hot-dip galvanizing. Hot-dip galvanizing is a materials science process designed to render the steel non-corroding. If this coating is breached, the zinc will act as a sacrifcial anode, so that the iron is protected by the zinc (aka cathodic protection). During galvanization, three alloys are formed: an iron-zinc alloy, a zinc-iron alloy and also a zinc alloy. The pre-treatment of the steel is crucially important in order to achieve a good bond. The following process steps are involved: degreasing, rinsing, pickling, re-rinsing, fl uxing, drying and hot-dipping. The coating thickness depends on the steel composition, the material thickness and the time spent in the zinc bath. In the galvanizing standard NEN-EN-ISO 1461, the minimum coating thickness are prescribed (as shown in following overview), just as the zinc shrinkage per year which will depend on environmental factors (see table entitled `Corrosion classes’). In addition, the zinc coating forms an excellent substrate for other post-treatments, such as applying a powder coating and coats of paint (better known as the duplex system). An added advantage of hot-dip galvanizing is that along the edges and pointy bits, where objects are usually extra susceptible to corrosion, the zinc coating is thicker because of the behaviour of the liquid. Minimum thicknesses of the zinc coating according to ISO 1461 - Using the hot-dip method Material thickness ≥ 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 85µm Material thickness ≥ 3 mm to < 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 70µm Material thickness ≥ 1,5 mm to < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 1,5 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm - Using the drum method Material thickness ≥ 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm |
|||||||||||
|
|
16488 |
CL-CCI41-36-DG |
DG
|
32-36
|
10
|
Default
|
|
||||
Workload
Additional information
Finishing
Hot-dip galvanized (EN ISO 1461) DG (dipped-galvanised):
Whenever cable support systems are exposed to the elements and/or caustic substances (such as petrochemical applications), they are given an additional treatment in the form of hot-dip galvanizing. Hot-dip galvanizing is a materials science process designed to render the steel non-corroding. If this coating is breached, the zinc will act as a sacrifcial anode, so that the iron is protected by the zinc (aka cathodic protection). During galvanization, three alloys are formed: an iron-zinc alloy, a zinc-iron alloy and also a zinc alloy. The pre-treatment of the steel is crucially important in order to achieve a good bond. The following process steps are involved: degreasing, rinsing, pickling, re-rinsing, fl uxing, drying and hot-dipping. The coating thickness depends on the steel composition, the material thickness and the time spent in the zinc bath. In the galvanizing standard NEN-EN-ISO 1461, the minimum coating thickness are prescribed (as shown in following overview), just as the zinc shrinkage per year which will depend on environmental factors (see table entitled `Corrosion classes’). In addition, the zinc coating forms an excellent substrate for other post-treatments, such as applying a powder coating and coats of paint (better known as the duplex system). An added advantage of hot-dip galvanizing is that along the edges and pointy bits, where objects are usually extra susceptible to corrosion, the zinc coating is thicker because of the behaviour of the liquid. Minimum thicknesses of the zinc coating according to ISO 1461 - Using the hot-dip method Material thickness ≥ 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 85µm Material thickness ≥ 3 mm to < 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 70µm Material thickness ≥ 1,5 mm to < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 1,5 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm - Using the drum method Material thickness ≥ 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm |
|||||||||||
|
|
16489 |
CL-CCI41-40-DG |
DG
|
36-40
|
10
|
Default
|
|
||||
Workload
Additional information
Finishing
Hot-dip galvanized (EN ISO 1461) DG (dipped-galvanised):
Whenever cable support systems are exposed to the elements and/or caustic substances (such as petrochemical applications), they are given an additional treatment in the form of hot-dip galvanizing. Hot-dip galvanizing is a materials science process designed to render the steel non-corroding. If this coating is breached, the zinc will act as a sacrifcial anode, so that the iron is protected by the zinc (aka cathodic protection). During galvanization, three alloys are formed: an iron-zinc alloy, a zinc-iron alloy and also a zinc alloy. The pre-treatment of the steel is crucially important in order to achieve a good bond. The following process steps are involved: degreasing, rinsing, pickling, re-rinsing, fl uxing, drying and hot-dipping. The coating thickness depends on the steel composition, the material thickness and the time spent in the zinc bath. In the galvanizing standard NEN-EN-ISO 1461, the minimum coating thickness are prescribed (as shown in following overview), just as the zinc shrinkage per year which will depend on environmental factors (see table entitled `Corrosion classes’). In addition, the zinc coating forms an excellent substrate for other post-treatments, such as applying a powder coating and coats of paint (better known as the duplex system). An added advantage of hot-dip galvanizing is that along the edges and pointy bits, where objects are usually extra susceptible to corrosion, the zinc coating is thicker because of the behaviour of the liquid. Minimum thicknesses of the zinc coating according to ISO 1461 - Using the hot-dip method Material thickness ≥ 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 85µm Material thickness ≥ 3 mm to < 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 70µm Material thickness ≥ 1,5 mm to < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 1,5 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm - Using the drum method Material thickness ≥ 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm |
|||||||||||
|
|
16490 |
CL-CCI41-44-DG |
DG
|
40-44
|
10
|
Default
|
|
||||
Workload
Additional information
Finishing
Hot-dip galvanized (EN ISO 1461) DG (dipped-galvanised):
Whenever cable support systems are exposed to the elements and/or caustic substances (such as petrochemical applications), they are given an additional treatment in the form of hot-dip galvanizing. Hot-dip galvanizing is a materials science process designed to render the steel non-corroding. If this coating is breached, the zinc will act as a sacrifcial anode, so that the iron is protected by the zinc (aka cathodic protection). During galvanization, three alloys are formed: an iron-zinc alloy, a zinc-iron alloy and also a zinc alloy. The pre-treatment of the steel is crucially important in order to achieve a good bond. The following process steps are involved: degreasing, rinsing, pickling, re-rinsing, fl uxing, drying and hot-dipping. The coating thickness depends on the steel composition, the material thickness and the time spent in the zinc bath. In the galvanizing standard NEN-EN-ISO 1461, the minimum coating thickness are prescribed (as shown in following overview), just as the zinc shrinkage per year which will depend on environmental factors (see table entitled `Corrosion classes’). In addition, the zinc coating forms an excellent substrate for other post-treatments, such as applying a powder coating and coats of paint (better known as the duplex system). An added advantage of hot-dip galvanizing is that along the edges and pointy bits, where objects are usually extra susceptible to corrosion, the zinc coating is thicker because of the behaviour of the liquid. Minimum thicknesses of the zinc coating according to ISO 1461 - Using the hot-dip method Material thickness ≥ 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 85µm Material thickness ≥ 3 mm to < 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 70µm Material thickness ≥ 1,5 mm to < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 1,5 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm - Using the drum method Material thickness ≥ 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm |
|||||||||||
|
|
16491 |
CL-CCI41-48-DG |
DG
|
44-48
|
10
|
Default
|
|
||||
Workload
Additional information
Finishing
Hot-dip galvanized (EN ISO 1461) DG (dipped-galvanised):
Whenever cable support systems are exposed to the elements and/or caustic substances (such as petrochemical applications), they are given an additional treatment in the form of hot-dip galvanizing. Hot-dip galvanizing is a materials science process designed to render the steel non-corroding. If this coating is breached, the zinc will act as a sacrifcial anode, so that the iron is protected by the zinc (aka cathodic protection). During galvanization, three alloys are formed: an iron-zinc alloy, a zinc-iron alloy and also a zinc alloy. The pre-treatment of the steel is crucially important in order to achieve a good bond. The following process steps are involved: degreasing, rinsing, pickling, re-rinsing, fl uxing, drying and hot-dipping. The coating thickness depends on the steel composition, the material thickness and the time spent in the zinc bath. In the galvanizing standard NEN-EN-ISO 1461, the minimum coating thickness are prescribed (as shown in following overview), just as the zinc shrinkage per year which will depend on environmental factors (see table entitled `Corrosion classes’). In addition, the zinc coating forms an excellent substrate for other post-treatments, such as applying a powder coating and coats of paint (better known as the duplex system). An added advantage of hot-dip galvanizing is that along the edges and pointy bits, where objects are usually extra susceptible to corrosion, the zinc coating is thicker because of the behaviour of the liquid. Minimum thicknesses of the zinc coating according to ISO 1461 - Using the hot-dip method Material thickness ≥ 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 85µm Material thickness ≥ 3 mm to < 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 70µm Material thickness ≥ 1,5 mm to < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 1,5 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm - Using the drum method Material thickness ≥ 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm |
|||||||||||
|
|
16492 |
CL-CCI41-52-DG |
DG
|
48-52
|
10
|
Default
|
|
||||
Workload
Additional information
Finishing
Hot-dip galvanized (EN ISO 1461) DG (dipped-galvanised):
Whenever cable support systems are exposed to the elements and/or caustic substances (such as petrochemical applications), they are given an additional treatment in the form of hot-dip galvanizing. Hot-dip galvanizing is a materials science process designed to render the steel non-corroding. If this coating is breached, the zinc will act as a sacrifcial anode, so that the iron is protected by the zinc (aka cathodic protection). During galvanization, three alloys are formed: an iron-zinc alloy, a zinc-iron alloy and also a zinc alloy. The pre-treatment of the steel is crucially important in order to achieve a good bond. The following process steps are involved: degreasing, rinsing, pickling, re-rinsing, fl uxing, drying and hot-dipping. The coating thickness depends on the steel composition, the material thickness and the time spent in the zinc bath. In the galvanizing standard NEN-EN-ISO 1461, the minimum coating thickness are prescribed (as shown in following overview), just as the zinc shrinkage per year which will depend on environmental factors (see table entitled `Corrosion classes’). In addition, the zinc coating forms an excellent substrate for other post-treatments, such as applying a powder coating and coats of paint (better known as the duplex system). An added advantage of hot-dip galvanizing is that along the edges and pointy bits, where objects are usually extra susceptible to corrosion, the zinc coating is thicker because of the behaviour of the liquid. Minimum thicknesses of the zinc coating according to ISO 1461 - Using the hot-dip method Material thickness ≥ 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 85µm Material thickness ≥ 3 mm to < 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 70µm Material thickness ≥ 1,5 mm to < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 1,5 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm - Using the drum method Material thickness ≥ 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm |
|||||||||||
|
|
16493 |
CL-CCI41-56-DG |
DG
|
52-56
|
10
|
Default
|
|
||||
Workload
Additional information
Finishing
Hot-dip galvanized (EN ISO 1461) DG (dipped-galvanised):
Whenever cable support systems are exposed to the elements and/or caustic substances (such as petrochemical applications), they are given an additional treatment in the form of hot-dip galvanizing. Hot-dip galvanizing is a materials science process designed to render the steel non-corroding. If this coating is breached, the zinc will act as a sacrifcial anode, so that the iron is protected by the zinc (aka cathodic protection). During galvanization, three alloys are formed: an iron-zinc alloy, a zinc-iron alloy and also a zinc alloy. The pre-treatment of the steel is crucially important in order to achieve a good bond. The following process steps are involved: degreasing, rinsing, pickling, re-rinsing, fl uxing, drying and hot-dipping. The coating thickness depends on the steel composition, the material thickness and the time spent in the zinc bath. In the galvanizing standard NEN-EN-ISO 1461, the minimum coating thickness are prescribed (as shown in following overview), just as the zinc shrinkage per year which will depend on environmental factors (see table entitled `Corrosion classes’). In addition, the zinc coating forms an excellent substrate for other post-treatments, such as applying a powder coating and coats of paint (better known as the duplex system). An added advantage of hot-dip galvanizing is that along the edges and pointy bits, where objects are usually extra susceptible to corrosion, the zinc coating is thicker because of the behaviour of the liquid. Minimum thicknesses of the zinc coating according to ISO 1461 - Using the hot-dip method Material thickness ≥ 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 85µm Material thickness ≥ 3 mm to < 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 70µm Material thickness ≥ 1,5 mm to < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 1,5 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm - Using the drum method Material thickness ≥ 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm |
|||||||||||
|
|
16494 |
CL-CCI41-60-DG |
DG
|
56-60
|
10
|
Default
|
|
||||
Workload
Additional information
Finishing
Hot-dip galvanized (EN ISO 1461) DG (dipped-galvanised):
Whenever cable support systems are exposed to the elements and/or caustic substances (such as petrochemical applications), they are given an additional treatment in the form of hot-dip galvanizing. Hot-dip galvanizing is a materials science process designed to render the steel non-corroding. If this coating is breached, the zinc will act as a sacrifcial anode, so that the iron is protected by the zinc (aka cathodic protection). During galvanization, three alloys are formed: an iron-zinc alloy, a zinc-iron alloy and also a zinc alloy. The pre-treatment of the steel is crucially important in order to achieve a good bond. The following process steps are involved: degreasing, rinsing, pickling, re-rinsing, fl uxing, drying and hot-dipping. The coating thickness depends on the steel composition, the material thickness and the time spent in the zinc bath. In the galvanizing standard NEN-EN-ISO 1461, the minimum coating thickness are prescribed (as shown in following overview), just as the zinc shrinkage per year which will depend on environmental factors (see table entitled `Corrosion classes’). In addition, the zinc coating forms an excellent substrate for other post-treatments, such as applying a powder coating and coats of paint (better known as the duplex system). An added advantage of hot-dip galvanizing is that along the edges and pointy bits, where objects are usually extra susceptible to corrosion, the zinc coating is thicker because of the behaviour of the liquid. Minimum thicknesses of the zinc coating according to ISO 1461 - Using the hot-dip method Material thickness ≥ 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 85µm Material thickness ≥ 3 mm to < 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 70µm Material thickness ≥ 1,5 mm to < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 1,5 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm - Using the drum method Material thickness ≥ 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm |
|||||||||||
|
|
16495 |
CL-CCI41-64-DG |
DG
|
60-64
|
10
|
Default
|
|
||||
Workload
Additional information
Finishing
Hot-dip galvanized (EN ISO 1461) DG (dipped-galvanised):
Whenever cable support systems are exposed to the elements and/or caustic substances (such as petrochemical applications), they are given an additional treatment in the form of hot-dip galvanizing. Hot-dip galvanizing is a materials science process designed to render the steel non-corroding. If this coating is breached, the zinc will act as a sacrifcial anode, so that the iron is protected by the zinc (aka cathodic protection). During galvanization, three alloys are formed: an iron-zinc alloy, a zinc-iron alloy and also a zinc alloy. The pre-treatment of the steel is crucially important in order to achieve a good bond. The following process steps are involved: degreasing, rinsing, pickling, re-rinsing, fl uxing, drying and hot-dipping. The coating thickness depends on the steel composition, the material thickness and the time spent in the zinc bath. In the galvanizing standard NEN-EN-ISO 1461, the minimum coating thickness are prescribed (as shown in following overview), just as the zinc shrinkage per year which will depend on environmental factors (see table entitled `Corrosion classes’). In addition, the zinc coating forms an excellent substrate for other post-treatments, such as applying a powder coating and coats of paint (better known as the duplex system). An added advantage of hot-dip galvanizing is that along the edges and pointy bits, where objects are usually extra susceptible to corrosion, the zinc coating is thicker because of the behaviour of the liquid. Minimum thicknesses of the zinc coating according to ISO 1461 - Using the hot-dip method Material thickness ≥ 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 85µm Material thickness ≥ 3 mm to < 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 70µm Material thickness ≥ 1,5 mm to < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 1,5 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm - Using the drum method Material thickness ≥ 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm |
|||||||||||
|
|
16496 |
CL-CCI41-70-DG |
DG
|
64-70
|
10
|
Default
|
|
||||
Workload
Additional information
Finishing
Hot-dip galvanized (EN ISO 1461) DG (dipped-galvanised):
Whenever cable support systems are exposed to the elements and/or caustic substances (such as petrochemical applications), they are given an additional treatment in the form of hot-dip galvanizing. Hot-dip galvanizing is a materials science process designed to render the steel non-corroding. If this coating is breached, the zinc will act as a sacrifcial anode, so that the iron is protected by the zinc (aka cathodic protection). During galvanization, three alloys are formed: an iron-zinc alloy, a zinc-iron alloy and also a zinc alloy. The pre-treatment of the steel is crucially important in order to achieve a good bond. The following process steps are involved: degreasing, rinsing, pickling, re-rinsing, fl uxing, drying and hot-dipping. The coating thickness depends on the steel composition, the material thickness and the time spent in the zinc bath. In the galvanizing standard NEN-EN-ISO 1461, the minimum coating thickness are prescribed (as shown in following overview), just as the zinc shrinkage per year which will depend on environmental factors (see table entitled `Corrosion classes’). In addition, the zinc coating forms an excellent substrate for other post-treatments, such as applying a powder coating and coats of paint (better known as the duplex system). An added advantage of hot-dip galvanizing is that along the edges and pointy bits, where objects are usually extra susceptible to corrosion, the zinc coating is thicker because of the behaviour of the liquid. Minimum thicknesses of the zinc coating according to ISO 1461 - Using the hot-dip method Material thickness ≥ 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 85µm Material thickness ≥ 3 mm to < 6 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 70µm Material thickness ≥ 1,5 mm to < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 1,5 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm - Using the drum method Material thickness ≥ 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 55µm Material thickness < 3 mm = min. zinc coating thickness (average) 45µm |
|||||||||||
No results
No results were found for your current search